Abstract
Purpose
To study the capability of diffusion-relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging (DR-CSI) on subtype classification and grade differentiation for small renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Histogram analysis for apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) was studied for comparison.
Materials and methods
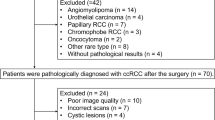
A total of 61 patients with small RCC (< 4 cm) were included in the retrospective study. MRI data were reviewed, including a multi-b (0–1500 s/mm2) multi-TE (51–200 ms) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence. Region of interest (ROI) was delineated manually on DWI to include solid tumor. For each patient, a D-T2 spectrum was fitted and segmented into 5 compartments, and the volume fractions VA, VB, VC, VD, VE were obtained. ADC mapping was calculated, and histogram parameters ADC 90th, 10th, median, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis were obtained. All MRI metrices were compared between clear cell RCC (ccRCC) and non-ccRCC group, and between high-grade and low-grade group. Receiver operator curve analysis was used to assess the corresponding diagnostic performance.
Results
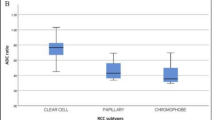
Significantly higher ADC 90th, ADC 10th and ADC median, and significantly lower DR-CSI VB was found for ccRCC compared to non-ccRCC. Significantly lower ADC 90th, ADC median and significantly higher VB was found for high-grade RCC compared to low-grade. For identifying ccRCC from non-ccRCC, VB showed the highest area under curve (AUC, 0.861) and specificity (0.882). For differentiating high- from low-grade, ADC 90th showed the highest AUC (0.726) and specificity (0.786), while VB also displayed a moderate AUC (0.715).
Conclusion
DR-CSI may offer improved accuracy in subtype identification for small RCC, while do not show better performance for small RCC grading compared to ADC histogram.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun M, Thuret R, Abdollah F, Lughezzani G, Schmitges J, Tian Z, Shariat SF, Montorsi F, Patard JJ, Perrotte P, Karakiewicz PI (2011) Age-adjusted incidence, mortality, and survival rates of stage-specific renal cell carcinoma in North America: a trend analysis. Eur Urol 59(1):135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.029
Jayson M, Sanders H (1998) Increased incidence of serendipitously discovered renal cell carcinoma. Urology 51(2):203–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(97)00506-2
Reuter VE (2006) The pathology of renal epithelial neoplasms. Semin Oncol 33(5):534–543. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.06.009
Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Blute ML (2003) Comparisons of outcome and prognostic features among histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 27(5):612–624. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-200305000-00005
O’Connor JPB, Rose CJ, Waterton JC, Carano RAD, Parker GJM, Jackson A (2015) Imaging intratumor heterogeneity: role in therapy response, resistance, and clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 21(2):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-14-0990
Sasiwimonphan K, Takahashi N, Leibovich BC, Carter RE, Atwell TD, Kawashima A (2012) Small (< 4 cm) renal mass: differentiation of angiomyolipoma without visible fat from renal cell carcinoma utilizing MR imaging. Radiology 263(1):160–168. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12111205
Heilbrun ME, Remer EM, Casalino DD, Beland MD, Bishoff JT, Blaufox MD, Coursey CA, Goldfarb S, Harvin HJ, Nikolaidis P, Preminger GM, Raman SS, Sahni A, Vikram R, Weinfeld RM (2015) ACR appropriateness criteria indeterminate renal mass. J Am Coll Radiol 12(4):333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2014.12.012
Schieda N, Lim RS, McInnes MDF, Thomassin I, Renard-Penna R, Tavolaro S, Cornelis FH (2018) Characterization of small (< 4 cm) solid renal masses by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: current evidence and further development. Diagn Interv Imaging 99(7–8):443–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2018.03.004
Flum AS, Hamoui N, Said MA, Yang XJ, Casalino DD, McGuire BB, Perry KT, Nadler RB (2016) Update on the diagnosis and management of renal angiomyolipoma. J Urol 195(4):834–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2015.07.126
Silverman SG, Gan YU, Mortele KJ, Tuncali K, Cibas ES (2006) Renal masses in the adult patient: the role of percutaneous biopsy. Radiology 240(1):6–22. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2401050061
Cornelis F, Tricaud E, Lasserre AS, Petitpierre F, Bernhard JC, Le Bras Y, Yacoub M, Bouzgarrou M, Ravaud A, Grenier N (2015) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the differentiation of low and high grade clear cell renal carcinoma. Eur Radiol 25(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3380-x
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, Martinez P, Matthews N, Stewart A, Tarpey P, Varela I, Phillimore B, Begum S, McDonald NQ, Butler A, Jones D, Raine K, Latimer C, Santos CR, Nohadani M, Eklund AC, Spencer-Dene B, Clark G, Pickering L, Stamp G, Gore M, Szallasi Z, Downward J, Futreal PA, Swanton C (2012) Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med 366(10):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1113205
McCroskey Z, Sim SJ, Selzman AA, Ayala AG, Ro JY (2017) Primary collision tumors of the kidney composed of oncocytoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma: a review. Ann Diagn Pathol 29:32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.04.011
Cornelis F, Tricaud E, Lasserre AS, Petitpierre F, Bernhard JC, Le Bras Y, Yacoub M, Bouzgarrou M, Ravaud A, Grenier N (2014) Routinely performed multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging helps to differentiate common subtypes of renal tumours. Eur Radiol 24(5):1068–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3107-z
Dai YM, Yao QY, Wu GY, Wu DM, Wu LM, Zhu L, Xue R, Xu JR (2016) Characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with diffusion kurtosis imaging: correlation between diffusion kurtosis parameters and tumor cellularity. NMR Biomed 29(7):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3535
Young JR, Coy H, Kim HJ, Douek M, Lo P, Pantuck AJ, Raman SS (2017) Performance of relative enhancement on multiphasic MRI for the differentiation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) from papillary and chromophobe RCC subtypes and oncocytoma. Am J Roentgenol 208(4):812–819. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.16.17152
Tomaszewski MR, Dominguez-Viqueira W, Ortiz A, Shi Y, Costello JR, Enderling H, Rosenberg SA, Gillies RJ (2021) Heterogeneity analysis of MRI T2 maps for measurement of early tumor response to radiotherapy. NMR Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4454
Kudou M, Nakanishi M, Kuriu Y, Murayama Y, Arita T, Kishimoto M, Konishi E, Goto M, Yamada K, Otsuji E (2020) Value of intra-tumor heterogeneity evaluated by diffusion-weighted MRI for predicting pathological stages and therapeutic responses to chemoradiotherapy in lower rectal cancer. J Cancer 11(1):168–176. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.38354
Langbein BJ, Szczepankiewicz F, Westin CF, Bay C, Maier SE, Kibel AS, Tempany CM, Fennessy FM (2021) A pilot study of multidimensional diffusion MRI for assessment of tissue heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Invest Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000796
Karaman MM, Sui Y, Wang H, Magin RL, Li YH, Zhou XJ (2016) Differentiating low- and high-grade pediatric brain tumors using a continuous-time random-walk diffusion model at high b-values. Magn Reson Med 76(4):1149–1157. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26012
Kim D, Doyle EK, Wisnowski JL, Kim JH, Haldar JP (2017) Diffusion–relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging: a multidimensional approach for probing microstructure. Magn Reson Med 78(6):2236–2249. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26629
Zhang Z, Wu HH, Priester A, Magyar C, Afshari Mirak S, Shakeri S, Mohammadian Bajgiran A, Hosseiny M, Azadikhah A, Sung K, Reiter RE, Sisk AE, Raman S, Enzmann DR (2020) Prostate microstructure in prostate cancer using 3-T MRI with diffusion–relaxation correlation spectrum imaging: validation with whole-mount digital histopathology. Radiology 296(2):348–355. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192330
Benjamini D, Basser PJ (2020) Multidimensional correlation MRI. NMR Biomed 33(12):e4226. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4226
Benjamini D, Priemer DS, Perl DP, Brody DL, Basser PJ (2022) Mapping astrogliosis in the individual human brain using multidimensional MRI. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac298
Liu F, Hu W, Sun Y, Shen Y, Zhou W, Dai Y, Gu L, Zhang M, Zhou Y (2022) Exploration of interstitial fibrosis in chronic kidney disease by diffusion–relaxation correlation spectrum MR imaging: a preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.28535
Dai Y, Hu W, Wu G, Wu D, Zhu M, Luo Y, Wang J, Zhou Y, Hu P (2023) Grading clear cell renal cell carcinoma grade using diffusion relaxation correlated MR spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging JMRI. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.28777
Delahunt B, Cheville JC, Martignoni G, Humphrey PA, Magi-Galluzzi C, McKenney J, Egevad L, Algaba F, Moch H, Grignon DJ, Montironi R, Srigley JR, Panel IRT (2013) The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1490–1504. https://doi.org/10.1097/pas.0b013e318299f0fb
Veraart J, Fieremans E, Novikov DS (2016) Diffusion MRI noise mapping using random matrix theory. Magn Reson Med 76(5):1582–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26059
Klein S, Staring M, Murphy K, Viergever MA, Pluim JPW (2010) Elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(1):196–205. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2009.2035616
Mytsyk Y, Dutka I, Yuriy B, Maksymovych I, Caprnda M, Gazdikova K, Rodrigo L, Kruzliak P, Illjuk P, Farooqi AA (2018) Differential diagnosis of the small renal masses: role of the apparent diffusion coefficient of the diffusion-weighted MRI. Int Urol Nephrol 50(2):197–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1761-1
Li AQ, Xing W, Li HJ, Hu Y, Hu DY, Li Z, Kamel IR (2018) Subtype differentiation of small (<= 4 cm) solid renal mass using volumetric histogram analysis of DWI at 3-T MRI. Am J Roentgenol 211(3):614–623. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.17.19278
Agnello F, Roy C, Bazille G, Galia M, Midiri M, Charles T, Lang H (2013) Small solid renal masses: characterization by diffusion-weighted MRI at 3 T. Clin Radiol 68(6):E301–E308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2013.01.002
Song JS, Hwang SB, Chung GH, Jin GY (2016) Intra-individual, inter-vendor comparison of diffusion-weighted MR imaging of upper abdominal organs at 3.0 Tesla with an emphasis on the value of normalization with the spleen. Korean J Radiol 17(2):209–217. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.2.209
Rosenkrantz AB, Niver BE, Fitzgerald EF, Babb JS, Chandarana H, Melamed J (2010) Utility of the apparent diffusion coefficient for distinguishing clear cell renal cell carcinoma of low and high nuclear grade. Am J Roentgenol 195(5):W344–W351. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.10.4688
Akinci O, Turkoglu F, Nalbant MO, Oner O, Inci E (2023) The effectiveness of volumetric MRI histogram analysis in renal cell carcinoma. Acad Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2023.03.029
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J, Ficarra V (2017) Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Disease Primers. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.9
Ji Y, Gagoski B, Hoge WS, Rathi Y, Ning LP (2021) Accelerated diffusion and relaxation–diffusion MRI using time-division multiplexing EPI. Magn Reson Med 86(5):2528–2541. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28894
Benjamini D, Basser PJ (2018) Towards clinically feasible relaxation–diffusion correlation MRI using MADCO. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 269:93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.02.001
Zaldumbide L, Erramuzpe A, Guarch R, Cortes JM, Lopez JI (2015) Large (> 3.8 cm) clear cell renal cell carcinomas are morphologically and immunohistochemically heterogeneous. Virchows Arch 466(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1673-8
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design were performed by [YD]. Material preparation and data collection were performed by [MZ], [SH], [YL], [XW], and [GW]. Data analysis were performed by [WH] and [DW]. The first draft of the manuscript was written and reviewed by [YD], [YZ] and [PH], and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Renji hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiaotong University, and the consents from patients were waived.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was waived for all individual participants included in the study for its retrospective nature.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 1–3.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Zhu, M., Hu, W. et al. To characterize small renal cell carcinoma using diffusion relaxation correlation spectroscopic imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient based histogram analysis: a preliminary study. Radiol med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-024-01819-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-024-01819-6