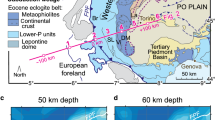
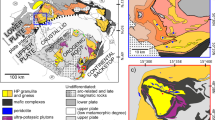
Abstract
The study of subduction-zone processes is a key to development of the plate tectonic theory. Plate interface interaction is a basic mechanism for the mass and energy exchange between Earth’s surface and interior. By developing the subduction channel model into continental collision orogens, insights are provided into tectonic processes during continental subduction and its products. The continental crust, composed of felsic to mafic rocks, is detached at different depths from subducting continental lithosphere and then migrates into continental subduction channel. Part of the subcontinental lithospheric mantle wedge, composed of peridotite, is offscrapped from its bottom. The crustal and mantle fragments of different sizes are transported downwards and upwards inside subduction channels by the corner flow, resulting in varying extents of metamorphism, with heterogeneous deformation and local anatexis. All these metamorphic rocks can be viewed as tectonic melanges due to mechanical mixing of crust- and mantle-derived rocks in the subduction channels, resulting in different types of metamorphic rocks now exposed in the same orogens. The crust-mantle interaction in the continental subduction channel is realized by reaction of the overlying ancient subcontinental lithospheric mantle wedge peridotite with aqueous fluid and hydrous melt derived from partial melting of subducted continental basement granite and cover sediment. The nature of premetamorphic protoliths dictates the type of collisional orogens, the size of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terranes and the duration of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Chopin C. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism; tracing continental crust into the mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2003, 212: 1–14
Liou J G, Ernst W G, Song S G, et al. Tectonics and HP-UHP metamorphism of northern Tibet-Preface. J Asian Earth Sci, 2009, 35: 191–198
Zheng Y-F, Zhang L F, McClelland W C, et al. Processes in continental collision zones: Preface. Lithos, 2012, 136–139: 1–9
Shreve R L, Cloos M. Dynamics of sediment subduction, mélange formation, and prism accretion. J Geophys Res, 1986, 91B: 10229–10245
Cloos M, Shreve R L. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, mélange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins, 1, Background and description. Pure Appl Geophys, 1988, 128: 456–500
Cloos M, Shreve R L. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, mélange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins, 2, Implications and discussion. Pure Appl Geophys, 1988, 128: 501–505
Zheng Y-F. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chem Geol, 2012, 328: 5–48
Beaumont C, Ellis S, Pfiffner A. Dynamics of sediment subduction-accretion at convergent margins: Short-term modes, long-term deformation, and tectonic implications. J Geophys Res, 1999, B104: 17573–17601
Gerya T V, Stöckhert B, Perchuk A L. Exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic rocks in a subduction channel: A numerical simulation. Tectonics, 2002, 21: 1056
Guillot S, Hattori K, Agard P, et al. Exhumation processes in oceanic and continental subduction contexts: A review. In: Lallemand S, Funiciello F, eds. Subduction Zone Geodynamics. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2009. 175–205
Zheng Y-F, Fu B, Gong B, et al. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci Rev, 2003, 62: 105–161
Zheng Y-F, Zhou J-B, Wu Y-B, et al. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. Intern Geol Rev, 2005, 47: 851–871
Rubatto D, Regis D, Hermann J, et al. Yo-yo subduction recorded by accessory minerals in the Italian Western Alps. Nat Geosci, 2011, 4: 338–342
Zheng Y-F. Fluid regime in continental subduction zones: Petrological insights from ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks. J Geol Soc Lond, 2009, 166: 763–782
Zheng Y-F, Xia Q-X, Chen R-X, et al. Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Earth Sci Rev, 2011, 107: 342–374
Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, Chen R-X, et al. Element mobility in mafic and felsic ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2007, 71: 5244–5266
Xia Q-X, Zheng Y-F, Zhou L-G. Dehydration and melting during continental collision: Constraints from element and isotope geochemistry of low-T/UHP granitic gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chem Geol, 2008, 247: 36–65
Gao X-Y, Zheng Y-F, Chen Y-X. Dehydration melting of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite in the Dabie orogen: Evidence from multiphase solid inclusions in garnet. J Metamorph Geol, 2012, 30: 193–212
Chen Y-X, Zheng Y-F, Hu, Z. Synexhumation anatexis of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Petrological evidence from granitic gneiss in the Sulu orogen. Lithos, 2013, 156–159: 69–96
Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, Zhang J, et al. Syn-exhumation magmatism during continental collision: Evidence from alkaline intrusives of Triassic age in the Sulu orogen, Chem Geol, 2012, 328: 70–88
Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, Wei C-S, et al. Origin of postcollisional magmatic rocks in the Dabie orogen: Implications for crust-mantle interaction and crustal architecture. Lithos, 2011, 126: 99–114
Dai L-Q, Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, et al. Zircon Hf-O isotope evidence for crust-mantle interaction during continental deep subduction. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2011, 308: 224–244
Dai L-Q, Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, et al. The nature of orogenic lithospheric mantle: Geochemical constraints from postcollisional mafic-ultramafic rocks in the Dabie orogen. Chem Geol, 2012, 334: 99–121
Yang Q-L, Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F. Modification of subcontinental lithospheric mantle above continental subduction zone: Constraints from geochemistry of Mesozoic gabbroic rocks in southeastern North China. Lithos, 2012, 146–147: 164–182
Yang Q-L, Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F. Slab-mantle interaction in continental subduction channel: Geochemical evidence from Mesozoic gabbroic intrusives in southeastern North China. Lithos, 2012, 155: 442–460
Zhang J, Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, et al. Zircon Hf-O isotope and whole-rock geochemical constraints on origin of postcollisional mafic to felsic dykes in the Sulu orogen. Lithos, 2012, 136–139: 225–245
Dong S-W, Li Q-S, Gao R, et al. Moho-mapping in the Dabie ultrahigh-pressure collisional orogen, Central China. Am J Sci, 2008, 308: 517–528
Luo Y H, Xu Y X, Yang Y J. Crustal structure beneath the Dabie orogenic belt from ambient noise tomography. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2012, 313–314: 12–22
Zhao Z-F, Zheng Y-F, Wei C S, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf and O isotopes constrain the crustal architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie orogen in China. Chem Geol, 2008, 253: 222–242
Sizova E, Gerya T V, Brown M. Exhumation mechanisms of melt-bearing ultrahigh pressure crustal rocks during collision of spontaneously moving plates. J Metamorph Geol, 2012, 30: 927–955
Warren C. Exhumation of (ultra-)high-pressure terranes: Concepts and mechanisms. Solid Earth, 2013, 4: 75–92
Davies J H, von Blanckenburg F. Slab break off: A model of lithosphere detachment and its test in the magmatism and deformation of collisional orogens. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1995, 129: 85–102
von Blanckenburg F, Davies J H. Slab breakoff: A model for syncollisional magmatism and tectonics in the Alps. Tectonics, 1995, 14: 120–131
Lardeaux J M, Ledru P, Daniel I, et al. The Variscan French Massif Central—A new addition to the ultrahigh pressure metamorphic ‘club’: Exhumation processes and geodynamic consequences. Tectonophysics, 2001, 332: 143–167
Beaumont C, Jamieson R A, Butler J P, et al. Crustal structure: A key constraint on the mechanism of ultra-high-pressure rock exhumation. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2009, 287: 116–129
Li Z H, Gerya T V. Polyphase formation and exhumation of high-to ultrahigh pressure rocks in continental subduction zone; numerical modeling and application to the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane in eastern China. J Geophys Res, 2009, 114: B09406
Zheng Y-F, Xiao W-J, Zhao G C. Introduction to tectonics of China. Gondwana Res, 2013, 23: 1189–1306
Brun J-P, Faccenna C. Exhumation of high-pressure rocks driven by slab rollback. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2008, 272: 1–7
Husson L, Brun J-P, Yamoto P, et al. Episodic slab rollback fosters exhumation of HP-UHP rocks. Geophys J Intern, 2009, 179: 1292–1300
Zheng Y-F, Chen R-X, Zhao Z-F. Chemical geodynamics of continental subduction-zone metamorphism: Insights from studies of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) core samples. Tectonophysics, 2009, 475: 327–358
Kylander-Clark A R C, Hacker B R, Mattinson C G. Size and exhumation rate of ultrahigh-pressure terranes linked to orogenic stage. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2012, 321–322: 115–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Zhao, Z. & Chen, Y. Continental subduction channel processes: Plate interface interaction during continental collision. Chin. Sci. Bull. 58, 4371–4377 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-6066-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-6066-x