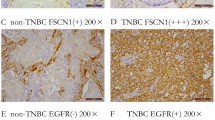
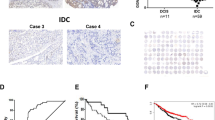
Abstract
CDK4/6 inhibitors are routinely recommended agents for the treatment of advanced HR+HER2− breast cancer. However, their therapeutic effectiveness in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains controversial. Here, we observed that the expression level of fibrous sheath interacting protein 1 (FSIP1) could predict the treatment response of TNBC to CDK4/6 inhibitors. High FSIP1 expression level was related to a poor prognosis in TNBC, which was associated with the ability of FSIP1 to promote tumor cell proliferation. FSIP1 downregulation led to slowed tumor growth and reduced lung metastasis in TNBC. FSIP1 knockout caused cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and reduced treatment sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors by inactivating the Nanog/CCND1/CDK4/6 pathway. FSIP1 could form a complex with Nanog, protecting it from ubiquitination and degradation, which may facilitate the rapid cell cycle transition from G0/G1 to S phase and exhibit enhanced sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Our findings suggest that TNBC patients with high FSIP1 expression levels may be suitable candidates for CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez-Fernández, M., and Malumbres, M. (2020). Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition. Cancer Cell 37, 514–529.
Bianchini, G., Balko, J.M., Mayer, I.A., Sanders, M.E., and Gianni, L. (2016). Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13, 674–690.
Cai, Z., Wang, J., Li, Y., Shi, Q., Jin, L., Li, S., Zhu, M., Wang, Q., Wong, L.L., Yang, W., et al. (2023). Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci China Life Sci 66, 94–109.
Cappell, K.M., Sinnott, R., Taus, P., Maxfield, K., Scarbrough, M., and Whitehurst, A.W. (2012). Multiple cancer testis antigens function to support tumor cell mitotic fidelity. Mol Cell Biol 32, 4131–4140.
Carey, L.A. (2021). Finding the positive in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Cancer 2, 476–478.
Chen, M., Wu, Y., Li, W., Zhang, X., Chen, L., Zheng, X., Zuo, X., Zhou, F., Hong, Y., Cheng, H., et al. (2020). Loss-of-function variants in FSIP1 identified by targeted sequencing are associated with one particular subtype of mucosal melanoma. Gene 759, 144964. Ciruelos, E., Villagrasa, P., Pascual, T., Oliveira, M., Pernas, S., Paré, L., Escrivá-de-Romaní, S., Manso, L., Adamo, B., Marténez, E., et al. (2020). Palbociclib and trastuzumab in HER2-positive advanced breast cancer: results from the phase II SOLTI-1303 PATRICIA trial. Clin Cancer Res 26, 5820–5829.
Costa, C., Wang, Y., Ly, A., Hosono, Y., Murchie, E., Walmsley, C.S., Huynh, T., Healy, C., Peterson, R., Yanase, S., et al. (2020). PTEN loss mediates clinical cross-resistance to CDK4/6 and PI3Kα inhibitors in breast cancer. Cancer Discov 10, 72–85.
Cretella, D., Fumarola, C., Bonelli, M., Alfieri, R., La Monica, S., Digiacomo, G., Cavazzoni, A., Galetti, M., Generali, D., and Petronini, P.G. (2019). Pre-treatment with the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib improves the efficacy of paclitaxel in TNBC cells. Sci Rep 9, 13014.
Fry, D.W., Harvey, P.J., Keller, P.R., Elliott, W.L., Meade, M.A., Trachet, E., Albassam, M., Zheng, X.X., Leopold, W.R., Pryer, N.K., et al. (2004). Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3, 1427–1438.
Gianni, L., Bisagni, G., Colleoni, M., Del Mastro, L., Zamagni, C., Mansutti, M., Zambetti, M., Frassoldati, A., De Fato, R., Valagussa, P., et al. (2018). Neoadjuvant treatment with trastuzumab and pertuzumab plus palbociclib and fulvestrant in HER2-positive, ER-positive breast cancer (NA-PHER2): an exploratory, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 19, 249–256.
Gil, C., and Martinez, A. (2021). Is drug repurposing really the future of drug discovery or is new innovation truly the way forward? Expert Opin Drug Discov 16, 829–831.
Goel, S., DeCristo, M.J., McAllister, S.S., and Zhao, J.J. (2018). CDK4/6 inhibition in cancer: beyond cell cycle arrest. Trends Cell Biol 28, 911–925.
Goodrich, D. W., Wang, N. P., Qian, Y. W., Lee, E. Y. H. P., and Lee, W. H. (1991). The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 67, 293–302.
Gucalp, A., Boyle, L.A., Alano, T., Arumov, A., Gounder, M.M., Patil, S., Feigin, K., Edelweiss, M., D’Andrea, G., Bromberg, J., et al. (2020). Phase II trial of bicalutamide in combination with palbociclib for the treatment of androgen receptor (+) metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 38, 1017.
Heurtier, V., Owens, N., Gonzalez, I., Mueller, F., Proux, C., Mornico, D., Clerc, P., Dubois, A., and Navarro, P. (2019). The molecular logic of Nanog-induced self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Commun 10, 1109.
Jiang, Y.Z., Ma, D., Suo, C., Shi, J., Xue, M., Hu, X., Xiao, Y., Yu, K.D., Liu, Y.R., Yu, Y., et al. (2019). Genomic and transcriptomic landscape of triple-negative breast cancers: subtypes and treatment strategies. Cancer Cell 35, 428–440.e5.
Ju, W., Zheng, R., Zhang, S., Zeng, H., Sun, K., Wang, S., Chen, R., Li, L., Wei, W., and He, J. (2023). Cancer statistics in Chinese older people, 2022: current burden, time trends, and comparisons with the US, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Sci China Life Sci 66, 1079–1091.
Liu, C., Sun, L., Yang, J., Liu, T., Yang, Y., Kim, S.M., Ou, X., Wang, Y., Sun, L., Zaidi, M., et al. (2018). FSIP1 regulates autophagy in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 13075–13080.
Liu, T., Zhang, H., Sun, L., Zhao, D., Liu, P., Yan, M., Zaidi, N., Izadmehr, S., Gupta, A., Abu-Amer, W., et al. (2017). FSIP1 binds HER2 directly to regulate breast cancer growth and invasiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 7683–7688.
Matsushime, H., Roussel, M.F., Ashmun, R.A., and Sherr, C.J. (1991). Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 65, 701–713.
McClendon, A.K., Dean, J.L., Rivadeneira, D.B., Yu, J.E., Reed, C.A., Gao, E., Farber, J.L., Force, T., Koch, W.J., and Knudsen, E.S. (2012). CDK4/6 inhibition antagonizes the cytotoxic response to anthracycline therapy. Cell Cycle 11, 2747–2755.
Munzone, E., Pagan, E., Bagnardi, V., Montagna, E., Cancello, G., Dellapasqua, S., Iorfida, M., Mazza, M., and Colleoni, M. (2021). Systematic review and meta-analysis of post-progression outcomes in ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer after CDK4/6 inhibitors within randomized clinical trials. ESMO Open 6, 100332.
Pushpakom, S., Iorio, F., Eyers, P.A., Escott, K.J., Hopper, S., Wells, A., Doig, A., Guilliams, T., Latimer, J., McNamee, C., et al. (2019). Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18, 41–58.
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Wagle, N.S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73, 17–48.
Spring, L.M., Wander, S.A., Andre, F., Moy, B., Turner, N.C., and Bardia, A. (2020). Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: past, present, and future. Lancet 395, 817–827.
Teh, J.L.F., Cheng, P.F., Purwin, T.J., Nikbakht, N., Patel, P., Chervoneva, I., Ertel, A., Fortina, P.M., Kleiber, I., HooKim, K., et al. (2018). In vivo E2F reporting reveals efficacious schedules of MEK1/2-CDK4/6 targeting and mTOR-S6 resistance mechanisms. Cancer Discov 8, 568–581.
Tolaney, S.M., Wardley, A.M., Zambelli, S., Hilton, J., Troso-Sandoval, T., Ricci, F., Im, S.A., Kim, S.B., Johnston, S.R.D., Chan, A., et al. (2019). MonarcHER: A randomized phase II study of abemaciclib plus trastuzumab with or without fulvestrant versus trastuzumab plus standard-of-care chemotherapy in women with HR+, HER2+ advanced breast cancer (ABC). Ann Oncol 30, v861–v862.
Tolaney, S.M., Wardley, A.M., Zambelli, S., Hilton, J.F., Troso-Sandoval, T.A., Ricci, F., Im, S.A., Kim, S.B., Johnston, S.R., Chan, A., et al. (2020). Abemaciclib plus trastuzumab with or without fulvestrant versus trastuzumab plus standard-of-care chemotherapy in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (monarcHER): a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 21, 763–775.
Turner, N.C., Ro, J., André, F., Loi, S., Verma, S., Iwata, H., Harbeck, N., Loibl, S., Huang Bartlett, C., Zhang, K., et al. (2015). Palbociclib in hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 373, 209–219.
Wang, R., Xu, K., Gao, F., Huang, J., and Guan, X. (2021). Clinical considerations of CDK4/6 inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1876, 188590.
Wu, S.Y., Wang, H., Shao, Z.M., and Jiang, Y.Z. (2021). Triple-negative breast cancer: new treatment strategies in the era of precision medicine. Sci China Life Sci 64, 372–388.
Xiong, Y., Connolly, T., Futcher, B., and Beach, D. (1991). Human D-type cyclin. Cell 65, 691–699.
Yan, X., Dai, J., Han, Y., You, Q., and Liu, Y. (2022). FSIP1 is associated with poor prognosis and can be used to construct a prognostic model in gastric cancer. Dis Markers 2022, 2478551.
Zhang, H., Luo, M., Jin, Z., Wang, D., Sun, M., Zhao, X., Zhao, Z., Lei, H., Li, M., and Liu, C. (2015). Expression and clinicopathological significance of FSIP1 in breast cancer. Oncotarget 6, 10658–10666.
Zhang, W., Sui, Y., Ni, J., and Yang, T. (2016). Insights into the Nanog gene: A propeller for stemness in primitive stem cells. Int J Biol Sci 12, 1372–1381.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82203804, 81872159), and 345 Talent Project of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals was followed in this study (2020PS395K). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. This study was approved by the institutional research ethics committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University. Information about the individual’s illness and tissue samples used in this study were obtained with the individual’s consent for publication.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Sun, L., Gu, X. et al. FSIP1 enhances the therapeutic sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer patients by activating the Nanog pathway. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2805–2817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-023-2343-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-023-2343-y