Abstract
Dopamine has emerged as a fundamental regulator of inflammation. In this regard, it has been shown that dopaminergic signalling pathways are key players promoting homeostasis between the central nervous system and the immune system. Dysregulation in the dopaminergic system affects both innate and adaptive immunity, contributing to the development of numerous autoimmune and inflammatory pathologies. This makes dopamine receptors interesting therapeutic targets for either the development of new treatments or repurposing of already available pharmacological drugs. Dopamine receptors are broadly expressed on different immune cells with multifunctional effects depending on the dopamine concentration available and the pattern of expression of five dopamine receptors displaying different affinities for dopamine. Thus, impaired dopaminergic signalling through different dopamine receptors may result in altered behaviour of immunity, contributing to the development and progression of autoimmune pathologies. In this review we discuss the current evidence involving the dopaminergic system in inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease. In addition, we summarise and analyse the therapeutic approaches designed to attenuate disease development and progression by targeting the dopaminergic system.

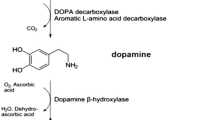
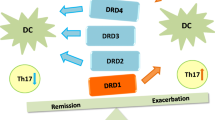
Targetting the dopaminergic system in autoimmunity.
Effector T-cells (Teff) orchestrate inflamamtion involved in autoimmunity, whilst regulatory T-cells (Tregs) suppress Teff activity promoting tolerance to self-constituents. Dopamine has emerged as a key regulator of Teff and Tregs function, thereby dopamine receptors have becoming important therapeutic targets in autoimmune disorders, especially in those affecting the brain and the gut, where dopamine levels strongly change with inflammation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas MM, Xu Z, Tan LCS (2018) Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease-east versus west. Mov Disord Clin Pract 5:14–28
Anderson MA, Burda JE, Ren Y, Ao Y, O'Shea TM, Kawaguchi R, Coppola G, Khakh BS, Deming TJ, Sofroniew MV (2016) Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature 532:195–200
Asano Y, Hiramoto T, Nishino R, Aiba Y, Kimura T, Yoshihara K, Koga Y, Sudo N (2012) Critical role of gut microbiota in the production of biologically active, free catecholamines in the gut lumen of mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303:G1288–G1295
Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA (2016) The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol 15:1257–1272
Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ (2007) Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet 369:1641–1657
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Berndt BE, Zhang M, Chen GH, Huffnagle GB, Kao JY (2007) The role of dendritic cells in the development of acute dextran sulfate sodium colitis. J Immunol 179:6255–6262
Bernstein CN, Rawsthorne P, Cheang M, Blanchard JF (2006) A population-based case control study of potential risk factors for IBD. Am J Gastroenterol 101:993–1002
Bezard E, Ferry S, Mach U, Stark H, Leriche L, Boraud T, Gross C, Sokoloff P (2003) Attenuation of levodopa-induced dyskinesia by normalizing dopamine D3 receptor function. Nat Med 9:762–767
Brochard V, Combadiere B, Prigent A, Laouar Y, Perrin A, Beray-Berthat V, Bonduelle O, Alvarez-Fischer D, Callebert J, Launay JM, Duyckaerts C, Flavell RA, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 119:182–192
Brown SJ, Mayer L (2007) The immune response in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 102:2058–2069
Buijs S, Krol M, de Voer G (2018) Healthcare utilization and costs of multiple sclerosis patients in the Netherlands: a healthcare claims database study. J Comp Eff Res 7:453–462
Burisch J, Jess T, Martinato M, Lakatos PL, EpiCom E (2013) The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J Crohns Colitis 7:322–337
Check JH, Katsoff B, Cohen R (2010) Novel highly effective medical treatment of severe treatment refractory Crohn's disease using sympathomimetic amines: case report. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16:1999–2000
Check JH, Katsoff B, Cohen R (2011a) Case report showing that a woman with ulcerative colitis refractory to standard therapy responded well to the sympathomimetic amine dextroamphetamine sulfate. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17:870–871
Check JH, Cohen R, Katsoff B, Check D (2011b) Hypofunction of the sympathetic nervous system is an etiologic factor for a wide variety of chronic treatment-refractory pathologic disorders which all respond to therapy with sympathomimetic amines. Med Hypotheses 77:717–725
Chen S, Le WD, Xie WJ, Alexianu ME, Engelhardt JI, Siklos L, Appel SH (1998) Experimental destruction of substantia nigra initiated by Parkinson disease immunoglobulins. Arch Neurol 55:1075–1080
Christiansen JR, Olesen MN, Otzen DE, Romero-Ramos M, Sanchez-Guajardo V (2016) Alpha-Synuclein vaccination modulates regulatory T cell activation and microglia in the absence of brain pathology. J Neuroinflammation 13:74
Contreras F, Prado C, Gonzalez H, Franz D, Osorio-Barrios F, Osorio F, Ugalde V, Lopez E, Elgueta D, Figueroa A, Lladser A, Pacheco R (2016) Dopamine receptor D3 signaling on CD4+ T cells favors Th1- and Th17-mediated immunity. J Immunol 196:4143–4149
Cosentino M, Fietta AM, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Bombelli R, Carcano E, Saporiti F, Meloni F, Marino F, Lecchini S (2007) Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells selectively express tyrosine hydroxylase and contain endogenous catecholamines subserving an autocrine/paracrine inhibitory functional loop. Blood 109:632–642
Cosentino M, Zaffaroni M, Trojano M, Giorelli M, Pica C, Rasini E, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Ghezzi A, Comi G, Livrea P, Lecchini S, Marino F (2012) Dopaminergic modulation of CD4+CD25(high) regulatory T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis patients during interferon-beta therapy. Neuroimmunomodulation 19:283–292
Cosentino M, Ferrari M, Kustrimovic N, Rasini E, Marino F (2015) Influence of dopamine receptor gene polymorphisms on circulating T lymphocytes: a pilot study in healthy subjects. Hum Immunol 76:747–752
Cosentino M, Zaffaroni M, Legnaro M, Bombelli R, Schembri L, Baroncini D, Bianchi A, Clerici R, Guidotti M, Banfi P, Bono G, Marino F (2016) Dopaminergic receptors and adrenoceptors in circulating lymphocytes as putative biomarkers for the early onset and progression of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 298:82–89
Cosentino M, Kustrimovic N, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Marino F (2018) cAMP levels in lymphocytes and CD4(+) regulatory T-cell functions are affected by dopamine receptor gene polymorphisms. Immunology 153:337–341
Damier P, Hirsch EC, Zhang P, Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F (1993) Glutathione peroxidase, glial cells and Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 52:1–6
De Virgilio A, Greco A, Fabbrini G, Inghilleri M, Rizzo MI, Gallo A, Conte M, Rosato C, Ciniglio Appiani M, de Vincentiis M (2016) Parkinson's disease: autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. Autoimmun Rev 15:1005–1011
Dendrou CA, Fugger L, Friese MA (2015) Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 15:545–558
Dijkstra CD, van der Voort ER, De Groot CJ, Huitinga I, Uitdehaag BM, Polman CH, Berkenbosch F (1994) Therapeutic effect of the D2-dopamine agonist bromocriptine on acute and relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 19:135–142
Dobryakova E, Genova HM, DeLuca J, Wylie GR (2015) The dopamine imbalance hypothesis of fatigue in multiple sclerosis and other neurological disorders. Front Neurol 6:52
Ehringer H, Hornykiewicz O (1998) Distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the human brain and their behavior in diseases of the extrapyramidal system. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 4:53–57
Eisenhofer G, Aneman A, Friberg P, Hooper D, Fandriks L, Lonroth H, Hunyady B, Mezey E (1997) Substantial production of dopamine in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:3864–3871
Elbaz A, Carcaillon L, Kab S, Moisan F (2016) Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol 172:14–26
Elgueta D, Aymerich MS, Contreras F, Montoya A, Celorrio M, Rojo-Bustamante E, Riquelme E, Gonzalez H, Vasquez M, Franco R, Pacheco R (2017) Pharmacologic antagonism of dopamine receptor D3 attenuates neurodegeneration and motor impairment in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology 113:110–123
Ernstsson O, Gyllensten H, Alexanderson K, Tinghog P, Friberg E, Norlund A (2016) Cost of illness of multiple sclerosis - a systematic review. PLoS One 11:e0159129
Feng T, Qin H, Wang L, Benveniste EN, Elson CO, Cong Y (2011) Th17 cells induce colitis and promote Th1 cell responses through IL-17 induction of innate IL-12 and IL-23 production. J Immunol 186:6313–6318
Foley FW, Traugott U, LaRocca NG, Smith CR, Perlman KR, Caruso LS, Scheinberg LC (1992) A prospective study of depression and immune dysregulation in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 49:238–244
Franz D, Contreras F, Gonzalez H, Prado C, Elgueta D, Figueroa C, Pacheco R (2015) Dopamine receptors D3 and D5 regulate CD4(+)T-cell activation and differentiation by modulating ERK activation and cAMP production. J Neuroimmunol 284:18–29
Frischer JM, Bramow S, Dal-Bianco A, Lucchinetti CF, Rauschka H, Schmidbauer M, Laursen H, Sorensen PS, Lassmann H (2009) The relation between inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis brains. Brain 132:1175–1189
Furlan R, Ardizzone S, Palazzolo L, Rimoldi A, Perego F, Barbic F, Bevilacqua M, Vago L, Bianchi Porro G, Malliani A (2006) Sympathetic overactivity in active ulcerative colitis: effects of clonidine. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R224–R232
Gagliani N, Vesely MCA, Iseppon A, Brockmann L, Xu H, Palm NW, de Zoete MR, Licona-Limón P, Paiva RS, Ching T, Weaver C, Zi X, Pan X, Fan R, Garmire LX, Cotton MJ, Drier Y, Bernstein B, Geginat J, Stockinger B, Esplugues E, Huber S, Flavell RA (2015) Th17 cells transdifferentiate into regulatory T cells during resolution of inflammation. Nature 523:221–225
Geremia A, Biancheri P, Allan P, Corazza GR, Di Sabatino A (2014) Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev 13:3–10
Giorelli M, Livrea P, Trojano M (2005) Dopamine fails to regulate activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes from multiple sclerosis patients: effects of IFN-beta. J Interf Cytokine Res 25:395–406
Gonzalez H, Pacheco R (2014) T-cell-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation involved in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroinflammation 11:201
Gonzalez H, Contreras F, Prado C, Elgueta D, Franz D, Bernales S, Pacheco R (2013) Dopamine receptor D3 expressed on CD4+ T cells favors neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons during Parkinson's disease. J Immunol 190:5048–5056
Gonzalez H, Elgueta D, Montoya A, Pacheco R (2014) Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol 274:1–13
Gonzalez H, Contreras F, Pacheco R (2015) Regulation of the neurodegenerative process associated to Parkinson's disease by CD4+ T-cells. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 10:561–575
Gross CC, Schulte-Mecklenbeck A, Runzi A, Kuhlmann T, Posevitz-Fejfar A, Schwab N, Schneider-Hohendorf T, Herich S, Held K, Konjevic M, Hartwig M, Dornmair K, Hohlfeld R, Ziemssen T, Klotz L, Meuth SG, Wiendl H (2016) Impaired NK-mediated regulation of T-cell activity in multiple sclerosis is reconstituted by IL-2 receptor modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E2973–E2982
Guigoni C, Aubert I, Li Q, Gurevich VV, Benovic JL, Ferry S, Mach U, Stark H, Leriche L, Hakansson K, Bioulac BH, Gross CE, Sokoloff P, Fisone G, Gurevich EV, Bloch B, Bezard E (2005) Pathogenesis of levodopa-induced dyskinesia: focus on D1 and D3 dopamine receptors. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11(Suppl 1):S25–S29
Hallett PJ, McLean JR, Kartunen A, Langston JW, Isacson O (2012) Alpha-Synuclein overexpressing transgenic mice show internal organ pathology and autonomic deficits. Neurobiol Dis 47:258–267
Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, Vollmer T, Antel J, Fox RJ, Bar-Or A, Panzara M, Sarkar N, Agarwal S, Langer-Gould A, Smith CH, Group HT (2008) B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 358:676–688
Hayter SM, Cook MC (2012) Updated assessment of the prevalence, spectrum and case definition of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 11:754–765
Herrmann JE, Imura T, Song B, Qi J, Ao Y, Nguyen TK, Korsak RA, Takeda K, Akira S, Sofroniew MV (2008) STAT3 is a critical regulator of astrogliosis and scar formation after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 28:7231–7243
Heyer MP, Pani AK, Smeyne RJ, Kenny PJ, Feng G (2012) Normal midbrain dopaminergic neuron development and function in miR-133b mutant mice. J Neurosci 32:10887–10894
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Hou S, Carson DM, Wu D, Klaw MC, Houle JD, Tom VJ (2016) Dopamine is produced in the rat spinal cord and regulates micturition reflex after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 285:136–146
Huot P, Johnston TH, Koprich JB, Aman A, Fox SH, Brotchie JM (2012) L-745,870 reduces L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned macaque model of Parkinson's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 342:576–585
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics C et al (2013) Analysis of immune-related loci identifies 48 new susceptibility variants for multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 45:1353–1360
Izcue A, Coombes JL, Powrie F (2009) Regulatory lymphocytes and intestinal inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 27:313–338
Jelcic I et al (2018) Memory B cells activate brain-homing, autoreactive CD4(+) T cells in multiple sclerosis. Cell 175(85–100):e123
Jostins L et al (2012) Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 491:119–124
Kast RE, Altschuler EL (2001) Remission of Crohn's disease on bupropion. Gastroenterology 121:1260–1261
Kawano M, Takagi R, Kaneko A, Matsushita S (2015) Berberine is a dopamine D1- and D2-like receptor antagonist and ameliorates experimentally induced colitis by suppressing innate and adaptive immune responses. J Neuroimmunol 289:43–55
Khan OA, Olek MJ (1995) Treatment of paroxysmal symptoms in multiple sclerosis with bromocriptine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:253
Kiesler P, Fuss IJ, Strober W (2015) Experimental models of inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:154–170
Kikuchi T, Morizane A, Doi D, Magotani H, Onoe H, Hayashi T, Mizuma H, Takara S, Takahashi R, Inoue H, Morita S, Yamamoto M, Okita K, Nakagawa M, Parmar M, Takahashi J (2017) Human iPS cell-derived dopaminergic neurons function in a primate Parkinson's disease model. Nature 548:592–596
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov SV, Murchison E, Hannon G, Abeliovich A (2007) A MicroRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 317:1220–1224
Kinchen J, Chen HH, Parikh K, Antanaviciute A, Jagielowicz M, Fawkner-Corbett D, Ashley N, Cubitt L, Mellado-Gomez E, Attar M, Sharma E, Wills Q, Bowden R, Richter FC, Ahern D, Puri KD, Henault J, Gervais F, Koohy H, Simmons A (2018) Structural remodeling of the human colonic mesenchyme in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 175(372–386):e317
Kordower JH, Olanow CW, Dodiya HB, Chu Y, Beach TG, Adler CH, Halliday GM, Bartus RT (2013) Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson's disease. Brain 136:2419–2431
Kowal SL, Dall TM, Chakrabarti R, Storm MV, Jain A (2013) The current and projected economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the United States. Mov Disord 28:311–318
Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Wronska A, Kohutnicka M, Czlonkowski A, Czlonkowska A (1999) The inflammatory reaction following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine intoxication in mouse. Exp Neurol 156:50–61
Kustrimovic N, Comi C, Magistrelli L, Rasini E, Legnaro M, Bombelli R, Aleksic I, Blandini F, Minafra B, Riboldazzi G, Sturchio A, Mauri M, Bono G, Marino F, Cosentino M (2018) Parkinson's disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naive and drug-treated patients. J Neuroinflammation 15:205
Laroni A, Armentani E, Kerlero de Rosbo N, Ivaldi F, Marcenaro E, Sivori S, Gandhi R, Weiner HL, Moretta A, Mancardi GL, Uccelli A (2016) Dysregulation of regulatory CD56(bright) NK cells/T cells interactions in multiple sclerosis. J Autoimmun 72:8–18
Lechin F, van der Dijs B, Insausti CL, Gomez F, Villa S, Lechin AE, Arocha L, Oramas O (1985) Treatment of ulcerative colitis with clonidine. J Clin Pharmacol 25:219–226
Levite M (2016) Dopamine and T cells: dopamine receptors and potent effects on T cells, dopamine production in T cells, and abnormalities in the dopaminergic system in T cells in autoimmune, neurological and psychiatric diseases. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 216:42–89
Li ZS, Schmauss C, Cuenca A, Ratcliffe E, Gershon MD (2006) Physiological modulation of intestinal motility by enteric dopaminergic neurons and the D2 receptor: analysis of dopamine receptor expression, location, development, and function in wild-type and knock-out mice. J Neurosci 26:2798–2807
Li R, Rezk A, Miyazaki Y, Hilgenberg E, Touil H, Shen P, Moore CS, Michel L, Althekair F, Rajasekharan S, Gommerman JL, Prat A, Fillatreau S, Bar-Or A, Canadian BciMST (2015) Proinflammatory GM-CSF-producing B cells in multiple sclerosis and B cell depletion therapy. Sci Transl Med 7:310ra166
Lieberknecht V, Junqueira SC, Cunha MP, Barbosa TA, de Souza LF, Coelho IS, Santos AR, Rodrigues AL, Dafre AL, Dutra RC (2017) Pramipexole, a dopamine D2/D3 receptor-preferring agonist, prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis development in mice. Mol Neurobiol 54:1033–1045
Lunati A, Lesage S, Brice A (2018) The genetic landscape of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 174:628–643
Ma Y, Tang C, Chaly T, Greene P, Breeze R, Fahn S, Freed C, Dhawan V, Eidelberg D (2010) Dopamine cell implantation in Parkinson's disease: long-term clinical and (18)F-FDOPA PET outcomes. J Nucl Med 51:7–15
Madsen KL, Malfair D, Gray D, Doyle JS, Jewell LD, Fedorak RN (1999) Interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice develop a primary intestinal permeability defect in response to enteric microflora. Inflamm Bowel Dis 5:262–270
Magro F, Vieira-Coelho MA, Fraga S, Serrao MP, Veloso FT, Ribeiro T, Soares-da-Silva P (2002) Impaired synthesis or cellular storage of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in human inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 47:216–224
Magro F, Fraga S, Ribeiro T, Soares-da-Silva P (2004) Decreased availability of intestinal dopamine in transmural colitis may relate to inhibitory effects of interferon-gamma upon L-DOPA uptake. Acta Physiol Scand 180:379–386
Magro F, Cunha E, Araujo F, Meireles E, Pereira P, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Veloso FT, Medeiros R, Soares-da-Silva P (2006) Dopamine D2 receptor polymorphisms in inflammatory bowel disease and the refractory response to treatment. Dig Dis Sci 51:2039–2044
Martini E, Krug SM, Siegmund B, Neurath MF, Becker C (2017) Mend your fences: the epithelial barrier and its relationship with mucosal immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:33–46
Mastronardi CA, Yu WH, McCann S (2001) Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha release is controlled by the central nervous system. Neuroimmunomodulation 9:148–156
Mayer L (2010) Evolving paradigms in the pathogenesis of IBD. J Gastroenterol 45:9–16
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
McKenna F, McLaughlin PJ, Lewis BJ, Sibbring GC, Cummerson JA, Bowen-Jones D, Moots RJ (2002) Dopamine receptor expression on human T- and B-lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and NK cells: a flow cytometric study. J Neuroimmunol 132:34–40
Melanson M, Grossberndt A, Klowak M, Leong C, Frost EE, Prout M, Le Dorze JA, Gramlich C, Doupe M, Wong L, Esfahani F, Gomori A, Namaka M (2010) Fatigue and cognition in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis treated with interferon beta. Int J Neurosci 120:631–640
Melnikov M, Belousova O, Murugin V, Pashenkov capital Em C, Boysmall ka CoCA (2016) The role of dopamine in modulation of Th-17 immune response in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 292:97–101
Mercado G, Castillo V, Soto P, Lopez N, Axten JM, Sardi SP, Hoozemans JJM, Hetz C (2018) Targeting PERK signaling with the small molecule GSK2606414 prevents neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 112:136–148
Mohr DC, Goodkin DE, Islar J, Hauser SL, Genain CP (2001) Treatment of depression is associated with suppression of nonspecific and antigen-specific T(H)1 responses in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 58:1081–1086
Nakano K, Higashi T, Hashimoto K, Takagi R, Tanaka Y, Matsushita S (2008) Antagonizing dopamine D1-like receptor inhibits Th17 cell differentiation: preventive and therapeutic effects on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:286–291
Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG (2018) Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 390:2769–2778
Nicol B, Salou M, Vogel I, Garcia A, Dugast E, Morille J, Kilens S, Charpentier E, Donnart A, Nedellec S, Jacq-Foucher M, le Frère F, Wiertlewski S, Bourreille A, Brouard S, Michel L, David L, Gourraud PA, Degauque N, Nicot AB, Berthelot L, Laplaud DA (2018) An intermediate level of CD161 expression defines a novel activated, inflammatory, and pathogenic subset of CD8(+) T cells involved in multiple sclerosis. J Autoimmun 88:61–74
Nizzoli G, Burrello C, Cribiu FM, Lovati G, Ercoli G, Botti F, Trombetta E, Porretti L, Todoerti K, Neri A, Giuffre MR, Geginat J, Vecchi M, Rescigno M, Paroni M, Caprioli F, Facciotti F (2018) Pathogenicity of in vivo generated intestinal Th17 lymphocytes is IFNgamma dependent. J Crohns Colitis 12:981–992
Oehlers SH, Flores MV, Hall CJ, Wang L, Ko DC, Crosier KE, Crosier PS (2017) A whole animal chemical screen approach to identify modifiers of intestinal neutrophilic inflammation. FEBS J 284:402–413
Olson TS, Reuter BK, Scott KG, Morris MA, Wang XM, Hancock LN, Burcin TL, Cohn SM, Ernst PB, Cominelli F, Meddings JB, Ley K, Pizarro TT (2006) The primary defect in experimental ileitis originates from a nonhematopoietic source. J Exp Med 203:541–552
Osorio-Barrios F, Prado C, Contreras F, Pacheco R (2018) Dopamine receptor D5 signaling plays a dual role in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis potentiating Th17-mediated immunity and favoring suppressive activity of regulatory T-cells. Front Cell Neurosci 12:192
Pacheco R (2017) Targeting dopamine receptor D3 signalling in inflammation. Oncotarget 8:7224–7225
Pacheco R, Contreras F, Zouali M (2014) The dopaminergic system in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 5:117
Papa I, Saliba D, Ponzoni M, Bustamante S, Canete PF, Gonzalez-Figueroa P, McNamara HA, Valvo S, Grimbaldeston M, Sweet RA, Vohra H, Cockburn IA, Meyer-Hermann M, Dustin ML, Doglioni C, Vinuesa CG (2017) TFH-derived dopamine accelerates productive synapses in germinal centres. Nature 547:318–323
Pinoli M, Marino F, Cosentino M (2017) Dopaminergic regulation of innate immunity: a review. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 12:602–623
Poewe W (2010) Parkinson disease: treatment of the nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:417–418
Poewe W, Antonini A, Zijlmans JC, Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets F (2010) Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: an old drug still going strong. Clin Interv Aging 5:229–238
Politis M, Wu K, Loane C, Brooks DJ, Kiferle L, Turkheimer FE, Bain P, Molloy S, Piccini P (2014) Serotonergic mechanisms responsible for levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease patients. J Clin Invest 124:1340–1349
Popovic M, Stanojevic Z, Tosic J, Isakovic A, Paunovic V, Petricevic S, Martinovic T, Ciric D, Kravic-Stevovic T, Soskic V, Kostic-Rajacic S, Shakib K, Bumbasirevic V, Trajkovic V (2015) Neuroprotective arylpiperazine dopaminergic/serotonergic ligands suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rats. J Neurochem 135:125–138
Powrie F, Mason D (1990) OX-22high CD4+ T cells induce wasting disease with multiple organ pathology: prevention by the OX-22low subset. J Exp Med 172:1701–1708
Prado C, Contreras F, Gonzalez H, Diaz P, Elgueta D, Barrientos M, Herrada AA, Lladser A, Bernales S, Pacheco R (2012) Stimulation of dopamine receptor D5 expressed on dendritic cells potentiates Th17-mediated immunity. J Immunol 188:3062–3070
Prado C, Bernales S, Pacheco R (2013) Modulation of T-cell mediated immunity by dopamine receptor d5. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 13:184–194
Prado C, Gaiazzi M, Gonzalez H, Ugalde V, Figueroa A, Osorio-Barrios FJ, Lopez E, Lladser A, Rasini E, Marino F, Zaffaroni M, Cosentino M, Pacheco R (2018) Dopaminergic stimulation of myeloid antigen-presenting cells attenuates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-activation Favouring the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Front Immunol 9:571
Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD, Silverberg MS, Goyette P, Huett A, Green T, Kuballa P, Barmada MM, Datta LW, Shugart YY, Griffiths AM, Targan SR, Ippoliti AF, Bernard EJ, Mei L, Nicolae DL, Regueiro M, Schumm LP, Steinhart AH, Rotter JI, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Daly MJ, Brant SR (2007) Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat Genet 39:596–604
Sagarduy A, Llorente J, Miguelez C, Morera-Herreras T, Ruiz-Ortega JA, Ugedo L (2016) Buspirone requires the intact nigrostriatal pathway to reduce the activity of the subthalamic nucleus via 5-HT1A receptors. Exp Neurol 277:35–45
Santana MB, Halje P, Simplicio H, Richter U, Freire MAM, Petersson P, Fuentes R, Nicolelis MAL (2014) Spinal cord stimulation alleviates motor deficits in a primate model of Parkinson disease. Neuron 84:716–722
Seeman P, Van Tol HH (1994) Dopamine receptor pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:264–270
Selvaraj S, Sun Y, Watt JA, Wang S, Lei S, Birnbaumer L, Singh BB (2012) Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves downregulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J Clin Invest 122:1354–1367
Seo DH, Che X, Kwak MS, Kim S, Kim JH, Ma HW, Kim DH, Kim TI, Kim WH, Kim SW, Cheon JH (2017) Interleukin-33 regulates intestinal inflammation by modulating macrophages in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci Rep 7:851
Shao W, Zhang SZ, Tang M, Zhang XH, Zhou Z, Yin YQ, Zhou QB, Huang YY, Liu YJ, Wawrousek E, Chen T, Li SB, Xu M, Zhou JN, Hu G, Zhou JW (2013) Suppression of neuroinflammation by astrocytic dopamine D2 receptors via alphaB-crystallin. Nature 494:90–94
Sharples SA, Koblinger K, Humphreys JM, Whelan PJ (2014) Dopamine: a parallel pathway for the modulation of spinal locomotor networks. Front Neural Circuits 8:55
Sharples SA, Humphreys JM, Jensen AM, Dhoopar S, Delaloye N, Clemens S, Whelan PJ (2015) Dopaminergic modulation of locomotor network activity in the neonatal mouse spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 113:2500–2510
Siegert RJ, Abernethy DA (2005) Depression in multiple sclerosis: a review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:469–475
Simms SL, Huettner DP, Kortagere S (2016) In vivo characterization of a novel dopamine D3 receptor agonist to treat motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology 100:106–115
Simunovic F, Yi M, Wang Y, Macey L, Brown LT, Krichevsky AM, Andersen SL, Stephens RM, Benes FM, Sonntag KC (2009) Gene expression profiling of substantia nigra dopamine neurons: further insights into Parkinson's disease pathology. Brain 132:1795–1809
Solis O, Garcia-Montes JR, Gonzalez-Granillo A, Xu M, Moratalla R (2017) Dopamine D3 receptor modulates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia by targeting D1 receptor-mediated striatal signaling. Cereb Cortex 27:435–446
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2018) Neurodegeneration and the ordered assembly of alpha-synuclein. Cell Tissue Res 373:137–148
Stoker TB, Torsney KM, Barker RA (2018) Emerging treatment approaches for Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci 12:693
Suarez LM, Solis O, Carames JM, Taravini IR, Solis JM, Murer MG, Moratalla R (2014) L-DOPA treatment selectively restores spine density in dopamine receptor D2-expressing projection neurons in dyskinetic mice. Biol Psychiatry 75:711–722
Suarez LM, Solis O, Aguado C, Lujan R, Moratalla R (2016) L-DOPA oppositely regulates synaptic strength and spine morphology in D1 and D2 striatal projection neurons in dyskinesia. Cereb Cortex 26:4253–4264
Sulzer D, Alcalay RN, Garretti F, Cote L, Kanter E, Agin-Liebes J, Liong C, McMurtrey C, Hildebrand WH, Mao X, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Oseroff C, Pham J, Sidney J, Dillon MB, Carpenter C, Weiskopf D, Phillips E, Mallal S, Peters B, Frazier A, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Sette A (2017) T cells from patients with Parkinson's disease recognize alpha-synuclein peptides. Nature 546:656–661
Thacker EL, Ascherio A (2008) Familial aggregation of Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis. Mov Disord 23:1174–1183
Tolstanova G, Deng X, Ahluwalia A, Paunovic B, Prysiazhniuk A, Ostapchenko L, Tarnawski A, Sandor Z, Szabo S (2015) Role of dopamine and D2 dopamine receptor in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 60:2963–2975
Tonini M, Cipollina L, Poluzzi E, Crema F, Corazza GR, De Ponti F (2004) Review article: clinical implications of enteric and central D2 receptor blockade by antidopaminergic gastrointestinal prokinetics. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:379–390
Utsumi H, Okuma Y, Kano O, Suzuki Y, Iijima M, Tomimitsu H, Hashida H, Kubo S, Suzuki M, Nanri K, Matsumura M, Murakami H, Hattori N, Tokyo Parkinson's Disease Study G (2013) Evaluation of the efficacy of pramipexole for treating levodopa-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson's disease. Intern Med 52:325–332
Vallone D, Picetti R, Borrelli E (2000) Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:125–132
Verstraeten A, Theuns J, Van Broeckhoven C (2015) Progress in unraveling the genetic etiology of Parkinson disease in a genomic era. Trends Genet 31:140–149
Wei L, Zhang C, Chen HY, Zhang ZJ, Ji ZF, Yue T, Dai XM, Zhu Q, Ma LL, He DY, Jiang LD (2015) Dopamine receptor DR2 expression in B cells is negatively correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Immunobiology 220:323–330
Winklhofer KF, Haass C (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:29–44
Yadav AP, Fuentes R, Zhang H, Vinholo T, Wang CH, Freire MA, Nicolelis MA (2014) Chronic spinal cord electrical stimulation protects against 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Sci Rep 4:3839
Yan Y, Jiang W, Liu L, Wang X, Ding C, Tian Z, Zhou R (2015) Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell 160:62–73
Zaffaroni M, Marino F, Bombelli R, Rasini E, Monti M, Ferrari M, Ghezzi A, Comi G, Lecchini S, Cosentino M (2008) Therapy with interferon-beta modulates endogenous catecholamines in lymphocytes of patients with multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol 214:315–321
Zizzo MG, Cavallaro G, Auteri M, Caldara G, Amodeo I, Mastropaolo M, Nuzzo D, Di Carlo M, Fumagalli M, Mosca F, Mule F, Serio R (2016) Postnatal development of the dopaminergic signaling involved in the modulation of intestinal motility in mice. Pediatr Res 80:440–447
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Programa de Apoyo a Centros con Financiamiento Basal AFB-170004 (to Fundación Ciencia & Vida) from “Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica de Chile (CONICYT)” and by grants FONDECYT-1170093 (to R.P.) from “Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico de Chile”, and MJFF-10332.01 (to R.P.) and MJFF-15076 (to R.P.) from Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson Research. PV is supported by “Progama PostDoc Hinge” from Fundación Ciencia & Vida.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal, P.M., Pacheco, R. Targeting the Dopaminergic System in Autoimmunity. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15, 57–73 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09834-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09834-5