Abstract
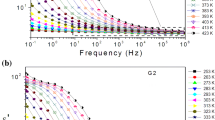
The synthetic fused quartz glasses with bare metal impurities have been analyzed by temperature-dependent electrical impedance spectroscopy. The complex electric impedance and the overlapping of the normalized dielectric modulus imply the single mechanism of dielectric and conduction relaxation in the fused quartz glass. Besides, the dependence of conductivity on temperature may attribute to the predominant electric relaxation to the delocalized or long range electronic hopping between the nonbridged dangling oxygen.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikushima AJ, Fujiwara T, Saito K (2000) Silica glass: a material for photonics. J Appl Phys 88:1201–1213
Xue SW, Proulx P, Boulos MI (2003) Effect of the coil angle in an inductively coupled plasma torch: a novel two-dimensional model. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 23:245–263
Baird WH (2009) An introduction to inertial navigation. Am J Phys 77:844–847
van Wiggeren GD, Roy R (1998) Optical communication with chaotic waveforms. Phys Rev Lett 81:3547–3550
Lee S (2001) Photolithography and selective etching of an array of quartz tuning fork resonators with improved impact resistance characteristics. Jpn Appl Phys 40:5164–5167
Ihlemann J (1992) Excimer laser ablaettion of fused-silica. Appl Surf Sci 54:193–200
Zhang J, Sugioka K, Takahashi T et al (2000) Dual-beam ablation of fused silica by multiwavelength excitation process using KrF excimer and F2 lasers. Appl Phys A 71:23–26
Chen YY, Wang J, Du JK et al (2013) Effects of mass layer imperfect bonding on the electrical impedance of a quartz crystal microbalance. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 56:2186–2191
Liu GQ, Huang X, Xia H et al (2013) Magnetoacoustic tomography with current injection. Chin Sci Bull 58:3600–3606
Pang Y, Liu CS (2013) Continuum description for the characteristic resistance sensed by a cylinder colliding against granular medium. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 56:1428–1436
Fanara S, Behrens H (2011) Proton conduction in hydrous glasses of the join CaAl2Si2O8-CaMgSi2O6: an impedance and infrared spectroscopic study. J Chem Phys 134:505–515
Goswami M, Deshpande SK, Kumar R et al (2010) Electrical behaviour of Li2O–ZnO–SiO2 glass and glass-ceramics system. J Phys Chem Solids 71:739–744
Rangarajan B, Bharadwaja SSN, Furman E et al (2010) Impedance spectroscopy studies of fresnoites in BaO–TiO2–SiO2 system. J Am Ceram Soc 93:522–530
Zhang QL, Liu Y, Yang H (2013) Voltage-dependent low-field resistivity of CaTiO3: Sc ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 24:999–1003
Peng F, Luo D, Sun H et al (2013) Diameter-controlled growth of aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes on quartz using molecular nanoclusters as catalyst precursors. Chin Sci Bull 58:433–439
Wang X, Shao Y, Gong P et al (2012) Effect of thermal cycling on the mechanical properties of Zr41Ti14Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 alloy. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 55:2357–2361
Zhao L, Feng JC, Tian XY et al (2011) Brazing of micrograin-filled quartz fiber reinforced silica composites and Invar using Ag21Cu4.5Ti alloy. Chin Sci Bull 56:2869–2873
Devautour-Vinot S, Cambon O, Prud’homme N et al (2007) Complex impedance spectroscopy of alkali impurities in as-grown, irradiated and annealed quartz. J Appl Phys 102:102–111
Szu SP, Lin CY (2003) AC impedance studies of copper doped silica glass. Mater Chem Phys 82:295–300
Yaohua Quartz Technology Development Co, Ltd., http://www.yaohuaquartz.com
Tielburger D, Merz R, Ehrenfels R et al (1992) Thermally activated relaxation processes in vitreous silica - an investigation by Brillouin-scattering at high-pressures. Phys Rev B 45:2750–2760
Ravaine D, Diard JP, Souquet JL (1975) Dielectric relaxation in alkali-metal oxide conductive glasses studied by complex impedance measurements. J Chem Soc 71:1935–1941
Kajihara K, Skuja L, Hirano M et al (2004) Interconversion between non-bridging oxygen hole center and peroxy radical in F2-laser-irradiated SiO2 glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 345:219–223
Zhu MK, Tang JL, Ke N et al (2011) Annealing effect on relaxor behaviours of spark plasma sintered Pb(Sc1/2Nb1/2)O3 superfine ceramics. Adv Appl Ceram 110:74–79
Ngai KL, Jonscher AK, White CT (1979) Origin of the universal dielectric response in condensed matter. Nature 277:185–189
Jonscher AK (1977) Universal dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Suresh S, Prasad M, Mouli VC (2010) AC conductivity and impedance measurements in alkali boro-tellurite glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 356:1599–1603
Ahlawat N, Sanghi S, Agarwal A et al (2008) Investigation of near constant loss contribution to conductivity in lithium bismo-silicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:3767–3772
Gerhardt R (1994) Impedance and dielectric-spectroscopy revisited- distinguishing localized relaxation from long-range conductivity. J Phys Chem Solids 55:1491–1506
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51172006) and the Center of Laser Fusion, CAEP (050110.3-2011HF-C-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Wu, X., Zhu, M. et al. Relaxation mechanism analysis of synthetic fused quartz glass investigated by electrical impedance spectra. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 3271–3275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0312-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0312-8