Abstract
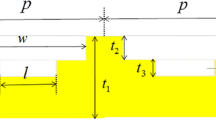
In this paper, a refractive index plasmonic nano-sensor based on a tunable perfect absorber has been proposed in the near-infrared region. The proposed sensor consists of a truncated cone resonator with more than 99% absorption and ultra-narrow bandwidth. Liquid crystal has been used in the designed nano-structure to tune the structure by variation of the incident angle and applying the external bias field to obtain the near perfect and ultra-narrow absorption peak. The proposed nano-sensor has a high sensitivity of 1363.63 nm/RIU and a high figure of merit of 1136.36 RIU−1 at the telecommunication wavelength of 1550 nm. Furthermore, after obtaining appropriate conditions for the liquid crystal layer, we have suggested a new resonator to boost the interaction of surface plasmons and the test medium. Therefore, the sensitivity and figure of merit are increased to the values of 1509 nm/RIU and 1257.5 RIU−1, respectively. This excellent performance of the sensor has huge potential for precision applications such as biomedical science and biosensor. Hence, the capability of the proposed nano-sensor in the field of histopathology for cancerous tissue diagnosis and detection of toxic and flammable gases to prevent endangering human health has been studied. In this case, the high sensitivity of 1368.06 nm/RIU and high figure of merit of 1179.36 RIU−1 have been obtained.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, New York
Svedendahl M, Chen S, Dmitriev A, Ka M (2009) Refractometric sensing using propagating versus localized surface plasmons: a direct comparison. Nano Lett 9:4428–4433
Dmitriev A (2012) Nanoplasmonic sensors. Springer, New York
Tong L, Wei H, Zhang S, Xu H (2014) Recent advances in plasmonic sensors. Sensors 14:7959–7973
Minh H, Endo T, Kerman K, Chikae M, Kim D (2007) A localized surface plasmon resonance based immunosensor for the detection of casein in milk. Sci Technol Adv Mater 8:331–338
Chen S, Svedendahl M, Käll M, Gunnarsson L, Dmitriev A (2009) Ultrahigh sensitivity made simple: nanoplasmonic label-free biosensing with an extremely low limit-of-detection for bacterial and cancer diagnostics. Nanotechnol. 20:434015–434024
Baranzadeh F, Nozhat N (2019) Tunable metasurface refractive index plasmonic nano-sensor utilizing an ITO thin layer in the near-infrared region. Appl Opt 58:2616–2623
Bingham JM, Anker JN, Kreno LE, Duyne RP (2010) Gas sensing with high-resolution localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132:17358–17359
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao L, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nano particles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Mock JJ, Smith DR, Schultz S (2003) Local refractive index dependence of plasmon resonance spectra from individual nanoparticles. Nano Lett 3:485–491
Dahlin AB, Chen S, Jonsson MP, Gunnarsson L, Ka M (2009) High-resolution microspectroscopy of plasmonic nanostructures for miniaturized biosensing. Anal Chem 81:6572–6580
Sherry LJ, Chang S, Schatz GC, Duyne RP, Wiley BJ, Xia Y (2005) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver nanocubes. Nano Lett 5:2034–2038
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir 20:6414–6420
Chen H, Kou X, Yang Z, Ni W, Wang J (2008) Shape- and size-dependent refractive index sensitivity of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:5233–5237
Verellen N, Dorpe PV, Huang C, Lodewijks K, Vandenbosch G, Lagae L, Moshchalkov V (2011) Plasmon line shaping using nanocrosses for high sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensing. Nano Lett 11:391–397
Chen J, Yuan J, Zhang Q, Ge HM, Tang CJ, Liu Y, Guo BN (2018) Dielectric waveguide-enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensing. Opt Mater Express 8:342–347
Wang L, Sang T, Gao J, Yin X, Qi H (2018) High-performance sensor achieved by hybrid guide-mode resonance / surface plasmon resonance platform. Appl Opt 57:338–7343
Chen Z, Wang C, Wang L, Jiang C, Zhu H (2013) Surface plasmonic resonance sensor by metal strip pair arrays. Opt Quant Electron 45:707–712
Chen J, Zhang Q, Peng C, Tang C, Shen X, Deng L, Park G (2018) Optical cavity-enhanced localized surface. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 30:728–731
Khoo IC (2007) Liquid crystals. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey
Yang DK, Wu ST (2015) Fundamentals of liquid crystal devices. Wiley, Chichester, West Sussex
Jerome B (1991) Surface effects and anchoring in liquid crystals. Rep Prog Phys 54:391–451
Khan W, Park S (2012) Configuration change of liquid crystal microdroplets coated with a novel polyacrylic acid block liquid crystalline polymer by protein adsorption. Lab Chip 12:4553–4559
Ahmadian D, Ghobadi C, Nourinia J (2015) Tunable plasmonic sensor with metal-liquid crystal-metal structure. IEEE Photonics J 7:1–10
Dodge MJ (1984) Refractive properties of magnesium fluoride. Appl Opt 23:1980–1985
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2012) Sensing using localised surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Commun 48:8999–9010
Ma Y (2013) Electro-optics and nonlinear optics of liquid crystal-plasmonic materials and structures PhD dissertation. Pennsylvania State University USA
Knoesen A, Moharam MG, Gaylord TK (1985) Electromagnetic propagation at interfaces and in waveguides in uniaxial crystals. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 38:171–178
Mbise GW, Bellac DL, Niklasson GA, Granqvist CG (1997) Angular selective window coatings: theory and experiments. J Phys D Appl Phys 30:2103–2122
Vgnatovich F, Ignatovich VK (2012) Optics of anisotropic media. Physics-Uspekhi 55:709–720
Reshetnyak VY, Pinkevych IP, Zadorozhnii VI, Evans DR (2015) Liquid crystal control of surface plasmon resonance sensor based on nanorods. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 613:110–120
Alavirad M, Mousavi SS, Roy L, Ave E (2013) Schottky-contact plasmonic dipole rectenna concept for biosensing. Opt Express 21:4328–4347
Koudela I, Yee SS (1999) Surface plasmon resonance sensors based on diffraction gratings and prism couplers: sensitivity comparison. Sensors Actuators B Chem 54:16–24
Gao D, Guan C, Wen Y, Zhong X, Yuan L (2014) Multi-hole fiber based surface plasmon resonance sensor operated at near-infrared wavelengths. Opt Commun 313:94–98
UC Irvine Environmental Health & Safety (2014) Toxic gas program, University of California, https://ehs.uci.edu
Fogiel M (1984) Handbook of mathematical, scientific, and engineering formulas, tables, functions, graphs, Transforms. Research and Education Association, Piscataway, New Jersey
Quirce S, Barranco P (2010) Cleaning agents and asthma. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 20:542–550
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP (2014) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 383:1490–1502
Carneiro I, Carvalho S, Silva V, Henrique R, Oliveira L, Tuchin V (2019) Kinetics of optical properties of human colorectal tissues during optical clearing: a comparative study between normal and pathological tissues during optical clearing: a comparative study. J Biomed Opt 23:121620–121612
Bahador H, Heidarzadeh H (2020) Analysis and simulation of a novel localized surface plasmonic highly sensitive refractive index sensor. Plasmonics 15:1273–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01144-4
Wei Z, Li X, Zhong N, Tan X, Zhang X, Liu H, Meng H, Liang R (2016) Analogue electromagnetically induced transparency based on low-loss metamaterial and its application in nanosensor and slow-light device. Plasmonics 12:641–647
Liu GD, Zhai X, Wang LL, Lin Q, Xia SX, Luo X, Zhao CJ (2018) A high-performance refractive index sensor based on Fano resonance in Si split-ring metasurface. Plasmonics 13:15–19
Qin L, Wu S, Deng J, Li L, Li X (2018) Tunable light absorbance by exciting the plasmonic gap mode for refractive index sensing. Opt Lett 43:1427–1430
Zhou P, Zheng G (2018) High-efficient light absorption of monolayer graphene via cylindrical dielectric arrays and the sensing application. Opt Mater 78:471–476
Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang T (2015) Nanoslit-microcavity-based narrow band absorber for sensing applications. Opt Express 23:20715–20720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baranzadeh, F., Nozhat, N. High Performance Plasmonic Nano-Biosensor Based on Tunable Ultra-Narrowband Perfect Absorber Utilizing Liquid Crystal. Plasmonics 16, 253–262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01285-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01285-6