Abstract
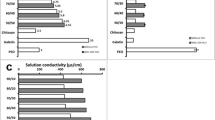
Electrospun blend nanofibers were fabricated from chitosan (1,000 kDa, 80% DDA) and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO; 900 kDa) at a ratio of 3:1 dispersed in 50% and 90% acetic acid. The influence of surfactants on the production of electrospun nanofibers was investigated by adding nonionic polyoxyethylene glycol dodecyl ether (Brij 35), anionic sodium dodecyl sulfate, or cationic dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide below, at, and above their specific critical micellar concentration to the polymer blend solution. Viscosity, conductivity, and surface tension of polymer solutions, as well as morphology and composition, of nanofibers containing surfactants were determined. Pure chitosan did not form fibers and was instead deposited as beads. Addition of PEO and an increasing concentration of surfactants induced spinnability and yielded larger fibers with diameters ranging from 10 to 240 nm. Surfactants affected morphology yielding needle-like, smooth, or beaded fibers. Compositional analysis revealed that nanofibers consisted of both polymers and surfactants with concentration of the constituents in nanofibers differing from that in polymer solutions. Results suggest that surfactants may modulate polymer–polymer interactions thus influencing the morphology and composition of deposited nanostructures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Burger, B.S. Hsiao, B. Chu, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 36, 333–368 (2006). doi:10.1146/annurev.matsci.36.011205.123537
Z.M. Huang, Y.Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol. 63(15), 2223–2253 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00178-7
M. Kumar, R.A.A. Muzzarelli, C. Muzzarelli, H. Sashiwa, A.J. Domb, Chem. Rev. 104(12), 6017–6084 (2004). doi:10.1021/cr030441b
R.A.A. Muzzarelli, Chitin (Pergamon, Oxford, 1977)
H.K. No, S.P. Meyers, W. Prinyawiwatkul, Z. Xu, J. Food Sci. 72(5), R87–R100 (2007). doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00383.x
L. Li, Y.L. Hsieh, Carbohydr. Res. 341(3), 374–381 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.carres.2005.11.028
Y.T. Jia, J. Gong, X.H. Gu, H.Y. Kim, J. Dong, X.Y. Shen, Carbohydr. Polym. 67(3), 403–409 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.06.010
B. Duan, C.H. Dong, X.Y. Yuan, K.D. Yao, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 15(6), 797–811 (2004). doi:10.1163/156856204774196171
A. Subramanian, H.-Y. Lin, D. Vu, G. Larsen, Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 40, 117–122 (2004)
K.H. Jung, M.W. Huh, W. Meng et al., J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 105(5), 2816–2823 (2007). doi:10.1002/app.25594
K. Ohkawa, K.I. Minato, G. Kumagai, S. Hayashi, H. Yamamoto, Biomacromolecules 7(11), 3291–3294 (2006). doi:10.1021/bm0604395
B.M. Min, S.W. Lee, J.N. Lim et al., Polymer (Guildf.) 45(21), 7137–7142 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2004.08.048
X.Y. Geng, O.H. Kwon, J.H. Jang, Biomaterials 26(27), 5427–5432 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.01.066
L. Yao, T.W. Haas, A. Guiseppi-Elie, G.L. Bowlin, D.G. Simpson, G.E. Wnek, Chem. Mater. 15(9), 1860–1864 (2003). doi:10.1021/cm0210795
T. Lin, H.X. Wang, H.M. Wang, X.G. Wang, Nanotechnology 15(9), 1375–1381 (2004). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/15/9/044
A. Helenius, D.R. McCaslin, E. Fries, C. Tanford, Methods Enzymol. 56, 734–749 (1979). doi:10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2
S. Wongsasulak, K.M. Kit, D.J. McClements, T. Yoovidhya, J. Weiss, Polymer (Guildf.) 48(2), 448–457 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2006.11.025
H. Fong, I. Chun, D.H. Reneker, Polymer (Guildf.) 40(16), 4585–4592 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00068-3
Y.M. Shin, M.M. Hohman, M.P. Brenner, G.C. Rutledge, Polymer (Guildf.) 42(25), 9955–9967 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00540-7
J.M. Deitzel, J. Kleinmeyer, D. Harris, N.C.B. Tan, Polymer (Guildf.) 42(1), 261–272 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00250-0
N. Bhattarai, M.Q. Zhang, Nanotechnology 18(45), 455601.1–455601.10 (2007). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/18/45/455601
H.L. Jiang, D.F. Fang, B.S. Hsiao, B. Chu, W.L. Chen, Biomacromolecules 5(2), 326–333 (2004). doi:10.1021/bm034345w
M. Spasova, N. Manolova, D. Paneva, L. Rashkov, Preparation of chitosan-containing nanofibres by electrospinning of chitosan/poly (ethylene oxide) blend solutions. e-Polymers, Art. No. 056. (2004)
J.B. Xie, Y.L. Hsieh, J. Mater. Sci. 38(10), 2125–2133 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1023763727747
L.F. Zhang, Y.L. Hsieh, Carbohydr. Polym. 71(2), 196–207 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.05.031
Y.S. Zhou, D.Z. Yang, J. Nie, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102(6), 5692–5697 (2006). doi:10.1002/app.25068
P. Gupta, C. Elkins, T.E. Long, G.L. Wilkes, Polymer (Guildf.) 46(13), 4799–4810 (2005)
Y. Wan, H. Wu, A.X. Yu, D.J. Wen, Biomacromolecules 7(4), 1362–1372 (2006). doi:10.1021/bm0600825
C.L. De Vasconcelos, P.M. Bezerril, D.E.S. dos Santos, T.N.C. Dantas, M.R. Pereira, J.L.C. Fonseca, Biomacromolecules 7(4), 1245–1252 (2006). doi:10.1021/bm050963w
Y. Hu, Y.M. Du, J.H. Yang, Y.F. Tang, J. Li, X.Y. Wang, Polymer (Guildf.) 48(11), 3098–3106 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2007.03.063
S. Zivanovic, J.J. Li, P.M. Davidson, K. Kit, Biomacromolecules 8, 1505–1510 (2007). doi:10.1021/bm061140p
C. Sawatari, T. Kondo, Macromolecules 32(6), 1949–1955 (1999). doi:10.1021/ma980900o
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Environmental Protection Agency Star Grant Program (grant number GR832372) and the Massachusetts Experiment Station supported by the Cooperative State Research, Extension, Education Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station (project nos. 831 and 911).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kriegel, C., Kit, K.M., McClements, D.J. et al. Influence of Surfactant Type and Concentration on Electrospinning of Chitosan–Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Blend Nanofibers. Food Biophysics 4, 213–228 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-009-9119-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-009-9119-6