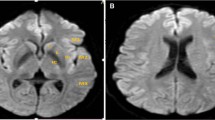
Abstract
Purpose
Cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) are small rounded lesions representing cerebral hemosiderin deposits surrounded by macrophages that results from previous microhemorrhages. The aim of this study was to review the distribution of cerebral microbleeds in patients with end-stage organ failure and their association with specific end-stage organ failure risk factors.
Materials and methods
Between August 2015 and June 2017, we evaluated 15 patients, 9 males, and 6 females, (mean age 65.5 years). Patients population was subdivided into three groups according to the organ failure: (a) chronic kidney failure (n = 8), (b) restrictive cardiomyopathy undergoing heart transplantation (n = 1), and (c) end-stage liver failure undergoing liver transplantation (n = 6). The MR exams were performed on a 3T MR unit and the SWI sequence was used for the detection of CMBs. CMBs were subdivided in supratentorial lobar distributed, supratentorial non-lobar distributed, and infratentorial distributed.
Results
A total of 91 microbleeds were observed in 15 patients. Fifty-nine CMBs lesions (64.8%) had supratentorial lobar distribution, 17 CMBs lesions (18.8%) had supratentorial non-lobar distribution and the remaining 15 CMBs lesions (16.4%) were infratentorial distributed. An overall predominance of supratentorial multiple lobar localizations was found in all types of end-stage organ failure. The presence of CMBs was significantly correlated with age, hypertension, and specific end-stage organ failure risk factors (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
CMBs are mostly founded in supratentorial lobar localization in end-stage organ failure. The improved detection of CMBs with SWI sequences may contribute to a more accurate identification of patients with cerebral risk factors to prevent complications during or after the organ transplantation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yates PA, Villemagne VL, Ellis KA, Desmond PM, Masters CL, Rowe CC (2014) Cerebral microbleeds: a review of clinical, genetic, and neuroimaging associations. Front Neurol 6(4):205
Linn J (2015) Imaging of cerebral microbleeds. Clin Neuroradiol 25(Suppl 2):167–175
Nandigam RN, Viswanathan A, Delgado P, Skehan ME, Smith EE, Rosand J, Greenberg SM, Dickerson BC (2009) MR imaging detection of cerebral microbleeds: effect of susceptibility-weighted imaging, section thickness, and field strength. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:338–343
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Roob G, Kleinert G, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, Hartung HP (1999) Histopathologic analysis of foci of signal loss on gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR images in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: evidence of microangiopathy-related microbleeds. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:637–642
Charidimou A, Krishnan A, Werring DJ, Jäger HR (2013) Cerebral microbleeds: a guide to detection and clinical relevance in different disease settings. Neuroradiology 55(6):655–674
Greenberg SM, Vernooij MW, Cordonnier C, Viswanathan A, Salman RA, Warach S, Launer LJ, Van Buchem MA, Breteler MM, Microbleed Study Group (2009) Cerebral microbleeds: a guide to detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol 8:165–174
Zhou H, Yang J, Xie P, Dong Y, You Y, Liu J (2017) Cerebral microbleeds, cognitive impairment, and MRI in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 470:14–19
Sparacia G, Speciale C, Banco A, Bencivinni F, Midiri M (2016) Accuracy of SWI sequences compared to T2*-weighted gradient echo sequences in the detection of cerebral cavernous malformations in the familial form. Neuroradiol J 29:326–335
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YC (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:19–30
Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:232–252
Sparacia G, Agnello F, La Tona G, Iaia A, Midiri F, Sparacia B (2017) Assessment of cerebral microbleeds by susceptibility-weighted imaging in Alzheimer’s disease patients: a neuroimaging biomarker of the disease. Neuroradiol J 30:330–335
Goos JD, van der Flier WM, Knol DL, Pouwels PJ, Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Wattjes MP (2011) Clinical relevance of improved microbleed detection by susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 42:1894–1900
Mori N, Miki Y, Kikuta K, Fushimi Y, Okada T, Urayama S, Sawamoto N, Fukuyama H, Hashimoto N, Togashi K (2008) Microbleeds in moyamoya disease: susceptibility-weighted imaging versus T2*-weighted imaging at 3 Tesla. Invest Radiol 43:574–579
Guo LF, Wang G, Zhu XY, Liu C, Cui L (2013) Comparison of ESWAN, SWI-SPGR, and 2D T2*-weighted GRE sequence for depicting cerebral microbleeds. Clin Neuroradiol 23:121–127
Shams S, Granberg T, Martola J, Charidimou A, Li X, Shams M, Fereshtehnejad SM, Cavallin L, Aspelin P, Wiberg-Kristoffersen M, Wahlund LO (2017) Cerebral microbleeds topography and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in cognitive impairment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37:1006–1013
Yakushiji Y (2015) Cerebral microbleeds: detection, associations and clinical implications. Front Neurol Neurosci 37:78–92
Poels MM, Ikram MA, Vernooij MW (2012) Improved MR imaging detection of cerebral microbleeds more accurately identifies persons with vasculopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1553–1556
Charidimou A, Wilson D, Shakeshaft C, Ambler G, White M, Cohen H, Yousry T, Al-Shahi Salman R, Lip G, Houlden H, Jäger HR, Brown MM, Werring DJ (2015) The Clinical Relevance of Microbleeds in Stroke study (CROMIS-2): rationale, design, and methods. Int J Stroke 10(Suppl A100):155–161
Ungvari Z, Tarantini S, Kirkpatrick AC, Csiszar A, Prodan CI (2017) Cerebral microhemorrhages: mechanisms, consequences, and prevention. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 312:H1128–H1143
Cordonnier C, Potter GM, Jackson CA, Doubal F, Keir S, Sudlow CL, Wardlaw JM, Al-Shahi Salman R (2009) Improving interrater agreement about brain microbleeds: development of the Brain Observer MicroBleed Scale (BOMBS). Stroke 40:94–99
van Veluw SJ, Charidimou A, van der Kouwe AJ, Lauer A, Reijmer YD, Costantino I, Gurol ME, Biessels GJ, Frosch MP, Viswanathan A, Greenberg SM (2016) Microbleed and microinfarct detection in amyloid angiopathy: a high-resolution MRI-histopathology study. Brain 139:3151–3162
Sepehry AA, Lang D, Hsiung GY, Rauscher A (2016) Prevalence of brain microbleeds in Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis on the influence of neuroimaging techniques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:215–222
Poliakova T, Levin O, Arablinskiy A, Vasenina E, Zerr I (2016) Cerebral microbleeds in early Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol 263:1961–1968
Chawla YK, Kashinath RC, Duseja A, Dhiman RK (2011) Predicting mortality across a broad spectrum of liver disease—an assessment of model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD), Child–Turcotte–Pugh (CTP) and creatinine-modified CTP scores. J Clin Exp Hepatol 1:161–168
Wilson D, Jäger HR, Werring DJ (2015) Anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in patients with cerebral microbleeds. Curr Atheroscler Rep 17:47
Charidimou A, Kakar P, Fox Z, Werring DJ (2013) Cerebral microbleeds and recurrent stroke risk: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack cohorts. Stroke 44:995–1001
Ueno H, Naka H, Ohshita T, Kondo K, Nomura E, Ohtsuki T, Kohriyama T, Wakabayashi S, Matsumoto M (2008) Association between cerebral microbleeds on T2*-weighted MR images and recurrent hemorrhagic stroke in patients treated with warfarin following ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1483–1486
The Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association (1994) Nomenclature and criteria for diagnosis of diseases of the heart and great vessels, 9th edn. Mass: Little, Brown & Co, Boston, pp 253–256
Gregoire SM, Chaudhary UJ, Brown MM, Yousry TA, Kallis C, Jäger HR, Werring DJ (2009) The Microbleed Anatomical Rating Scale (MARS): reliability of a tool to map brain microbleeds. Neurology 73:1759–1766
Wu Z, Mittal S, Kish K, Yu Y, Hu J, Haacke EM (2009) Identification of calcification with MRI using susceptibility-weighted imaging: a case study. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:177–182
Lau WL, Huisa BN, Fisher M (2017) The cerebrovascular-chronic kidney disease connection: perspectives and mechanisms. Transl Stroke Res 8:67–76
Kim SH, Shin DW, Yun JM, Lee JE, Lim JS, Cho BL, Kwon HM, Park JH (2017) Kidney dysfunction and cerebral microbleeds in neurologically healthy adults. PLoS One 12:e0172210
Ovbiagele B, Wing JJ, Menon RS, Burgess RE, Gibbons MC, Sobotka I, German L, Shara NM, Fernandez S, Jayam-Trouth A, Edwards DF, Kidwell CS (2013) Association of chronic kidney disease with cerebral microbleeds in patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 44:2409–2413
Watanabe A (2007) Cerebral microbleeds and intracerebral hemorrhages in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 16:30–33
Li L, Fisher M, Lau WL, Moradi H, Cheung A, Thai G, Handwerker J, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2015) Cerebral microbleeds and cognitive decline in a hemodialysis patient: case report and review of literature. Hemodial Int 19:E1–E7
Song TJ, Kim J, Lee HS, Nam CM, Nam HS, Kim YD, Heo JH (2014) Distribution of cerebral microbleeds determines their association with impaired kidney function. J Clin Neurol 10:222–228
Haley KE, Greenberg SM, Gurol ME (2013) Cerebral microbleeds and macrobleeds: should they influence our recommendations for antithrombotic therapies? Curr Cardiol Rep 15:425
Lee SH, Ryu WS, Roh JK (2009) Cerebral microbleeds are a risk factor for warfarin-related intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 72:171–176
Teperman LW (2013) Impact of pretransplant hepatic encephalopathy on liver posttransplantation outcomes. Int J Hepatol. 2013:952828
Rovira A, Alonso J, Córdoba J (2008) MR imaging findings in hepatic encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1612–1621
Kim YD, Song D, Heo JH, Kim SU, Kim BK, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Kim KJ, Han KH (2015) Relationship between cerebral microbleeds and liver stiffness determined by transient elastography. PLoS One 10:e0139227
Achiriloaie AF, Kido D, Wycliffe D, Jacobson JP (2011) White matter microsusceptibility changes in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. J Radiol Case Rep 5:1–7
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Gianvincenzo Sparacia, MD. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Ethical standards
Our retrospective cohort study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Research Review Board (IRRB) of our institution, and informed consent form was waived.
Informed consent
Written informed consent to the MR exam was obtained from all subjects (human participants, patients) in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sparacia, G., Cannella, R., Lo Re, V. et al. Assessment of cerebral microbleeds by susceptibility-weighted imaging at 3T in patients with end-stage organ failure. Radiol med 123, 441–448 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-0863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-0863-x