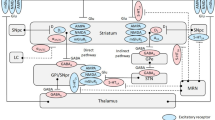
Abstract
The neurotransmitter dopamine acts via two major classes of receptors, D1-type and D2-type. D1 receptors are highly expressed in the striatum and can also be found in the cerebral cortex. Here we review the role of D1 dopamine signaling in two major domains: L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease and cognition in neuropsychiatric disorders. While there are many drugs targeting D2-type receptors, there are no drugs that specifically target D1 receptors. It has been difficult to use selective D1-receptor agonists for clinical applications due to issues with bioavailability, binding affinity, pharmacological kinetics, and side effects. We propose potential therapies that selectively modulate D1 dopamine signaling by targeting second messengers downstream of D1 receptors, allosteric modulators, or by making targeted modifications to D1-receptor machinery. The development of therapies specific to D1-receptor signaling could be a new frontier in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariano M A, Sibley D R (1994). Dopamine receptor distribution in the rat CNS: elucidation using anti-peptide antisera directed against D1A and D3 subtypes. Brain Res, 649(1–2): 95–110
Arnsten A F, Cai J X, Murphy B L, Goldman-Rakic P S (1994). Dopamine D1 receptor mechanisms in the cognitive performance of young adult and aged monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 116(2): 143–151
Aubert I, Guigoni C, Håkansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N, Bioulac B H, Gross C E, Fisone G, Bloch B, Bezard E (2005). Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol, 57(1): 17–26
Bartus R T, Baumann T L, Siffert J, Herzog C D, Alterman R, Boulis N, Turner D A, Stacy M, Lang A E, Lozano A M, Olanow C W (2013). Safety/feasibility of targeting the substantia nigra with AAV2- neurturin in Parkinson patients. Neurology, 80(18): 1698–1701
Bergson C, Mrzljak L, Smiley J F, Pappy M, Levenson R, Goldman-Rakic P S (1995). Regional, cellular, and subcellular variations in the distribution of D1 and D5 dopamine receptors in primate brain. J Neurosci, 15(12): 7821–7836
Berthet A, Porras G, Doudnikoff E, Stark H, Cador M, Bezard E, Bloch B (2009). Pharmacological analysis demonstrates dramatic alteration of D1 dopamine receptor neuronal distribution in the rat analog of LDOPA- induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci, 29(15): 4829–4835
Blanchet P J, Konitsiotis S, Chase T N (1998). Amantadine reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys. Mov Disord, 13(5): 798–802
Boyden E S, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K (2005). Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci, 8(9): 1263–1268
Calabresi P, Di Filippo M, Ghiglieri V, Picconi B (2008). Molecular mechanisms underlying levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Mov Disord, 23(Suppl 3): S570–S579
Carter M E, de Lecea L (2011). Optogenetic investigation of neural circuits in vivo. Trends Mol Med, 17(4): 197–206
Castner S A, Goldman-Rakic P S (2004). Enhancement of working memory in aged monkeys by a sensitizing regimen of dopamine D1 receptor stimulation. J Neurosci, 24(6): 1446–1450
Castner S A, Williams G V, Goldman-Rakic P S (2000). Reversal of antipsychotic-induced working memory deficits by short-term dopamine D1 receptor stimulation. Science, 287(5460): 2020–2022
Cavanagh J F, Frank M J (2014). Frontal theta as a mechanism for cognitive control. Trends Cogn Sci, 18(8): 414–421
Charifson P S, Bowen J P, Wyrick S D, Hoffman A J, Cory M, McPhail A T, Mailman R B (1989). Conformational analysis and molecular modeling of 1-phenyl-, 4-phenyl-, and 1-benzyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines as D1 dopamine receptor ligands. J Med Chem, 32(9): 2050–2058
Cools R, Barker R A, Sahakian B J, Robbins T W (2001). Enhanced or impaired cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease as a function of dopaminergic medication and task demands. Cereb Cortex, 11(12): 1136–1143
Cools R, D’Esposito M (2011). Inverted-U-shaped dopamine actions on human working memory and cognitive control. Biol Psychiatry, 69 (12): e113–e125
Cools R, Stefanova E, Barker R A, Robbins T W, Owen A M (2002). Dopaminergic modulation of high-level cognition in Parkinson’s disease: the role of the prefrontal cortex revealed by PET. Brain, 125 (Pt 3): 584–594
Costa A, Peppe A, Dell’Agnello G, Caltagirone C, Carlesimo G A (2009). Dopamine and cognitive functioning in de novo subjects with Parkinson’s disease: effects of pramipexole and pergolide on working memory. Neuropsychologia, 47(5): 1374–1381
Creese I, Burt D R, Snyder S H (1976). Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science, 192(4238): 481–483
Cui G, Jun S B, Jin X, Pham M D, Vogel S S, Lovinger D M, Costa R M (2013). Concurrent activation of striatal direct and indirect pathways during action initiation. Nature, 494(7436): 238–242
Darmopil S, Martín A B, De Diego I R, Ares S, Moratalla R (2009). Genetic inactivation of dopamine D1 but not D2 receptors inhibits LDOPA- induced dyskinesia and histone activation. Biol Psychiatry, 66 (6): 603–613
Farrell M S, Pei Y, Wan Y, Yadav P N, Daigle T L, Urban D J, Lee HM, Sciaky N, Simmons A, Nonneman R J, Huang X P, Hufeisen S J, Guettier J M, Moy S S, Wess J, Caron M G, Calakos N, Roth B L (2013). A Gas DREADD mouse for selective modulation of cAMP production in striatopallidal neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38 (5): 854–862
Fawzi A B, Macdonald D, Benbow L L, Smith-Torhan A, Zhang H, Weig B C, Ho G, Tulshian D, Linder M E, Graziano M P (2001). SCH-202676: An allosteric modulator of both agonist and antagonist binding to G protein-coupled receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 59(1): 30–37
Feenstra M G, Teske G, Botterblom M H, De Bruin J P (1999). Dopamine and noradrenaline release in the prefrontal cortex of rats during classical aversive and appetitive conditioning to a contextual stimulus: interference by novelty effects. Neurosci Lett, 272(3): 179–182
Feenstra M G, Vogel M, Botterblom M H, Joosten R N, de Bruin J P (2001). Dopamine and noradrenaline efflux in the rat prefrontal cortex after classical aversive conditioning to an auditory cue. Eur J Neurosci, 13(5): 1051–1054
Fienberg A A, Hiroi N, Mermelstein P G, Song W, Snyder G L, Nishi A, Cheramy A, O’Callaghan J P, Miller D B, Cole D G, Corbett R, Haile C N, Cooper D C, Onn S P, Grace A A, Ouimet C C, White F J, Hyman S E, Surmeier D J, Girault J, Nestler E J, Greengard P (1998). DARPP-32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science, 281(5378): 838–842
Flores-Hernández J, Cepeda C, Hernández-Echeagaray E, Calvert C R, Jokel E S, Fienberg A A, Greengard P, Levine M S (2002). Dopamine enhancement of NMDA currents in dissociated mediumsized striatal neurons: role of D1 receptors and DARPP-32. J Neurophysiol, 88(6): 3010–3020
Frederick A L, Yano H, Trifilieff P, Vishwasrao H D, Biezonski D, Mészáros J, Urizar E, Sibley D R, Kellendonk C, Sonntag K C, Graham D L, Colbran R J, Stanwood G D, Javitch J A (2015). Evidence against dopamine D1/D2 receptor heteromers. Mol Psychiatry, doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.166
Friedman J H, Lannon M C (1989). Clozapine in the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology, 39(9): 1219–1221
Fuster J (2008) The Prefrontal Cortex, 4th Edition. Academic Press, New York, NY
Gangarossa G, Longueville S, De Bundel D, Perroy J, Hervé D, Girault J A, Valjent E (2012). Characterization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus, 22(12): 2199–2207
Gerfen C R, Miyachi S, Paletzki R, Brown P (2002). D1 dopamine receptor supersensitivity in the dopamine-depleted striatum results from a switch in the regulation of ERK1/2/MAP kinase. J Neurosci, 22(12): 5042–5054
Goldman-Rakic P S (1998). The cortical dopamine system: role in memory and cognition. Adv Pharmacol, 42: 707–711
Goldman-Rakic P S, Castner S A, Svensson T H, Siever L J, Williams G V (2004). Targeting the dopamine D1 receptor in schizophrenia: insights for cognitive dysfunction. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 174 (1): 3–16
Goldman-Rakic P S, Muly E C 3rd, Williams G V (2000). D(1) receptors in prefrontal cells and circuits. Brain Res Brain Res Rev, 31(2–3): 295–301
Grace A A, Floresco S B, Goto Y, Lodge D J (2007). Regulation of firing of dopaminergic neurons and control of goal-directed behaviors. Trends Neurosci, 30(5): 220–227
Green M F, Harvey P D (2014). Cognition in schizophrenia: Past, present, and future. Schizophr Res Cogn, 1(1): e1–e9
Guttman M, Seeman P (1985). L-dopa reverses the elevated density of D2 dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s diseased striatum. J Neural Transm, 64(2): 93–103
Ha C M, Park D, Han J K, Jang J I, Park J Y, Hwang E M, Seok H, Chang S (2012). Calcyon forms a novel ternary complex with dopamine D1 receptor through PSD-95 protein and plays a role in dopamine receptor internalization. J Biol Chem, 287(38): 31813–31822
Hagger C, Buckley P, Kenny J T, Friedman L, Ubogy D, Meltzer H Y (1993). Improvement in cognitive functions and psychiatric symptoms in treatment-refractory schizophrenic patients receiving clozapine. Biol Psychiatry, 34(10): 702–712
Hall H, Sedvall G, Magnusson O, Kopp J, Halldin C, Farde L (1994). Distribution of D1- and D2-dopamine receptors, and dopamine and its metabolites in the human brain. Neuropsychopharmacology, 11 (4): 245–256
Hanrieder J, Ljungdahl A, Fälth M, Mammo SE, Bergquist J, Andersson M (2011) L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia is associated with regional increase of striatal dynorphin peptides as elucidated by imaging mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP 10:M111.009308
Hernandez-Lopez S, Tkatch T, Perez-Garci E, Galarraga E, Bargas J, Hamm H, Surmeier D J (2000). D2 dopamine receptors in striatal medium spiny neurons reduce L-type Ca2+ currents and excitability via a novel PLC[beta]1-IP3-calcineurin-signaling cascade. J Neurosci, 20(24): 8987–8995
Hoare S R, Coldwell M C, Armstrong D, Strange P G (2000). Regulation of human D(1), d(2(long)), d(2(short)), D(3) and D(4) dopamine receptors by amiloride and amiloride analogues. Br J Pharmacol, 130 (5): 1045–1059
Hoffman B, Cho S J, Zheng W, Wyrick S, Nichols D E, Mailman R B, Tropsha A (1999). Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling of dopamine D(1) antagonists using comparative molecular field analysis, genetic algorithms-partial least-squares, and K nearest neighbor methods. J Med Chem, 42(17): 3217–3226
Jenner P (2008). Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat Rev Neurosci, 9(9): 665–677
Karlsson P, Smith L, Farde L, Härnryd C, Sedvall G, Wiesel F A (1995). Lack of apparent antipsychotic effect of the D1-dopamine receptor antagonist SCH39166 in acutely ill schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 121(3): 309–316
Kätzel D, Nicholson E, Schorge S, Walker M C, Kullmann D M (2014). Chemical-genetic attenuation of focal neocortical seizures. Nat Commun, 5: 3847
Kemppainen N, Ruottinen H, Nâgren K, Rinne J O (2000). PET shows that striatal dopamine D1 and D2 receptors are differentially affected in AD. Neurology, 55(2): 205–209
Khor S P, Hsu A (2007). The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Clin Pharmacol, 2(3): 234–243
Klein C, Gordon J, Pollak L, Rabey J M (2003). Clozapine in Parkinson’s disease psychosis: 5-year follow-up review. Clin Neuropharmacol, 26(1): 8–11
Kravitz A V, Freeze B S, Parker P R L, Kay K, Thwin M T, Deisseroth K, Kreitzer A C (2010). Regulation of parkinsonian motor behaviours by optogenetic control of basal ganglia circuitry. Nature, 466(7306): 622–626
LaHoste G J, Henry B L, Marshall J F (2000). Dopamine D1 receptors synergize with D2, but not D3 or D4, receptors in the striatum without the involvement of action potentials. J Neurosci, 20(17): 6666–6671
Land B B, Narayanan N S, Liu R J, Gianessi C A, Brayton C E, Grimaldi D M, Sarhan M, Guarnieri D J, Deisseroth K, Aghajanian G K, DiLeone R J (2014). Medial prefrontal D1 dopamine neurons control food intake. Nat Neurosci, 17(2): 248–253
Lapish C C, Kroener S, Durstewitz D, Lavin A, Seamans J K (2007). The ability of the mesocortical dopamine system to operate in distinct temporal modes. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 191(3): 609–625
Lee S P, Xie Z, Varghese G, Nguyen T, O’Dowd B F, George S R (2000). Oligomerization of dopamine and serotonin receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology, 23(4 Suppl): S32–S40
Lemberger T, Parlato R, Dassesse D, Westphal M, Casanova E, Turiault M, Tronche F, Schiffmann S N, Schütz G (2007). Expression of Cre recombinase in dopaminoceptive neurons. BMC Neurosci, 8(1): 4
LeWitt P A, Rezai A R, Leehey M A, Ojemann S G, Flaherty A W, Eskandar E N, Kostyk S K, Thomas K, Sarkar A, Siddiqui M S, Tatter S B, Schwalb J M, Poston K L, Henderson J M, Kurlan R M, Richard I H, Van Meter L, Sapan C V, During M J, Kaplitt M G, Feigin A (2011). AAV2-GAD gene therapy for advanced Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, sham-surgery controlled, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol, 10(4): 309–319
Lidow M S, Goldman-Rakic P S, Gallager D W, Rakic P (1991). Distribution of dopaminergic receptors in the primate cerebral cortex: quantitative autoradiographic analysis using [3H]raclopride, [3H] spiperone and [3H]SCH23390. Neuroscience, 40(3): 657–671
Mailman R B, Murthy V (2010). Third generation antipsychotic drugs: partial agonism or receptor functional selectivity? Curr Pharm Des, 16(5): 488–501
Mattila P M, Röyttä M, Lönnberg P, Marjamäki P, Helenius H, Rinne J O (2001). Choline acetytransferase activity and striatal dopamine receptors in Parkinson’s disease in relation to cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol, 102(2): 160–166
Narayanan N S, Guarnieri D J, DiLeone R J (2010). Metabolic hormones, dopamine circuits, and feeding. Front Neuroendocrinol, 31(1): 104–112
Narayanan N S, Land B B, Solder J E, Deisseroth K, DiLeone R J (2012). Prefrontal D1 dopamine signaling is required for temporal control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109(50): 20726–20731
Narayanan N S, Rodnitzky R L, Uc E Y (2013). Prefrontal dopamine signaling and cognitive symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Rev Neurosci, 24(3): 267–278
Neumeyer J L, Kula N S, Bergman J, Baldessarini R J (2003). Receptor affinities of dopamine D1 receptor-selective novel phenylbenzazepines. Eur J Pharmacol, 474(2–3): 137–140
Parker K L, Alberico S L, Miller A D, Narayanan N S (2013a). Prefrontal D1 dopamine signaling is necessary for temporal expectation during reaction time performance. Neuroscience, 255: 246–254
Parker K L, Chen K H, Kingyon J R, Cavanagh J F, Narayanan N S (2014). D1-dependent 4 Hz oscillations and ramping activity in rodent medial frontal cortex during interval timing. J Neurosci, 34 (50): 16774–16783
Parker K L, Lamichhane D, Caetano M S, Narayanan N S (2013b). Executive dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and timing deficits. Front Integr Neurosci, 7: 75
Perreault ML, Hasbi A, O’Dowd B F, George S R (2011). The dopamine d1-d2 receptor heteromer in striatal medium spiny neurons: evidence for a third distinct neuronal pathway in Basal Ganglia. Front Neuroanat, 5: 31
Phillips A G, Ahn S, Floresco S B (2004). Magnitude of dopamine release in medial prefrontal cortex predicts accuracy of memory on a delayed response task. J Neurosci, 24(2): 547–553
Pifl C, Nanoff C, Schingnitz G, Schütz W, Hornykiewicz O (1992). Sensitization of dopamine-stimulated adenylyl cyclase in the striatum of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated rhesus monkeys and patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem, 58(6): 1997–2004
Pisani A, Shen J (2009). Levodopa-induced dyskinesia and striatal signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(9): 2973–2974
Pizzolato G, Chierichetti F, Fabbri M, Cagnin A, Dam M, Ferlin G, Battistin L (1996). Reduced striatal dopamine receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: single photon emission tomography study with the D2 tracer [123I]-IBZM. Neurology, 47(4): 1065–1068
Porras G, Berthet A, Dehay B, Li Q, Ladepeche L, Normand E, Dovero S, Martinez A, Doudnikoff E, Martin-Négrier M L, Chuan Q, Bloch B, Choquet D, Boué-Grabot E, Groc L, Bezard E (2012). PSD-95 expression controls L-DOPA dyskinesia through dopamine D1 receptor trafficking. J Clin Invest, 122(11): 3977–3989
Rashid A J, So C H, Kong M M C, Furtak T, El-Ghundi M, Cheng R, O’Dowd B F, George S R (2007). D1-D2 dopamine receptor heterooligomers with unique pharmacology are coupled to rapid activation of Gq/11 in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104(2): 654–659
Rektorová I, Rektor I, Bares M, Dostál V, Ehler E, Fanfrdlová Z, Fiedler J, Klajblová H, Kulist’ák P, Ressner P, Svátová J, Urbánek K, Velísková J (2005). Cognitive performance in people with Parkinson’s disease and mild or moderate depression: effects of dopamine agonists in an add-on to L-dopa therapy. Eur J Neurol, 12 (1): 9–15
Roberts B M, Seymour P A, Schmidt C J, Williams G V, Castner S A (2010). Amelioration of ketamine-induced working memory deficits by dopamine D1 receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 210 (3): 407–418
Rodnitzky R L, Narayanan N S (2014). Amantadine’s role in the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Neurology, 82(4): 288–289
Rossetti Z L, Carboni S (2005). Noradrenaline and dopamine elevations in the rat prefrontal cortex in spatial working memory. J Neurosci, 25 (9): 2322–2329
Santana N, Mengod G, Artigas F (2009). Quantitative analysis of the expression of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in pyramidal and GABAergic neurons of the rat prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex, 19(4): 849–860
Santini E, Valjent E, Usiello A, Carta M, Borgkvist A, Girault J A, Hervé D, Greengard P, Fisone G (2007). Critical involvement of cAMP/ DARPP-32 and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signaling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J Neurosci, 27(26): 6995–7005
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic P S (1991). D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: involvement in working memory. Science, 251 (4996): 947–950
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic P S (1994). The role of D1-dopamine receptor in working memory: local injections of dopamine antagonists into the prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkeys performing an oculomotor delayed-response task. J Neurophysiol, 71(2): 515–528
Schultz W (1997). Dopamine neurons and their role in reward mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 7(2): 191–197
Schultz W (2001). Reward signaling by dopamine neurons. Neuroscientist, 7(4): 293–302
Seeman P (1987). Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse, 1(2): 133–152
Seeman P, Chau-Wong M, Tedesco J, Wong K (1975). Brain receptors for antipsychotic drugs and dopamine: direct binding assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 72(11): 4376–4380
Sesack S R, Carr D B, Omelchenko N, Pinto A (2003). Anatomical substrates for glutamate-dopamine interactions: evidence for specificity of connections and extrasynaptic actions. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1003(1): 36–52
Shuen J A, Chen M, Gloss B, Calakos N (2008). Drd1a-tdTomato BAC transgenic mice for simultaneous visualization of medium spiny neurons in the direct and indirect pathways of the basal ganglia. J Neurosci, 28(11): 2681–2685
Soriano A, Vendrell M, Gonzalez S, Mallol J, Albericio F, Royo M, Lluís C, Canela E I, Franco R, Cortés A, Casadó V (2010). A hybrid indoloquinolizidine peptide as allosteric modulator of dopamine D1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 332(3): 876–885
Sun P, Wang J, Gu W, Cheng W, Jin G Z, Friedman E, Zheng J, Zhen X (2009). PSD-95 regulates D1 dopamine receptor resensitization, but not receptor-mediated Gs-protein activation. Cell Res, 19(5): 612–624
Takahashi H, Kato M, Takano H, Arakawa R, Okumura M, Otsuka T, Kodaka F, Hayashi M, Okubo Y, Ito H, Suhara T (2008). Differential contributions of prefrontal and hippocampal dopamine D(1) and D(2) receptors in human cognitive functions. J Neurosci, 28(46): 12032–12038
Taylor J L, Bishop C, Walker P D (2005). Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor contributions to L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the dopaminedepleted rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 81(4): 887–893
Taymans J M, Kia H K, Groenewegen H J, Leysen J E, Langlois X (2005). Bilateral control of brain activity by dopamine D1 receptors: evidence from induction patterns of regulator of G protein signaling 2 and c-fos mRNA in D1-challenged hemiparkinsonian rats. Neuroscience, 134(2): 643–656
Ungless M A, Magill P J, Bolam J P (2004). Uniform inhibition of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area by aversive stimuli. Science, 303(5666): 2040–2042
Vijayraghavan S, Wang M, Birnbaum S G, Williams G V, Arnsten A F T (2007). Inverted-U dopamine D1 receptor actions on prefrontal neurons engaged in working memory. Nat Neurosci, 10(3): 376–384
Watanabe M, Kodama T, Hikosaka K (1997). Increase of extracellular dopamine in primate prefrontal cortex during a working memory task. J Neurophysiol, 78(5): 2795–2798
Westin J E, Vercammen L, Strome E M, Konradi C, Cenci M A (2007). Spatiotemporal pattern of striatal ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a rat model of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and the role of dopamine D1 receptors. Biol Psychiatry, 62(7): 800–810
Wilkinson L S, Humby T, Killcross A S, Torres E M, Everitt B J, Robbins T W (1998). Dissociations in dopamine release in medial prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum during the acquisition and extinction of classical aversive conditioning in the rat. Eur J Neurosci, 10(3): 1019–1026
Williams G V, Goldman-Rakic P S (1995). Modulation of memory fields by dopamine D1 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Nature, 376(6541): 572–575
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Saito H (1996). Effect of conditioned fear stress on dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett, 209(3): 201–203
Zahrt J, Taylor J R, Mathew R G, Arnsten A F T (1997). Supranormal stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors in the rodent prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance. J Neurosci, 17(21): 8528–8535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YC., Alberico, S.L., Emmons, E. et al. New therapeutic strategies targeting D1-type dopamine receptors for neuropsychiatric disease. Front. Biol. 10, 230–238 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1360-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-015-1360-4