Abstract
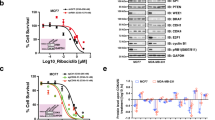
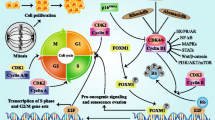
CDK4/6 inhibitors are the standard treatment in advanced HR+/HER2− breast cancer patients. Nevertheless, the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is inevitable and the strategies to overcome resistance are of great interest. Here, we show that the palbociclib-resistant breast cancer cells expressed significantly higher levels of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins because of upregulated protein synthesis. Silencing Cyclin D1 or CDK4 led to cell cycle arrest while silencing Cyclin E1 or CDK2 restored the sensitivity to palbociclib. Furthermore, PI3K/mTOR pathway was hyper-activated in palbociclib-resistant cells, leading to more phosphorylated 4E-BP1 and higher levels of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 translation. Targeting PI3K/mTOR pathway with a specific PI3Kα inhibitor (BYL719) or an mTOR inhibitor (everolimus) reduced the protein levels of Cyclin D1 and CDK4, and restored the sensitivity to palbociclib. The tumor samples expressed significantly higher levels of Cyclin D1, CDK4, p-AKT and p-4E-BP1 after progression on palbociclib treatment. In conclusion, our findings suggest that overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins lead to the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor and PI3K/mTOR inhibitors are able to restore the sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors, which provides the biomarker and rationale for the combinational use of CDK4/6 inhibitors and PI3K/mTOR inhibitors after CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Averous, J., Fonseca, B.D., and Proud, C.G. (2008). Regulation of cyclin D1 expression by mTORC1 signaling requires eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1. Oncogene 27, 1106–1113.
Bardia, A., Hurvitz, S.A., DeMichele, A., Clark, A.S., Zelnak, A., Yardley, D.A., Karuturi, M., Sanft, T., Blau, S., Hart, L., et al. (2021). Phase I/II trial of exemestane, ribociclib, and everolimus in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer after progression on CDK4/6 inhibitors (TRINITI-1). Clin Cancer Res 27, 4177–4185.
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R.L., Torre, L.A., and Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J Clin 68, 394–424.
Chandarlapaty, S., and Razavi, P. (2019). Cyclin E mRNA: assessing cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activation state to elucidate breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. J Clin Oncol 37, 1148–1150.
Chou, T.C. (2006). Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev 58, 621–681.
Chou, T.C. (2010). Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 70, 440–446.
Ciruelos, E.M., Rugo, H.S., Mayer, I.A., Levy, C., Forget, F., Delgado Mingorance, J.I., Safra, T., Masuda, N., Park, Y.H., Juric, D., et al. (2021). Patient-reported outcomes in patients with PIK3CA-mutated hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer from SOLAR-1. J Clin Oncol 39, 2005–2015.
Cortés, J., Im, S.A., Holgado, E., Perez-Garcia, J.M., Schmid, P., and Chavez-MacGregor, M. (2017). The next era of treatment for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: triplet combination-based endocrine therapies. Cancer Treatment Rev 61, 53–60.
Finn, R.S., Liu, Y., Zhu, Z., Martin, M., Rugo, H.S., Diéras, V., Im, S.A., Gelmon, K.A., Harbeck, N., Lu, D.R., et al. (2020). Biomarker analyses of response to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition and endocrine therapy in women with treatment-Naïve metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 26, 110–121.
Formisano, L., Lu, Y., Servetto, A., Hanker, A.B., Jansen, V.M., Bauer, J. A., Sudhan, D.R., Guerrero-Zotano, A.L., Croessmann, S., Guo, Y., et al. (2019). Aberrant FGFR signaling mediates resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. Nat Commun 10, 1373.
Hortobagyi, G.N., Paluch-Shimon, S., Petrakova, K., Villanueva, C., Chan, A., Nusch, A., Yap, Y.S., Hart, L., Favret, A., Marschner, N., et al. (2018). First-line ribociclib (RIB) + letrozole (LET) in hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2−) advanced breast cancer (ABC): MONALEESA-2 biomarker analyses. J Clin Oncol 36, 1022.
Gobbini, E., Ezzalfani, M., Dieras, V., Bachelot, T., Brain, E., Debled, M., Jacot, W., Mouret-Reynier, M.A., Goncalves, A., Dalenc, F., et al. (2018). Time trends of overall survival among metastatic breast cancer patients in the real-life ESME cohort. Eur J Cancer 96, 17–24.
Gopalan, P.K., Villegas, A.G., Cao, C., Pinder-Schenck, M., Chiappori, A., Hou, W., Zajac-Kaye, M., Ivey, A.M., and Kaye, F.J. (2018). CDK4/6 inhibition stabilizes disease in patients with p16-null non-small cell lung cancer and is synergistic with mTOR inhibition. Oncotarget 9, 37352–37366.
Herrera-Abreu, M.T., Palafox, M., Asghar, U., Rivas, M.A., Cutts, R.J., Garcia-Murillas, I., Pearson, A., Guzman, M., Rodriguez, O., Grueso, J., et al. (2016). Early adaptation and acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 76, 2301–2313.
Jansen, V.M., Bhola, N.E., Bauer, J.A., Formisano, L., Lee, K.M., Hutchinson, K.E., Witkiewicz, A.K., Moore, P.D., Estrada, M.V., Sánchez, V., et al. (2017). Kinome-wide RNA interference screen reveals a role for PDK1 in acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in ER-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 77, 2488–2499.
Kawasome, H., Papst, P., Webb, S., Keller, G.M., Johnson, G.L., Gelfand, E.W., and Terada, N. (1998). Targeted disruption of p70s6k defines its role in protein synthesis and rapamycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 5033–5038.
Kettner, N.M., Vijayaraghavan, S., Durak, M.G., Bui, T., Kohansal, M., Ha, M.J., Liu, B., Rao, X., Wang, J., Yi, M., et al. (2019). Combined inhibition of STAT3 and DNA repair in palbociclib-resistant ER-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 25, 3996–4013.
Lai, H., Wang, R., Li, S., Shi, Q., Cai, Z., Li, Y., and Liu, Y. (2020). LIN9 confers paclitaxel resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells by upregulating CCSAP. Sci China Life Sci 63, 419–428.
Li, Q., Liu, J., Jiang, Z., and Liu, Q. (2020). CSCO breast cancer guideline: precise, economical and oriental. Sci China Life Sci 63, 1410–1412.
Liang, J., and Slingerland, J.M. (2003). Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2, 336–342.
Lin, N.U., Vanderplas, A., Hughes, M.E., Theriault, R.L., Edge, S.B., Wong, Y.N., Blayney, D.W., Niland, J.C., Winer, E.P., and Weeks, J.C. (2012). Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer 118, 5463–5472.
Ma, C.X., Gao, F., Luo, J., Northfelt, D.W., Goetz, M., Forero, A., Hoog, J., Naughton, M., Ademuyiwa, F., Suresh, R., et al. (2017). NeoPalAna: neoadjuvant palbociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor, and anastrozole for clinical stage 2 or 3 estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23, 4055–4065.
Mitchell, D.C., Menon, A., and Garner, A.L. (2020). Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibits the translational repressor 4E-BP1 to promote cap-dependent translation during mitosis-G1 transition. FEBS Lett 594, 1307–1318.
Muise-Helmericks, R.C., Grimes, H.L., Bellacosa, A., Malstrom, S.E., Tsichlis, P.N., and Rosen, N. (1998). Cyclin D expression is controlled post-transcriptionally via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 273, 29864–29872.
O’Brien, N.A., McDermott, M.S.J., Conklin, D., Luo, T., Ayala, R., Salgar, S., Chau, K., DiTomaso, E., Babbar, N., Su, F., et al. (2020). Targeting activated PI3K/mTOR signaling overcomes acquired resistance to CDK4/6-based therapies in preclinical models of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 22, 89.
O’Leary, B., Cutts, R.J., Liu, Y., Hrebien, S., Huang, X., Fenwick, K., André, F., Loibl, S., Loi, S., Garcia-Murillas, I., et al. (2018). The genetic landscape and clonal evolution of breast cancer resistance to palbociclib plus fulvestrant in the PALOMA-3 trial. Cancer Discovery 8, 1390–1403.
Olanich, M.E., Sun, W., Hewitt, S.M., Abdullaev, Z., Pack, S.D., and Barr, F.G. (2015). CDK4 amplification reduces sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibition in fusion-positive rhabdomyosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 21, 4947–4959.
Olmez, I., Brenneman, B., Xiao, A., Serbulea, V., Benamar, M., Zhang, Y., Manigat, L., Abbas, T., Lee, J., Nakano, I., et al. (2017). Combined CDK4/6 and mTOR inhibition is synergistic against glioblastoma via multiple mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 23, 6958–6968.
Pandey, K., An, H.J., Kim, S.K., Lee, S.A., Kim, S., Lim, S.M., Kim, G.M., Sohn, J., and Moon, Y.W. (2019). Molecular mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: a review. Int J Cancer 145, 1179–1188.
Qin, X., Jiang, B., and Zhang, Y. (2016). 4E-BP1, a multifactor regulated multifunctional protein. Cell Cycle 15, 781–786.
Rugo, H.S., Lerebours, F., Ciruelos, E., Drullinsky, P., Ruiz-Borrego, M., Neven, P., Park, Y.H., Prat, A., Bachelot, T., Juric, D., et al. (2021). Alpelisib plus fulvestrant in PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer after a CDK4/6 inhibitor (BYLieve): one cohort of a phase 2, multicentre, open-label, non-comparative study. Lancet Oncol 22, 489–498.
Sharma, P., and Allison, J.P. (2015). The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 348, 56–61.
Slamon, D.J., Neven, P., Chia, S., Fasching, P.A., De Laurentiis, M., Im, S. A., Petrakova, K., Bianchi, G.V., Esteva, F.J., Martin, M., et al. (2018). Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol 36, 2465–2472.
SledgeJr., G.W., Toi, M., Neven, P., Sohn, J., Inoue, K., Pivot, X., Burdaeva, O., Okera, M., Masuda, N., Kaufman, P.A., et al. (2017). MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 35, 2875–2884.
Teh, J.L.F., Cheng, P.F., Purwin, T.J., Nikbakht, N., Patel, P., Chervoneva, I., Ertel, A., Fortina, P.M., Kleiber, I., HooKim, K., et al. (2018). In vivo E2F reporting reveals efficacious schedules of MEK1/2-CDK4/6 targeting and mTOR-S6 resistance mechanisms. Cancer Discov 8, 568–581.
Turner, N.C., Liu, Y., Zhu, Z., Loi, S., Colleoni, M., Loibl, S., DeMichele, A., Harbeck, N., André, F., Bayar, M.A., et al. (2019). Cyclin E1 expression and palbociclib efficacy in previously treated hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 37, 1169–1178.
Turner, N.C., Slamon, D.J., Ro, J., Bondarenko, I., Im, S.A., Masuda, N., Colleoni, M., DeMichele, A., Loi, S., Verma, S., et al. (2018). Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 379, 1926–1936.
VanArsdale, T., Boshoff, C., Arndt, K.T., and Abraham, R.T. (2015). Molecular pathways: targeting the Cyclin D—CDK4/6 axis for cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res 21, 2905–2910.
Vora, S.R., Juric, D., Kim, N., Mino-Kenudson, M., Huynh, T., Costa, C., Lockerman, E.L., Pollack, S.F., Liu, M., Li, X., et al. (2014). CDK 4/6 inhibitors sensitize PIK3CA mutant breast cancer to PI3K inhibitors. Cancer Cell 26, 136–149.
Yang, C., Li, Z., Bhatt, T., Dickler, M., Giri, D., Scaltriti, M., Baselga, J., Rosen, N., and Chandarlapaty, S. (2017). Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene 36, 2255–2264.
Yang, Y., Liu, J., Peng, M., Su, F., Xie, X., Liu, Z., Wu, J., Wei, W., Zhou, D., Li, W., et al. (2020). Introduction of a multicenter online database for non-metastatic breast cancer in China. Sci China Life Sci 63, 1417–1420.
Yoshida, A., Bu, Y., Qie, S., Wrangle, J., Camp, E.R., Hazard, E.S., Hardiman, G., de Leeuw, R., Knudsen, K.E., and Diehl, J.A. (2019). SLC36A1-mTORC1 signaling drives acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Sci Adv 5, eaax6352.
Young, R.J., Waldeck, K., Martin, C., Foo, J.H., Cameron, D.P., Kirby, L., Do, H., Mitchell, C., Cullinane, C., Liu, W., et al. (2014). Loss of CDKN2A expression is a frequent event in primary invasive melanoma and correlates with sensitivity to the CDK4/6 inhibitor PD0332991 in melanoma cell lines. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 27, 590–600.
Zhu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, C., Chu, J., Wu, Y., Li, Y., Liu, J., Li, Q., Li, S., Shi, Q., et al. (2018). Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells are resistant to DNA-damaging chemotherapy because of upregulated BARD1 and BRCA1. Nat Commun 9, 1595.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Notional Natural Science Foundation of China (82061148016, 81630074, 81872141, 81702630, 81672622), Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Key Projects (201804020076), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2019A1515010146), and Beijing Medical Award Foundation (YXJL-2020-0941-0760), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021TQ0384, 2021M703731).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Wang, J., Li, Y. et al. Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 94–109 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2140-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2140-8