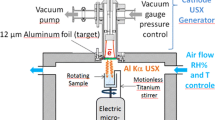
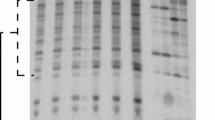
Abstract
To evaluate the influence of the DNA concentration in the aqueous solution on DNA radiation damage, the plasmid DNA in the presence or absence of Mannitol (scavenger of free radical OH•) was irradiated by 7Li ions and γ rays at various DNA concentrations. Gel electrophoresis analysis revealed that the DNA damage of single and double strand breaks induced by irradiation became more severe at lower DNA concentration. In the condition of γ-ray irradiation, most of double strand breaks (DSB) damage was neutralized and less associated with DNA concentration in the presence of mannitol. However, under 7Li irradiation, DSB damage could not be cleared by mannitol but was gradually aggravated with decreasing DNA concentrations. These findings imply that under low-LET irradiation, most of the DSB damage is generated by free radical OH• diffusion, and thus may be counteracted by scavengers, while at higher-LET irradiation, quite a fraction of DSB induction is caused by direct ionizing energy deposition of heavy ions, which cannot be eliminated. This work also indicates that the proportion between free radical damage and direct ionizing damage is a constant which is independent of DNA concentration when the DNA concentration is under a certain value (50 ng/μL). Our study sheds light on the underlying mechanisms in the DNA radiation damage process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang C X., Mei M T. Space Radiobiology (in Chinese). Guangzhou: Zhongshan University Press, 1995. 23–24
Xia S X, Chen J P, et al. Radiobiology (in Chinese). Beijing: The Academy of Military Medical Science Press, 1998. 1–21
Du H B, Qiu G Y, Du Y H. Study on plasmid supercoiled DNA damage induced by three types of radiation. Acta Biophysica Sinica, 1997, 13(2): 261–266
Yu Z L, Huo Y P. Review in low energy ion biology. J Anhui Agricul Univ, 1994, 21(3): 221–225
Milligan J R, Aguilerra J A, Ward J F. Variation of single-strand break yield with scavenger concentration for plasmid DNA irradiated in aqueous solution. Radiat Res, 1993, 133: 151–157
Milligan J R, Ward J F. Yield of single-strand breaks due to attack on DNA by scavenger-derived radicals. Radiat Res, 1994, 137: 295–299
Shao C L, Yu Z L, Masahiro Saito. Reaction rate coefficients of hydroxyl radical-induced DNA single-and α-type double-strand breaks. Radiat Environ Biophys, 2000, 39: 121–124
Kong F Q, Zhao K, Zhan Y et al. Analysis of length distribution of short DNA fragments induced by 7Li ions using the random-breakage model. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(9): 841–844
Deppman A, Echeimberg J O, Gouveia A N, et al. Radiation interaction with DNA. Brazilian J Phys, 2004, 34(3A): 958–961
Yang M J, Kong F Q, Zhan Y et al. A study of protective action of different scavengers on DNA damage induced by γ ray. Nuclear Tech, 2007, 30: 255–258
Aslam Siddiqi M, Bothe E. Single-and double-strand break formation of DNA irradiation in aqueous solution: Dependence on dose and OH radical scavenger concentration. Radiat Res, 1987, 112: 449–463
Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol, 1985, 32: 115–154
Zhou L J, Fang Y Z, Zhang Y P, et al. The effect of γ-ray irradiation on plasmid pBR 322 DNA. J Radiat Res Radiat Proc, 1993, 11(1): 28–30
Sui L, Zhao K, Ni M N, et al. Investigation of DNA strand breaks induced by 7Li and 12C ions. High Energy Phys Nuclear Phys, 2004, 28(10): 1126–1130
Spotheim-Maurizot M, Charlier M, Sabattier R. DNA radiolysis by fast neutrons. Int J Radiat Biol, 1990, 57: 301–313
Zhao K, Sui L, Kong FQ, et al, Investigation of DNA damage induced by high LET 7Li ions. In: Proceedings of China-Korea Joint Symposium on Nuclear Technique Application in Agriculture and Life Science, 2007, April, 22–25, Hangzhou, Institute of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences; Zhejiang University, 2007. 174–177
Cao T G, Ma Y Z, Zhuo Y. Track structure of proton and α particle in water. High Energy Phys Nuclear Phys, 2004, 28(4): 377–381
Sui L, Guo J Y, Kong F Q, et al. Investigation of direct interaction of DNA damage induced by high LET 7Li ions. Nuclear Tech, 2007, 30: 250–254
Yu X, Ye C Q, Zhou P K. The DNA strand breaks effect irradiated by heavy ions. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering (in Chinese), 1997, 10(4): 310–312
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10435020)
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, F., Wang, X., Ni, M. et al. The DNA concentration effect on DNA radiation damage induced by 7Li ions and γ rays. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 2758–2763 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0320-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0320-7