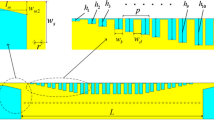
Abstract
A novel dual-band conformal surface plasmon (CSP) waveguide is designed and well studied in this paper. In earlier research studies, we have recognized that electromagnetic field of CSP waveguide are always confined to a sub-wavelength area and have a strong potential to be applied in device designing. However, almost all of the earlier CSP structures are mainly focus on the fundamental mode characteristics, such as fundamental resonance frequency. Here we propose a innovative dual inverted-L periodical structure with excellent performance not only on the fundamental mode but also on a new upper mode. This structure operates in microwave frequency range and shows outstanding frequency tunability characteristic. Being different from frequency characteristics in the earlier CSP waveguides, which always used to be designed single-frequency device, the novel dual-band frequency tunability characteristics of proposed dual inverted-L structure have an advantage in dual-frequency device design. In present paper, we also realize a tunable dual-frequency filter by changing the scaling factor of dual inverted-L stubs. In this case, its secondary operation frequency range can be tuned from 15 to 16.2 GHz.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The data used in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01937
Xiong X, Wang M et al (2021) Constructing an achromatic polarization-dependent bifocal metalens with height -gradient metastructures. Opt Lett 46:1193–1196. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.414668
Chen J, Liu ZQ et al (2020) Electrically modulating and switching infrared absorption of monolayer graphene in metamaterials. Carbon 162:187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.02.032
Chen J, Wang LH, Park GS et al (2019) Photonic microcavity-enhanced magnetic plasmon resonance of metamaterials for sensing applications. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 31(2). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2018.2881989
Chen L, Zhu YM, Zhuang SL et al (2019) Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and micro-cavity components for probing samples: a review. Front Inf Technol Electron Eng 20(5):591–607. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.1800633
Zhou J, Chen L, Zhu YM et al (2020) Terahertz on-chip sensing by exciting higher radial order spoof localized surface plasmons. Appl Phys Express 13:012014. https://doi.org/10.7567/1882-0786/ab5eb3
Zhou XP, Chen Z et al (2019) Multiple Fano resonances in spoof plasmon resonators of corrugated cylinder-ring structure. Phys Scr 94:115804. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ab1ed2
Pendry JB (2004) Mimicking surface plasmons with structured surfaces. Science 305(5685):847–848. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1098999
Garcia-Vidal FJ, Martín-Moreno L, Pendry JB (2005) Surfaces with holes in them: new plasmonic metamaterials. J Opt Pure Appl Opt 7(2):S97. https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4258/7/2/013
Hibbins AP (2005) Experimental verification of designer surface plasmons. Science 308(5722):670–672. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1109043
Nahata A, Cui A, Kumar G et al (2011) Planar terahertz waveguides based on complementary split ring resonators. Opt Express 19(2):1072–1080. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.19.001072
Navarro-Cía M, Beruete M, Sorolla M et al (2011) Enhancing the dual-band guiding capabilities of coaxial spoof plasmons via use of transmission line concepts. Plasmonics 6(2):295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9203-x
Maier SA, Andrews SR, Martín-Moreno L et al (2006) Terahertz surface plasmon-polariton propagation and focusing on periodically corrugated metal wires. Phys Rev Lett 97(17):176805. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.176805
Fernandezdominguez AI, Garciavidal FJ, Martincano D et al (2010) Domino plasmons for subwavelength terahertz circuitry. Opt Express 18(2):754. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.000754
Ma Y, Zhou J, Wang Z (2010) Surface plasmon waves on structured metal surface with periodic grooves modified by perpendicular cuts. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 22(7):450–452. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2010.2040987
Hooper IR, Tremain B, Dockrey JA et al (2014) Massively sub-wavelength guiding of electromagnetic waves. Sci Rep 4:7495. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07495
Gao X, Hui Shi J, Shen X et al (2013) Ultrathin dual-band surface plasmonic polariton waveguide and frequency splitter in microwave frequencies. Appl Phys Lett 102(15):824. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4802739
Liao Z, Zhao J, Pan BC et al (2014) Broadband transition between microstrip line and conformal surface plasmon waveguide. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(31):315103. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/31/315103
Ma HF, Shen X, Cheng Q et al (2014) Broadband and high-efficiency conversion from guided waves to spoof surface plasmon polaritons. Laser Photonics Rev 8(1):146–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201300118
Zhang W, Zhu G, Sun L et al (2015) Trapping of surface plasmon wave through gradient corrugated strip with underlayer ground and manipulating its propagation. Appl Phys Lett 106(2):021104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4905675
Liu L, Li Z, Xu B et al (2015) Dual-band trapping of spoof surface plasmon polaritons and negative group velocity realization through microstrip line with gradient holes. Appl Phys Lett 107(20):847. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935976
Zhao S, Zhang HC, Zhao J et al (2017) An ultra-compact rejection filter based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons. Sci Rep 7:10576. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11332-8
Shen X, Cui TJ (2013) Planar plasmonic metamaterial on a thin film with nearly zero thickness. Appl Phys Lett 102(21):211909. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4808350
Shen X, Cui TJ, Martin-Cano D et al (2013) Conformal surface plasmons propagating on ultrathin and flexible films. Proc Nat Acad Sci 110(1):40–45. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1210417110
Kianinejad A, Chen ZN, Qiu CW (2018) Full modeling, loss reduction, and mutual coupling control of spoof surface plasmon-based meander slow wave transmission lines. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 66(8):3764–3772. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2018.2841857
Liu X, Feng Y, Zhu B, Zhao J, Jiang T (2016) Backward spoof surface wave in plasmonic metamaterial of ultrathin metallic structure. Sci Rep 6:20448. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20448
Liang Y, Yu H, AnakAgungAlitApriyana JC, Li NY, Sun LL (2016) On-chip sub-terahertz surface plasmon polariton transmission lines with mode converter in CMOS. Sci Rep 6:30063. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30063
Aghadjani M, Mazumder P (2015) THz polarizer controller based on cylindrical spoof surface plasmon polariton (C-SSPP). IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol 5(4):556–563. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTHZ.2015.2439677
Aghadjani M, Erementchouk M, Mazumder P (2016) Spoof surface plasmon polariton beam splitter. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol PP(99). https://doi.org/10.1109/TTHZ.2016.2599289
Zhou YJ, Yang BJ (2015) Planar spoof plasmonic ultra-wideband filter based on low-loss and compact terahertz waveguide corrugated with dumbbell grooves. Appl Opt 14(54):4529–4533. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.54.004529
Ye LF, Xiao YF, Liu YH, Zhang L, Cai GX, Liu QH (2016) Strongly confined spoof surface plasmon polaritons waveguiding enabled by planar staggered plasmonic waveguides. Sci Rep 6:38528. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38528
Funding
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds of West Anhui University under grant no. WGKQ2021010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yijiao Fang contributed to the conception and data analyses of the study. Yijiao Fang is the corresponding author and also the first author. Jiangwei Zhong contributed to the constructive discussions of the study. Jiangwei Zhong is the second author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Y., Zhong, J. A Novel Dual-Band Conformal Surface Plasmon Waveguide with Tunable Frequency Response in Large Scale. Plasmonics 17, 613–619 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01545-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01545-z