Abstract
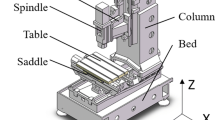
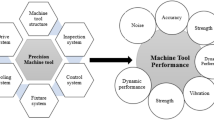
A novel approach, which can be used for dynamic characteristics analysis of machine tools based on unit structure (US), is reported in this paper. The concepts of unit structures for design of machine tools are defined. In order to satisfy the dynamic characteristics requirement of high natural frequency and light-weight of US, a design method of multi-disciplinary optimization of NSGA-II about unit structures driven by natural frequency and mass is developed. Through analyzing the unit structures, key factors affecting the natural frequency and mass are extracted, and the mathematical models of natural frequency and mass about unit structures are also established by using central composite design and response surface model. The goal of high natural frequency and light-weight is reached by using the multi-objective genetic algorithms. The Pareto optimal set is also obtained. The dynamic behavior of US is investigated by the experimental modal analysis. To show the efficiency of the proposed novel method, the example of YKW51250 gear shaping machine bed is used. Through optimization of NSGA-II about US of YKW51250 machine bed, the natural frequency of YKW51250 gear shaping machine bed is increased by 30.4% and its mass decreased by 5.2% comparing with the original design. By studying the dynamic characteristics of the simplified machine tools bed, useful laws are obtained, and these laws can be used in primary design of NC machine tools structures. The optimal method based on US can be also applied to the dynamic optimal design of machine tools and other similar equipments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang C, Zhang B C, Wan Z Q, et al. A method for static a eroelastic analysis based on the high-order panel method and modal method. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54: 741–748
Huang J T, Gao Z H. Buffeting numerical simulation coupled with aerodynamics and structure based on MDDES. Sci China Tech Sci, 2013, 56: 1550–1560
Loh S K, Faris W F, Hamdi M, et al. Vibrational characteristics of piping system in air conditioning outdoor unit. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54: 1154–1168
Lee S W, Mayor R, Ni J. Dynamic analysis of a mesoscale machine tool. J Manuf Sci Eng, 2006, 128: 194–203
Zaeh M, Siedl D. A new method for simulation of machining performance by integrating finite element and multi-body simulation for machine tools. Ann CIRP, 2007, 56: 383–386
Zhang G P, Huang Y M, Shi W H, et al. Predicting dynamic behaviours of a whole machine tool structure based on computer-aided engineering. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2003, 43: 699–706
Jaspreet D, Bartosz P, Reuven K, et al. Dynamics of the arch-type reconfigurable machine tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf, 2006, 47: 326–334
Yu H L, Wang Y Q, Chen H L, et al. Optimization for machine tool column combining response surface model with multi-objective genetic algorithm. J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ, 2012, 46: 80–85
Bai Z F, Zhao Y, Ma W L, et al. Modal analysis for small satellite system with finite element method. In: 2nd International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aerospace and Astronautics (ISSCAA), 2008. 1–5
Du P A, Yu Y T, Gan E Z, et al. Finite element modeling for computer motherboard modal analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, 2005, 4: 2101–2105
Astm S. Standard Test Method for Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus, and Poisson’s Ratio by Impulse Excitation of Vibration. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2003. 1876–1878
Alfano M, Pagnotta L. Determining the elastic properties of isotropic materials by modal vibration testing of rectangular thin plates. J Sound Vibrat, 2006, 293: 426–439
Schwarz B J, Richardson M H. Experimental Modal Analysis. Application Note Vibrant Technology, Inc, 1999. 1–12
Kennes P, Anthonis J, Clijmans L, et al. Construction of a portable test rig to perform experimental modal analysis on mobile agricultural machinery. J Sound Vibrat, 1999, 228: 421–441
Stanbribge A B, Ewins O J. Modal testing using a scanning laser doppler vibrometer. Mech Syst Signal Process, 1999, 13: 255–270
Kwon K S, Lee C W. Random excitation for modal testing of rotating machinery: Use of modulation technique. J Sound Vibrat, 2000, 234: 297–309
Hollkamp J J, Gordon R W. Modal test experiences with a jet engine fan model. J Sound Vibrat, 2001, 248: 151–165
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Chen, L. A novel method of dynamic characteristics analysis of machine tool based on unit structure. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1052–1062 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5524-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5524-2