Abstract
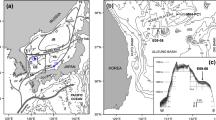
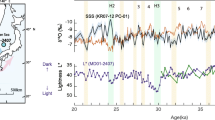
This paper reports high-resolution biomarker records of the last 260 ka for core MD05-2904 from the northern South China Sea (SCS). The sea surface temperature (SST) record using the U k′37 index reveals a minimum of 21.5°C (MIS 2) and a maximum of 28.3°C (MIS 5.5), for a temperature difference of almost 7°C, and provides the longest high-resolution U k′37 SST record in northern SCS. The content of odd-number long chain n-alkanes and several n-alkanes indexes such as the CPI, ACL and the C31/C27 ratio, all reveal generally higher values during the glacials and lower values during the interglacials. Terrestrial input as indicated by n-alkane content was mostly controlled by sea-level changes: During the glacials, lower sea-level exposed the continental shelf to enable rivers to transport more terrestrial materials to the slope; and the situation reverses during the interglacials. The n-alkane indexes changes reveal more n-alkanes from contemporary vegetation during glacials as a result of the proximity of the core site to the source region, while the increases in ACL and C31/C27 ratio during glacials indicate a change to more grassy vegetation. However, the highest values for CPI, ACL and the C31/C27 ratio all occurred during late MIS 3, and it was suggested that this period was characterized by a strong summer monsoon-dominated humid climate which resulted in a denser vegetation for the exposed continental shelf region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelejero C, Grimalt J O, Heilig S, et al. High-resolution U k′37 temperature reconstructions in the South China Sea over the past 220 kyr. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14(2): 224–231
Pelejero C. Terrigenous n-alkane input in the South China Sea: high-resolution records and surface sediments. Chem Geol, 2003, 200: 89–103
Hu J F, Peng P A, Jia G D, et al. Biological markers and their carbon isotopes as an approach to the paleoenvironmental reconstruction of Nansha area, South China Sea, during the last 30 ka. Org Geochem, 2002, 33: 1197–1204
Sun X J, Li X, Luo Y L. Vegetation and climate on the Sunda Shelf of the South China Sea during the Last Glactiation-pollen results from station 17962. Acta Bot Sin, 2002, 44(6): 746–752
Li X, Sun X J. Palynological records since Last Glacial Maximum form a deep sea core in southern South China Sea. Quat Sci (in Chinese), 1999, 6: 526–535
Sun X J, Luo Y L. Pollen record of the last 280 ka from deep-sea sediments of the northern South China Sea. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci (in Chinese), 2001, 31(10): 846–853
Laj C, Wang P X, Balut Y, et al. MD147-Marco Polo IMAGES XII Cruise Report. France: Institut Paul-Emile Victor (IPEV), 2005
Bühring C, Sarnthein M, Erlenkeuser H. Toward a high-resolution stable isotope stratigraphy of the last 1.1 m.y.: Site 1144, South China Sea. In: Prell W L, Wang P, Blum P, et al.: Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 184. College Station Texas. 2004. 1–29
Pelejero C, Grimalt J O. The correlation between the U k′37 index and sea surface temperatures in the warm boundary: the South China Sea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1997, 61(22): 4789–4797
Zhao M X, Huang C Y, Wang C C, et al. A millennial-scale U k′37 sea-surface temperature record from the South China Sea (8°N) over the last 150 kyr: Monsoon and sea-level influence. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol, 2006, 236(2): 39–55
Eglinton G, Hamilton R J. Leaf epicuticcular waxes. Science, 1967, 156: 1322–1335
Meyers P A, Ishiwatari R. Lacustrine organic geochemistry-and overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org Geochem, 1993, 20: 867–900
Chen M T, Shiau L J, Yu P S, et al. 500000-Year records of carbonate, organic carbon, and foraminiferal sea-surface temperature from the southeastern South China Sea (near Palawan Island), Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol, 2003, 197: 113–131
Huang W, Wang P X. The Statistics of Sediment Mass in the South China Sea: Method and Result. Adv Earth Sci (in Chinese), 2006, 21(5): 465–473
Higginson M J, Maxwell J R, Altabet M A. Nitrogen isotope and chlorin paleoproductivity records from the Northern South China Sea: remote vs. local forcing of millennia-and orbital-scale variability. Mar Geol, 2003, 201: 223–250
Shi Y F, Yu G, Liu X D, et al. Reconstruction of the 30–40 ka BP enhanced Indian monsoon climate based on geological records from the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol, 2001, 169: 69–83
Luo Y L, Sun X J. Vegetation evolution in the northern South China Sea region since 40 ka BP—an attempt to reconstruct palaeovegetation based on biomization. Acta Bot Sin, 2001, 43(11): 1202–1206
Sun X J, Li X, Chen H C. Evidence for natural fire and climate history since 37 ka BP in the northern part of the South China Sea. China Sea. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2000, 43(5): 487–493
Maffei M. Chemotaxonomic significance of leaf wax alkanes in the Gramineae. Biochem System Ecol, 1996, 24: 53–64
Zhang Z H, Zhao M X, Eglinton G, et al. Leaf wax lipids as paleovegetational and paleoenvironmental proxies for the Chinese Loess Plateau over the last 170 ka. Quat Sci Rev, 2006, 25: 575–594
Hinrichs K U, Rinna J, Rullkoetter J. Late Quaternary paleoenvironmental conditions indicated by marine and terrestrial molecular biomarkers in sediments from the Santa Barbara Basin. In: Wilson R C, Tharp V L, eds. Proceedings of the Fourteenth Annual Pacific Climate Workshop. California Department of Water Resources, 1997. 1–9
Kawamura K, Ishimura Y, Yamazaki K. Four years’ observations of terrestrial lipid class compounds in marine aerosols from the western North Pacific. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 2003, 17, 10.1029/2001GB001810
Luo Y L, Sun X J. Vegetation evolution during the Last Penultimate Glacial Cycle: a high-resolution pollen record from ODP site 1144, the South China Sea. Mar Geol Quat Geol (in Chinese), 2003, 23(1): 19–25
Luo Y L, Sun X J. Vegetation evolution and millennial-scale climatic fluctuations since Last Glacial Maximum in pollen record from northern South China Sea. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(8): 793–799
Sun X J, Li X. A pollen record of the last 37 ka in deep sea core 17940 from the northern slope of the South China Sea. Mar Geol, 1999, 156: 227–244
Luo Y L, Chen H C, Wu G X, et al. Records of natural fire and climate history during the last three glacial-interglacial cycles around the South China Sea—charcoal record from the ODP 1144, in South China Sea. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2001, 44(10): 897–904
Luo Y L, Sun X J, Chen H C. Millions years record of natural fire and climate history in the northern South China Sea—charcoal record from the deep sea core ODP 1144. Chin Sci Bul (in Chinese), 2006, 51(8): 942–950
Cerling T E, Harris J M, MacFadden B J, et al. Global vegetation change through the Miocene/Pliocene boundary. Nature, 1997, 389: 153–158
He J, Wang P X. Vegetation change in late Miocene and evolution of photosynthesis. Adv Earth Sci, 2005, 6: 618–626
Schwark L, Zink K, Lechterbeck J. Reconstruction of postglacial to early Holocene vegetation history in terrestrial Central Europe via cuticular lipid biomarkers and pollen records from lake sediments. Geology, 2002, 30: 463–466
Zheng Z, Lei Z Q. A 400,000 year record of vegetational and climatic changes from a volcanic basin, Leizhou Peninsula, southern China. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol, 1999, 145: 339–362
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40676032, 40776029 and 40403012) and the Innovation Research Group of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40621063)
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Zhao, M., Li, L. et al. Sea surface temperature and terrestrial biomarker records of the last 260 ka of core MD05-2904 from the northern South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 2376–2384 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0289-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0289-2