Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate tolerance and biochemical control rates of salvage external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) in patients with local relapse from prostate cancer (PC) after high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as primary treatment.
Methods
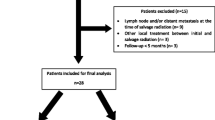
Twenty-four patients presented biochemical failure of PC. Salvage EBRT to the residual prostate was performed with moderate hypofractionation schedule (MHRT) in 28 fractions (n = 16) or with extreme hypofractionation schedule (SBRT) in 5 fractions (n = 8) by means of image-guided volumetric modulation arc therapy. In case of MHRT, the median dose was 71.4 Gy, whereas in case of SBRT it was 32.5 Gy.
Results
The median follow-up was 28 months. The median PSA nadir was 0.26 ng/mL. In case of MHRT, the median PSA nadir was 0.15 ng/mL and occurred within a median time of 19 months. In case of SBRT, the median PSA nadir was 0.64 ng/mL and occurred within a median time of 8 months. No G3 higher acute or late toxicity after EBRT was observed. Only three patients presented with G2 acute GI toxicity (actinic proctitis). Twelve patients experienced acute G1 GU toxicity: 8/16 of men treated with MHRT and 4/8 of men treated with SBRT. Complete local control of disease was achieved in 23/24 patients (96%).
Conclusions
Our data confirm the feasibility and the low toxicity of salvage EBRT with both schedules of treatment after HIFU failure. The findings of low acute toxicity and good biochemical control rates are encouraging, but a larger number of patients and a longer follow-up are needed to confirm these results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamdy FC, Donovan JL, Lane JA, Mason M, Metcalfe C, Holding P, Davis M, Peters TJ, Turner EL, Martin RM, Oxley J, Robinson M, Staffurth J, Walsh E, Bollina P, Catto J, Doble A, Doherty A, Gillatt D, Kockelbergh R, Kynaston H, Paul A, Powell P, Prescott S, Rosario DJ, Rowe E, Neal DE, ProtecT Study Group (2016) 10-Year outcomes after monitoring, surgery, or radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 375(15):1415–1424. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1606220(Epub 2016 Sep 14)
Alongi F, Liardo RL, Iftode C, Lopci E, Villa E, Comito T, Tozzi A, Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Mancosu P, Tomatis S, Bellorofonte C, Arturo C, Scorsetti M (2014) 11C choline PET guided salvage radiotherapy with volumetric modulation arc therapy and hypofractionation for recurrent prostate cancer after HIFU failure: preliminary results of tolerability and acute toxicity. Technol Cancer Res Treat 13(5):395–401. https://doi.org/10.7785/tcrtexpress.2013.600268(Epub 2013 Aug 31)
Madersbacher S et al (2003) High-energy shockwaves and extracorporeal high-intensity focused ultrasound. J Endourol 17:667
Poissonnier L et al (2007) Control of prostate cancer by transrectal HIFU in 227 patients. Eur Urol 51:381
Gelet A et al (1999) Local control of prostate cancer by transrectal high intensity focused ultrasound therapy: preliminary results. J Urol 161:156
Elterman DS et al (2011) Results of high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of prostate cancer: early Canadian experience at a single center. Can J Urol 18:6037
Crouzet S et al (2014) Whole-gland ablation of localized prostate cancer with high-intensity focused ultrasound: oncologic outcomes and morbidity in 1002 patients. Eur Urol 65:907
EAU guidelines. https://uroweb.org/guidelines/2019. Accessed Jan 2020
Ramsay CR et al (2015) Ablative therapy for people with localised prostate cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 19:1
Dearnaley D, Syndikus I, Mossop H, Khoo V, Birtle A, Bloomfield D, Graham J, Kirkbride P, Logue J, Malik Z, Money-Kyrle J, O’Sullivan JM, Panades M, Parker C, Patterson H, Scrase C, Staffurth J, Stockdale A, Tremlett J, Bidmead M, Mayles H, Naismith O, South C, Gao A, Cruickshank C, Hassan S, Pugh J, Griffin C, Hall E, CHHiP Investigators (2016) Conventional versus hypofractionated high-dose intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 CHHiP trial. Lancet Oncol 17(8):1047–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30102-4(Epub 2016 Jun 20)
Lee WR, Dignam JJ, Amin MB, Bruner DW, Low D, Swanson GP, Shah AB, D’Souza DP, Michalski JM, Dayes IS, Seaward SA, Hall WA, Nguyen PL, Pisansky TM, Faria SL, Chen Y, Koontz BF, Paulus R, Sandler HM (2016) Randomized phase III noninferiority study comparing two radiotherapy fractionation schedules in patients with low-risk prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 34(20):2325–2332. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.67.0448(Epub 2016 Apr 4)
Incrocci L, Wortel RC, Alemayehu WG, Aluwini S, Schimmel E, Krol S, van der Toorn PP, Jager H, Heemsbergen W, Heijmen B, Pos F (2016) Hypofractionated versus conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for patients with localised prostate cancer (HYPRO): final efficacy results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 17(8):1061–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30070-5(Epub 2016 Jun 20)
Catton CN, Lukka H, Gu CS, Martin JM, Supiot S, Chung PWM, Bauman GS, Bahary JP, Ahmed S, Cheung P, Tai KH, Wu JS, Parliament MB, Tsakiridis T, Corbett TB, Tang C, Dayes IS, Warde P, Craig TK, Julian JA, Levine MN (2017) Randomized trial of a hypofractionated radiation regimen for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 35(17):1884–1890. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.7397(Epub 2017 Mar 15)
Nicosia L, Mazzola R, Rigo M, Figlia V, Giaj-Levra N, Napoli G, Ricchetti F, Corradini S, Ruggieri R, Alongi F (2019) Moderate versus extreme hypofractionated radiotherapy: a toxicity comparative analysis in low- and favorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02983-3
Zilli T, Scorsetti M, Zwahlen D, Franzese C, Förster R, Giaj-Levra N, Koutsouvelis N, Bertaut A, Zimmermann M, D’Agostino GR, Alongi F, Guckenberger M, Miralbell R (2018) ONE SHOT—single shot radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: study protocol of a single arm, multicenter phase I/II trial. Radiat Oncol 13(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1112-0(Erratum in: Radiat Oncol 2018 Sep 19;13(1):182)
Alongi F, Mazzola R, Fiorentino A, Corradini S, Aiello D, Figlia V, Gregucci F, Ballario R, Cavalleri S, Ruggieri R (2019) Phase II study of accelerated Linac-based SBRT in five consecutive fractions for localized prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 195(2):113–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-018-1338-7(Epub 2018 Jul 12)
De Bari B, Arcangeli S, Ciardo D, Mazzola R, Alongi F, Russi EG, Santoni R, Magrini SM, Jereczek-Fossa BA, on the behalf of the Italian Association of Radiation Oncology (AIRO) (2016) Extreme hypofractionation for early prostate cancer: biology meets technology. Cancer Treat Rev 50:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.08.005(Epub 2016 Aug 29)
D’Agostino G, Franzese C, De Rose F, Franceschini D, Comito T, Villa E, Alongi F, Liardo R, Tomatis S, Navarria P, Mancosu P, Reggiori G, Cozzi L, Scorsetti M (2016) High-quality Linac-based stereotactic body radiation therapy with flattening filter free beams and volumetric modulated arc therapy for low-intermediate risk prostate cancer: a mono-institutional experience with 90 patients. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 28(12):e173–e178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clon.2016.06.013(Epub 2016 Jul 4)
Alongi F, Fiorentino A, De Bari B (2015) SBRT and extreme hypofractionation: a new era in prostate cancer treatments? Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 20(6):411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2014.09.005(Epub 2014 Oct 22)
Blana A, Brown SC, Chaussy C, Conti GN, Eastham JA, Ganzer R, Murat FJ, Pasticier G, Rebillard X, Rewcastle JC, Robertson CN, Thuroff S, Ward JF (2009) High-intensity focused ultrasound for prostate cancer: comparative definitions of biochemical failure. BJU Int 104(8):1058–1062. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08518.x(Epub 2009 Apr 17)
Nguyen PL, Chen MH, Hoffman KE, Katz MS, D’Amico AV (2009) Predicting the risk of pelvic node involvement among men with prostate cancer in the contemporary era. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(1):104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.07.053(Epub 2009 Mar 13)
Lawton CA, Michalski J, El-Naqa I, Buyyounouski MK, Lee WR, Menard C, O’Meara E, Rosenthal SA, Ritter M, Seider M (2009) RTOG GU Radiation oncology specialists reach consensus on pelvic lymph node volumes for high-risk prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(2):383–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.08.002(Epub 2008 Oct 22)
De Bari B, Mazzola R, Aiello D, Aloi D, Gatta R, Corradini S, Salgarello M, Alongi F (2019) ((68)Ga)-PSMA-PET/CT for the detection of postoperative prostate cancer recurrence: Possible implications on treatment volumes for radiation therapy. Cancer Radiother 23(3):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2018.09.003(Epub 2019 May 12)
Vavassori V, Alongi F, D’Agostino GA, Della Bosca E, Scorsetti M (2015) Lymph-node relapsed prostate cancer management and PET-driven external beam radiotherapy: salvage or palliative treatment? Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 59(4):411–419 (Epub 2015 Sep 1)
Chapelon JY, Rouvière O, Crouzet S, Gelet A (2016) Prostate focused ultrasound therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol 880:21–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_2
Rouvière O, Girouin N, Glas L et al (2010) Prostate cancer transrectal HIFU ablation: detection of local recurrences using T2-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol 20:48–55
Burger IA (2019) 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MR detects local recurrence occult on mpMRI in prostate cancer patients after HIFU. J Nucl Med 60(8):1118–1123
Riviere J, Bernhard JC, Robert G, Wallerand H, Deti E, Maurice-Tison S, Ardiet JM, Maire JP, Richaud P, Ferriere JM, Ballanger P, Gelet A, Pasticier G (2010) Salvage radiotherapy after high-intensity focused ultrasound for recurrent localised prostate cancer. Eur Urol 58(4):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.003(Epub 2010 Jun 11)
Katz A (2017) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer: a ten-year analysis. Cureus 9(9):e1668. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1668
Kishan AU, Dang A, Katz AJ, Mantz CA, Collins SP, Aghdam N, Chu FI, Kaplan ID, Appelbaum L, Fuller DB, Meier RM, Loblaw DA, Cheung P, Pham HT, Shaverdian N, Jiang N, Yuan Y, Bagshaw H, Prionas N, Buyyounouski MK, Spratt DE, Linson PW, Hong RL, Nickols NG, Steinberg ML, Kupelian PA, King CR (2019) Long-term outcomes of stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk and intermediate-risk prostate cancer. JAMA Netw Open 2(2):e188006. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.8006
Pasticier G, Chapet O, Badet L, Ardiet JM, Poissonnier L, Murat FJ, Martin X, Gelet A (2008) Salvage radiotherapy after high-intensity focused ultrasound for localized prostate cancer: early clinical results. Urology 72(6):1305–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2008.02.064
Ripert T, Bayoud Y, Messaoudi R, Ménard J, Azémar MD, Duval F, Nguyen TD, Staerman F (2012) Salvage radiotherapy after high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment for localized prostate cancer: feasibility, tolerance and efficacy. Can Urol Assoc J 6(5):E179–E183. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.10137(Epub 2011 May 1)
Munoz F, Guarneri A, Botticella A, Gabriele P, Moretto F, Panaia R, Ruggieri A, D’Urso L, Muto G, Filippi AR, Ragona R, Ricardi U (2013) Salvage external beam radiotherapy for recurrent prostate adenocarcinoma after high-intensity focused ultrasound as primary treatment. Urol Int 90(3):288–293. https://doi.org/10.1159/000345631(Epub 2013 Jan 30)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was performed with IRB approval.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigo, M., Mazzola, R., Napoli, G. et al. Post-HIFU locally relapsed prostate cancer: high-dose salvage radiotherapy guided by molecular imaging. Radiol med 125, 491–499 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01148-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01148-4