Abstract
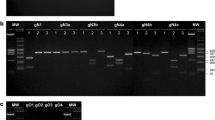
To explore the impact of gene polymorphism of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) on virus virulence, the full-length UL144 gene and partial sequence of glycoprotein B (UL55) gene were sequenced and analyzed for 23 clinical strains of HCMV isolated from urine samples of pediatric patients with congenital or postnatal HCMV infection. Among the 23 isolates, 13 (57 %) were UL144 genotype 1A, 3(13 %) were UL144 genotypes 2 and 7(30 %) were UL144 genotype 3; geographic differences in genotype distribution were found for both UL144 and gB gene. No UL144 genotypes 1B and 1C were found in this study while these two genotypes were common in HCMV strains isolated in the US. Our results also demonstrated that for all clinical strains of gB genotypes I, III and UL144 genotypes 1A, 2, and 3 found in this study, mother-to-fetus vertical transmission was possible.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mocarski ES (1996) Cytomegalovirus and their replication. In: Fields BN, Howley PM, Knipe DM (eds) Fields virology, vol 2. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 2447–2492
Ho M (1990) Epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections. Rev Infect Dis 12:S701
Pignatelli S, Dal Monte P, Rossini G et al (2004) Genetic polymorphisms among human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) wildtype strains. Rev Med Virol 14:383–410
Lurain NS, Kapell KS, Huang DD et al (1999) Human cytomegalovirus UL144 open reading frame: sequence hypervariability in low-passage clinical isolates. J Virol 73:10040–10050
Bale JF Jr, Petheram SJ, Robertson M et al (2001) Human cytomegalovirusαsequence and UL144 variability in strains from infected children. J Med Virol 65:90–96
Murayama T, Takegoshi M, Tanuma J et al (2005) Analysis of human cytomegalovirus UL144 variability in low-passage clinical isolates in Japan. Intervirology 48:201–206
Mao ZQ, He R, Sun M et al (2007) The association between polymorphisms of HCMV UL144 ORF and clinical manifestations in 73 strains with congenital and/or perinatal HCMV infection. Arch Virol 152:115–124
Chou S, Dennison KM (1991) Analysis of interstrain variation in cytomegalovirus glyco-protein B sequences encoding neutralization-related epitopes. J Infect Dis 163:1229–1234
Trincado DE, Scott GM, White PA et al (2000) Human cytomegalovirus strains associated with congenital and perinatal infection. J Med Virol 61:481–487
Jin H, Wang X, Li S (2007) Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B genotype correlates with different symptoms of infected infants. Intervirology 50:219–223
Mousavi-Jazi M, Sundqvist V, Linde A et al (2000) Growth phenotypes of cytomegalovirus isolates do not correlate with glycoprotein B, major immediate early genotypes or antiviral sensitivity. J Med Virol 62:117–126
Isaacson MK, Compton T (2009) Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B is required for virus entry and cell-to-cell spread, but not for virion attachment, assembly, or egress. J Virol 83:3891–3903
Meyer-Konig U, Vogelberg C, Bongarts A et al (1998) Glycoprotein B genotype correlates with cell tropism in vivo of human cytomegalovirus infection. J Med Virol 55:75–81
Yan H, Koyano S, Inami Y et al (2008) Genetic variations in the gB, UL144 and UL149 genes of human cytomegalovirus strains collected from congenitally and postnatally infectedJapanese children. Arch Virol 153:667–674
Humar A, Kumar D, Gilbert C et al (2003) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) glycoprotein B genotypes and response to antiviral therapy, in solid-organ-transplant recipients with CMV disease. J Infect Dis 188:581–584
Sarcinella L, Mazzulli T, Willey B et al (2002) Cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B genotype does not correlate with outcomes in liver transplant patients. J Clin Virol 24:99–105
Bale JF Jr, Murph JR, Demmler GJ et al (2000) Intrauterine cytomegalovirus infection and glycoprotein B genotypes. J Infect Dis 182:933–936
Barbi M, Binda S, Caroppo S et al (2001) CMV gB genotypes and outcome of vertical transmission: study on dried blood spots of congenitally infected babies. J Clin Virol 21:75–79
Tanaka K, Numazaki K, Tsutsumi H (2005) Human cytomegalovirus genetic variability in strains isolated from Japanese children. J Med Virol 76:356–360
Wada K, Mizuno S, Kato K et al (1997) Cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B sequence variation among Japanese bone marrowtransplant recipients. Intervirology 40:215–219
Chern KC, Chandler DB, Martin DF et al (1998) Glycoprotein B subtyping of cytomegalovirus in the vitreous of patients with AIDS and CMV retinitis. J Infect Dis 178:1149–1153
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Innovation Platform Open Funds for Universities in Hunan Province (09K022 and 11K010), the Cooperative Innovation Center of Engineering and New Products for Developmental Biology of Hunan Province.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Li, L., Huang, C. et al. Polymorphism of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL144 gene in low passage clinical isolates. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 3120–3126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0353-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0353-z