Abstract
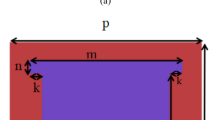
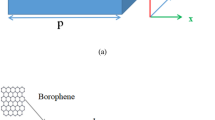
We propose an ultrasensitive and tunable mid-infrared sensor based on plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) in a monolayer black phosphorus metasurface. Results show that there are two PIT windows, each of which occurs when the long axis of the metasurface is placed along the MBP’s armchair and zigzag crystal directions, respectively. The corresponding sensors based on these PIT effects show high sensitivities of 7.62 THz/RIU and 7.36 THz/RIU. Both PIT frequencies can be tuned statically by varying the geometric parameters or dynamically by changing the electron doping of monolayer black phosphorus, making the sensors adaptable to tackle with a variety of scenarios. We expect that this work will advance the engineering of metasurfaces based on monolayer black phosphorus and promote their sensing applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available upon request.
References
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):218-221
Niu X, Hu X, Yan Q, Zhu J, Cheng H, Huang Y, Lu C, Fu Y, Gong Q (2019) Plasmon-induced transparency effect for ultracompact on-chip devices. Nanophotonics 8(7):1125-1149
Yang X, Hu X, Chai Z, Lu C, Yang H, Gong Q (2014) Tunable ultracompact chip-integrated multichannel filter based on plasmon-induced transparencies. Appl Phys Lett 104(22):221114
Xiao S, Wang T, Liu T, Yan X, Li Z, Xu C (2018) Active modulation of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz hybrid metal-graphene metamaterials. Carbon 126:271-278
Bai Y, Chen K, Liu H, Bu T, Cai B, Xu J, Zhu Y (2015) Optically controllable terahertz modulator based on electromagnetically-induced-transparency-like effect. Opt Commun 353:83–89
Zhang L, Dong Z, Wang YM, Liu Y, Zhang S, Yang JK, Qiu C (2015) Dynamically configurable hybridization of plasmon modes in nanoring dimer arrays. Nanoscale 7(28):12018-12022
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Giessen H (2009) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103-1107
Pan W, Yan Y, Ma Y, Shen D (2019) A terahertz metamaterial based on electromagnetically induced transparency effect and its sensing performance. Opt Commun 431:115-119
Yan X, Yang M, Zhang Z, Liang L, Wei D, Wang M, Yao J (2019) The terahertz electromagnetically induced transparency-like metamaterials for sensitive biosensors in the detection of cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 126:485-492
Hu S, Liu D, Yang H, Wang H, Wang Y (2019) Staggered H-shaped metamaterial based on electromagnetically induced transparency effect and its refractive index sensing performance. Opt Commun 450:202-207
Yang M, Liang L, Zhang Z, Xin Y, Wei D, Song X, Yao J (2019) Electromagnetically induced transparency-like metamaterials for detection of lung cancer cells. Opt Express 27(14):19520-19529
He X (2015) Tunable terahertz graphene metamaterials. Carbon 82:229-237
Amin M, Farhat M, Baˇgci H (2013) A dynamically reconfigurable Fano metamaterial through graphene tuning for switching and sensing applications. Sci Rep 3(1):2105
Shi X, Han D, Dai Y, Yu Z, Sun Y, Chen H, Liu X, Zi J (2013) Plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in nanostructure graphene. Opt Express 21(23):28438-28443
Jia W, Ren P, Jia Y, Fan C (2019) Active control and large group delay in graphene-based terahertz metamaterials. J Phys Chem C 123(30):18560-18564
Xiao B, Tong S, Fyffe A, Shi Z (2020) Tunable electromagnetically induced transparency based on graphene metamaterials. Opt Express 28(3):4048-4057
Asgari S, Shokati E, Granpayeh N (2019) High-efficiency tunable plasmonically induced transparency-like effect in metasurfaces composed of graphene nano-rings and ribbon arrays and its application. Appl Optics 58(13):3664-3670
Churchill HO, Jarilloherrero P (2014) Two-dimensional crystals: Phosphorus joins the family. Nat Nanotechnol 9(5):330–331
Xia F, Wang H, Jia Y (2014) Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat Commun 5(1):4458
Rodin AS, Carvalho A, Neto AHC (2014) Strain-induced gap modification in black phosphorus. Phys Rev Lett 112(17):176801
Wang X, Jones AM, Seyler KL, Tran V, Jia Y, Zhao H, Xia F (2015) Highly anisotropic and robust excitons in monolayer black phosphorus. Nat Nanotechnol 10(6):517-521
Castellanosgomez A (2015) Black phosphorus: Narrow gap, wide applications. J Phys Chem Lett 6(21):4280-4291
Abbas AN, Liu B, Chen L, Ma Y, Cong S, Aroonyadet N, Kopf M, Nilges T, Zhou C (2015) Black phosphorus gas sensors. ACS Nano 9(5):5618-5624
Cho S, Lee Y, Koh H, Jung H, Kim J, Yoo H, Kim J, Jung H (2016) Superior chemical sensing performance of black phosphorus: Comparison with MoS2 and graphene. Adv Mater 28(32):7020-7028
Liu H, Hu K, Yan D, Chen R, Zou Y, Liu H, Wang S (2018) Recent advances on black phosphorus for energy storage, catalysis, and sensor applications. Adv Mater 30(32):1800295
Ge X, Xia Z, Guo S (2019) Recent advances on black phosphorus for biomedicine and biosensing. Adv Func Mater 29:1900318
Wu L, Guo J, Wang Q, Lu S, Dai X, Xiang Y, Fan D (2017) Sensitivity enhancement by using few-layer black phosphorus-graphene/TMDCs heterostructure in surface plasmon resonance biochemical sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 249:542-548
Dai X, Chen H, Qiu C, Wu L, Xiang Y (2020) Ultrasensitive multiple guided-mode biosensor with few-layer black phosphorus. J Lightwave Technol 38(6):1564-1571
Han L, Wang L, Xing H, Chen X (2019) Anisotropic plasmon induced transparency in black phosphorus nanostrip trimer. Opt Mater Express 9(2):352-361
Liu C, Li H, Xu H, Zhao M, Wu K (2019) Slow light effect based on tunable plasmon-induced transparency of monolayer black phosphorus. J Phys D: Appl Phys 52(40):405203
Liu C, Li H, Xu H, Zhao M, Xiong C, Zhang B, Wu K (2019) Tunable plasmon-induced transparency absorbers based on few-layer black phosphorus ribbon metamaterials. J Opt Soc Am B 36(11):3060-3065
Liu C, Li H, Xu H, Zhao M, Xiong C, Li M, Ruan B, Zhang B, Wu K (2020) Dynamically tunable excellent absorber based on plasmon-induced absorption in black phosphorus nanoribbon. J Appl Phys 127(12):163301
Liu Z, Aydin K (2016) Localized surface plasmons in nanostructured monolayer black phosphorus. Nano Lett 16(6):3457–3462
Li H, Lin W, Xing H, Chen X (2018) Active tuning of mid-infrared surface plasmon resonance and its hybridization in black phosphorus sheet array. ACS Photonics 5(9):3828–3837
Low T, Roldan R, Wang H, Xia F, Avouris P, Moreno LM, Guinea F (2014) Plasmons and screening in monolayer and multilayer black phosphorus. Phys Rev Lett 113(10):106802
Lin C, Grassi R, Low T, Helmy AS (2016) Multilayer black phosphorus as a versatile mid-infrared electro-optic material. Nano Lett 16(3):1683-1689
Funding
This work was supported by the Shenzhen Research Foundation (Grant Nos. JCYJ20180507182444250, JCYJ20180508152903208, JCYJ20190808143801672) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61875133 and 11874269).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.C. and G.L. proposed the concept. H.C. performed the simulations. All authors analyzed the data and discussed the results. H.C. wrote the draft manuscript. H.C. and G.L. edited the manuscript. X.D. and G.L. supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Xiong, L., Hu, F. et al. Ultrasensitive and Tunable Sensor Based on Plasmon-Induced Transparency in a Black Phosphorus Metasurface. Plasmonics 16, 1071–1077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01374-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01374-0