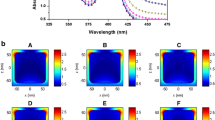
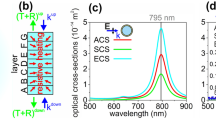
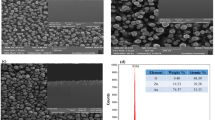
Abstract
Au-core/Pt-shell nanorods (Au@Pt NRs) have been prepared by a Au nanorod-mediated growth method, and they exhibit high electromagnetic field enhancements under coupling conditions. Boosted by a long-range effect of the high electromagnetic field generated by the Au core, the electromagnetic field enhancement can be controlled by changing the morphology of the nanostructures. In this study, we report the results on the simulations of the electromagnetic field enhancement using a finite difference time domain (FDTD) method, taking the real shapes of the Au@Pt NRs into account. Due to the “hot spot” effect, the electromagnetic field can be localized between the Pt nanodots. The electromagnetic field enhancement is found to be rather independent of the Pt content, whereas the local roughness and small sharp features might significantly modify the near-field. As the electromagnetic field enhancement can be tuned by the distribution of Pt nanodots over the Au-core, Au@Pt NRs can find potential applications in related areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. H. Xia and Y. N. Xia, Gold nanocages as multifunctional materials for nanomedicine, Front. Phys. 9(3), 378 (2014)
S. Linic, P. Christopher, H. Xin, and A. Marimuthu, Catalytic and photocatalytic transformations on metal nanoparticles with targeted geometric and plasmonic properties, Acc. Chem. Res. 46(8), 1890 (2013)
R. Ghosh Chaudhuri, and S. Paria, Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications, Chem. Rev. 112(4), 2373 (2012)
O. Nicoletti, F. de La Pe˜na, R. K. Leary, D. J. Holland, C. Ducati, and P. A. Midgley, Three-dimensional imaging of localized surface plasmon resonances of metal nanoparticles, Nature 502(7469), 80 (2013)
Y. L. Zhao, Y. L. Song, W. G. Song, W. Liang, X. Y. Jiang, Z. Y. Tang, H. X. Xu, Z. X. Wei, Y. Q. Liu, M. H. Liu, L. Jiang, X. H. Bao, L. J. Wan, and C. L. Bai, Progress of nanoscience in China, Front. Phys. 9(3), 257 (2014)
Z. Y. Li, Nanophotonics in China: Overviews and highlights, Front. Phys. 7(6), 601 (2012)
J. S. Miao, W. D. Hu, Y. L. Jing, W. J. Luo, L. Liao, A. L. Pan, S. W. Wu, J. X. Cheng, X. S. Chen, and W. Lu, Surface plasmon-enhanced photodetection in few layer MoS2 phototransistors with Au nanostructure arrays, Small 11(20), 2392 (2015)
S. P. Zhang, H. Wei, K. Bao, U. Hakanson, N. J. Halas, P. Nordlander, and H. X. Xu, Chiral surface plasmon polari-tons on metallic nanowires, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(9), 096801 (2011)
S. J. Barrow, X. Wei, J. S. Baldauf, A. M. Funston, and P. Mulvaney, The surface plasmon modes of self-assembled gold nanocrystals, Nat. Commun. 3, 1275 (2012)
L. M. Tong and H. X. Xu, Frontiers of plasmonics, Front. Phys. 9(1), 1 (2014)
R. A. Alvarez-Puebla, A. Agarwal, P. Manna, B. P. Khanal, P. Aldeanueva-Potel, E. Carbó-Argibay, N. Pazos-Pérez, L. Vigderman, E. R. Zubarev, N. A. Kotov, and L. M. Liz-Marzan, Gold nanorods 3D-supercrystals as surface enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy substrates for the rapid detection of scrambled prions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108(20), 8157 (2011)
E. C. Le Ru and P. G. Etchegoin, Single-molecule surfaceenhanced Raman spectroscopy, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 63(1), 65 (2012)
G. McNay, D. Eustace, W. E. Smith, K. Faulds, and D. Graham, Surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS) and surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering (SERRS): A review of applications, Appl. Spectrosc. 65(8), 825 (2011)
Y. S. Yamamoto, M. Ishikawa, Y. Ozaki, and T. Itoh, Fundamental studies on enhancement and blinking mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and basic applications of SERS biological sensing, Front. Phys. 9(1), 31 (2014)
Z. Kim, Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman scattering: Current status and future perspective, Front. Phys. 9(1), 25 (2014)
Y. Zhang, J. Qian, D. Wang, Y. L. Wang, and S. L. He, Multifunctional gold nanorods with ultrahigh stability and tunability for in vivo fluorescence imaging, SERS detection, and photodynamic therapy, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(4), 1148 (2013)
N. A. Hatab, C. H. Hsueh, A. L. Gaddis, S. T. Retterer, J. H. Li, G. Eres, Z. Zhang, and B. Gu, Free-standing optical gold bowtie nanoantenna with variable gap size for enhanced raman spectroscopy, Nano Lett. 10(12), 4952 (2010)
K. H. Su, S. Durant, J. M. Steele, Y. Xiong, C. Sun, and X. Zhang, Raman enhancement factor of a single tunable nanoplasmonic resonator, J. Phys. Chem. B 110(9), 3964 (2006)
L. J. Sherry, R. Jin, C. A. Mirkin, G. C. Schatz, and R. P. Van Duyne, Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy of single silver triangular nanoprisms, Nano Lett. 6(9), 2060 (2006)
S. Wang, D. F. Pile, C. Sun, and X. Zhang, Nanopin plasmonic resonator array and its optical properties, Nano Lett. 7(4), 1076 (2007)
Y. Z. He, J. X. Fu, and Y. P. Zhao, Oblique angle deposition and its applications in plasmonics, Front. Phys. 9(1), 47 (2014)
F. Z. Cong, H. Wei, X. R. Tian, and H. X. Xu, A facile synthesis of branched silver nanowire structures and its applications in surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Front. Phys. 7(5), 521 (2012)
W. Y. Rao, Q. Li, Y. Z. Wang, T. Li, and L. J. Wu, Comparison of photoluminescence quantum yield of single gold nanobipyramids and gold nanorods, ACS Nano 9(3), 2783 (2015)
S. Khatua, P. M. Paulo, H. Yuan, A. Gupta, P. Zijlstra, and M. Orrit, Resonant plasmonic enhancement of singlemolecule fluorescence by individual gold nanorods, ACS Nano 8(5), 4440 (2014)
Z. L. Zhang, L. Chen, S. X. Sheng, M. T. Sun, H. R. Zheng, K. Q. Chen, and H. X. Xu, High-vacuum tip enhanced Raman spectroscopy, Front. Phys. 9(1), 17 (2014)
B. Sharma, R. R. Frontiera, A. I. Henry, E. Ringe, and R. P. Van Duyne, SERS: Materials, applications, and the future, Mater. Today 15(1–2), 16 (2012)
K. Ikeda, J. Sato, N. Fujimoto, N. Hayazawa, S. Kawata, and K. Uosaki, Plasmonic enhancement of Raman scattering on non-SERS-active platinum substrates, J. Phys. Chem. C 113(27), 11816 (2009)
J. F. Li, Z. L. Yang, B. Ren, G. K. Liu, P. P. Fang, Y. X. Jiang, D. Y. Wu, and Z. Q. Tian, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using gold-core platinum-shell nanoparticle film electrodes: toward a versatile vibrational strategy for electrochemical interfaces, Langmuir 22(25), 10372 (2006)
Z. Q. Tian, B. Ren, J. F. Li, and Z. L. Yang, Expanding generality of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with borrowing SERS activity strategy, Chem. Commun. (34), 3514 (2007)
L. P. Xia, Z. Yang, S. Y. Yin, W. R. Guo, J. L. Du, and C. L. Du, Hole arrayed metal-insulator-metal structure for surface enhanced Raman scattering by self-assembling polystyrene spheres, Front. Phys. 9(1), 64 (2014)
N. R. Jana, L. Gearheart, and C. J. Murphy, Seed-mediated growth approach for shape-controlled synthesis of spheroidal and rod-like gold nanoparticles using a surfactant template, Adv. Mater. 13(18), 1389 (2001)
D. W. Lynch and W. R. Hunter, in: Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids, edited by E. D. Palik, New York: Academic Press, 1985, pp 350–356
M. Grzelczak, J. Pérez-Juste, B. Rodríguez-González, and L. M. Liz-Marzán, Influence of silver ions on the growth mode of platinum on gold nanorods, J. Mater. Chem. 16(40), 3946 (2006)
M. Grzelczak, J. Perez-Juste, F. J. García de Abajo, and L. M. Liz-Marzán, Optical properties of platinum-coated gold nanorods, J. Phys. Chem. C 111(17), 6183 (2007)
L. L. Feng, X. C. Wu, L. R. Ren, Y. J. Xiang, W. W. He, K. Zhang, W. Y. Zhou, and S. S. Xie, Well-controlled synthesis of Au@Pt nanostructures by gold-nanorod-seeded growth, Chem. Eur. J. 14(31), 9764 (2008)
Z. L. Wang, M. Mohamed, S. Link, and M. El-Sayed, Crystallographic facets and shapes of gold nanorods of different aspect ratios, Surf. Sci. 440(1–2), L809 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JB., Long, L., Zhang, YS. et al. Optical properties of Au-core Pt-shell nanorods studied using FDTD simulations. Front. Phys. 11, 118501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-015-0528-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-015-0528-3