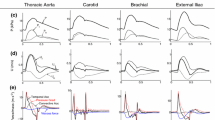
Abstract
The propagation of waves in the arteries is generally described using Fourier analysis in terms of periodic wavetrains formed by the superposition of a mean value and sinusoidal waves at the fundamental frequency (defined by the heart rate) and its harmonics. There is, however, an alternative way to describe waves in the vasculature based upon the method-of-characteristics solution of 1-D conservation laws. This method, wave intensity analysis (WIA), can be used to describe periodic waves but can also be used to describe the propagation of non-periodic waves that cannot be practically described in terms of sinusoidal wavetrains. As a means of demonstrating how WIA defines a wave, we used data gathered in a simple bench-top experiment where a single disturbance propagated along a single elastic tube and was reflected and re-reflected between a closed and a relatively open end. Results demonstrate that forward- and backward-travelling peaks of intensity usefully define wave interactions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hollander EH, Dobson GM, Wang JJ, Parker KH, Tyberg JV (2004) Direct and series transmission of left atrial pressure perturbations to the pulmonary artery: a study using wave-intensity analysis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H267–H275. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00505.2002
Hollander EH, Wang JJ, Dobson GM, Parker KH, Tyberg JV (2001) Negative wave reflections in pulmonary arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H895–H902
Kenner T, Wetterer E (1967) Experimental studies on a tube model of impedance continuously increased toward the periphery. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere 295:99–118. doi:10.1007/BF00362742
Lighthill MJ (1959) Introduction to Fourier analysis and generalised functions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Newman DL, Masters NJ, McNulty JF (1975) Pulse-wave reflection in elastic tubes. Med Biol Eng 13:720–726. doi:10.1007/BF02477333
O’Rourke MF Clinical applications of impedance analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 1:1, 8 A.D.
Parker KH (2008) An itroduction to wave intensity analysis. http://www.bg.ic.ac.uk/research/intro_to_wia/welcome.html
Parker KH, Jones CJH (1990) Forward and backward running waves in the arteries: analysis using the method of characteristics. J Biomech Eng 112:322–326. doi:10.1115/1.2891191
Riemann G (1953) The Collected Works of Bernhard Riemann. Dover, New York
Sun Y, Belenkie I, Wang JJ, Tyberg JV (2006) Assessment of right ventricular diastolic suction in dogs with the use of wave intensity analysis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H3114–H3121.doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00853.2005
Sun Y-H, Anderson TJ, Parker KH, Tyberg JV (2000) Wave-intensity analysis: a new approach to coronary dynamics. J Appl Physiol 89:1636–1644
Taylor MG (1959) An experimental determination of the propagation of fluid oscillations in a tube with a visco-elastic wall; together with an analysis of the characteristics required in an electrical analogue. Phys Med Biol 4:63–82. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/4/1/308
Wang Z, Jalali F, Sun YH, Wang JJ, Parker KH, Tyberg JV (2005) Assessment of left ventricular diastolic suction in dogs using wave-intensity analysis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H1641–H1651. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00181.2004
Womersley JR (1958) Oscillatory flow in arteries: the reflection of the pulse wave at junctions and rigid inserts in the arterial system. Phys Med Biol 2:178–187. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/2/2/305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JJ., Shrive, N.G., Parker, K.H. et al. “Wave” as defined by wave intensity analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 47, 189–195 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-008-0403-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-008-0403-2