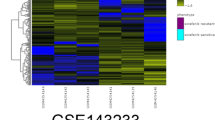
Abstract
The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been dominated by multikinase inhibitors for more than a decade. However, drug resistance can severely restrict the efficacy of these drugs. Using CRISPR/CAS9 genome library screening, we evaluated Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) as a key regulator of sorafenib’s susceptibility in HCC. We also investigated whether KEAP1’s knockdown can stabilize nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) protein levels that led to sorafenib’s resistance, including an NRF2 inhibitor that can synergize with sorafenib to abolish HCC’s growth in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we clarified that fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an important downstream regulator of NRF2 in HCC. Intriguingly, we observed that FGF21 bound to NRF2 through the C-terminus of FGF21, thereby stabilizing NRF2 by reducing its ubiquitination and generating a positive feedback loop in sorafenib-resistant HCC. These findings, therefore, propose that targeting FGF21 is a promising strategy to combat HCC sorafenib’s resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Badman, M.K., Pissios, P., Kennedy, A.R., Koukos, G., Flier, J.S., and Maratos-Flier, E. (2007). Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab 5, 426–437.
Bruix, J., Qin, S., Merle, P., Granito, A., Huang, Y.H., Bodoky, G., Pracht, M., Yokosuka, O., Rosmorduc, O., Breder, V., et al. (2017). Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 389, 56–66.
Bruix, J., Reig, M., and Sherman, M. (2016). Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 150, 835–853.
Chen, J., Jin, R., Zhao, J., Liu, J., Ying, H., Yan, H., Zhou, S., Liang, Y., Huang, D., Liang, X., et al. (2015). Potential molecular, cellular and microenvironmental mechanism of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 367, 1–11.
Chen, J., Yu, Y., Ji, T., Ma, R., Chen, M., Li, G., Li, F., Ding, Q., Kang, Q., Huang, D., et al. (2016). Clinical implication of Keap1 and phosphorylated Nrf2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med 5, 2678–2687.
Chen, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system to drug resistance in breast cancer. Adv Sci 5, 1700964.
Chowdhury, I., Mo, Y., Gao, L., Kazi, A., Fisher, A.B., and Feinstein, S.I. (2009). Oxidant stress stimulates expression of the human peroxiredoxin 6 gene by a transcriptional mechanism involving an antioxidant response element. Free Radic Biol Med 46, 146–153.
Coskun, T., Bina, H.A., Schneider, M.A., Dunbar, J.D., Hu, C.C., Chen, Y., Moller, D.E., and Kharitonenkov, A. (2008). Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 149, 6018–6027.
Dodson, M., Castro-Portuguez, R., and Zhang, D.D. (2019). NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol 23, 101107.
Finn, R.S., Qin, S., Ikeda, M., Galle, P.R., Ducreux, M., Kim, T.Y., Kudo, M., Breder, V., Merle, P., Kaseb, A.O., et al. (2020). Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 382, 1894–1905.
Fisher, F.M., and Maratos-Flier, E. (2016). Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol 78, 223–241.
Gao, L., Wang, X., Tang, Y., Huang, S., Hu, C.A.A., and Teng, Y. (2017). FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36, 8.
Geng, L., Lam, K.S.L., and Xu, A. (2020). The therapeutic potential of FGF21 in metabolic diseases: from bench to clinic. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16, 654–667.
Hayes, J.D., and Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. (2014). The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 39, 199–218.
Housden, B.E., and Perrimon, N. (2016). Comparing CRISPR and RNAi-based screening technologies. Nat Biotechnol 34, 621–623.
Huang, H.C., Nguyen, T., and Pickett, C.B. (2000). Regulation of the antioxidant response element by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of NF-E2-related factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 12475–12480.
Huppke, P., Weissbach, S., Church, J.A., Schnur, R., Krusen, M., Dreha-Kulaczewski, S., Kühn-Velten, W.N., Wolf, A., Huppke, B., Millan, F., et al. (2017). Activating de novo mutations in NFE2L2 encoding NRF2 cause a multisystem disorder. Nat Commun 8, 818.
Jackson, A.L., and Linsley, P.S. (2010). Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9, 57–67.
Ji, L., Lin, Z., Wan, Z., Xia, S., Jiang, S., Cen, D., Cai, L., Xu, J., and Cai, X. (2020). miR-486–3p mediates hepatocellular carcinoma sorafenib resistance by targeting FGFR4 and EGFR. Cell Death Dis 11, 250.
Jimenez, T., Barrios, A., Tucker, A., Collazo, J., Arias, N., Fazel, S., Baker, M., Halim, M., Huynh, T., Singh, R., et al. (2020). DUSP9-mediated reduction of pERK1/2 supports cancer stem cell-like traits and promotes triple negative breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res 10, 3487–3506.
Kim, B.R., Lee, G.Y., Yu, H., Maeng, H.J., Oh, T.J., Kim, K.M., Moon, J. H., Lim, S., Jang, H.C., and Choi, S.H. (2018). Suppression of Nrf2 attenuates adipogenesis and decreases FGF21 expression through PPAR gamma in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 497, 1149–1153.
Kubo, E., Chhunchha, B., Singh, P., Sasaki, H., and Singh, D.P. (2017). Sulforaphane reactivates cellular antioxidant defense by inducing Nrf2/ARE/Prdx6 activity during aging and oxidative stress. Sci Rep 7, 14130.
Lee, D., Xu, I.M.J., Chiu, D.K.C., Leibold, J., Tse, A.P.W., Bao, M.H.R., Yuen, V.W.H., Chan, C.Y.K., Lai, R.K.H., Chin, D.W.C., et al. (2019). Induction of oxidative stress through inhibition of thioredoxin reductase 1 is an effective therapeutic approach for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 69, 1768–1786.
Lee, H., Park, B.C., Soon Kang, J., Cheon, Y., Lee, S., and Jae Maeng, P. (2020). MAM domain containing 2 is a potential breast cancer biomarker that exhibits tumour-suppressive activity. Cell Prolif 53, e12883.
Li, D., and Li, Y. (2020). The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5, 108.
Li, W., Xu, H., Xiao, T., Cong, L., Love, M.I., Zhang, F., Irizarry, R.A., Liu, J.S., Brown, M., and Liu, X.S. (2014). MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biol 15, 554.
Lin, Z., Xia, S., Liang, Y., Ji, L., Pan, Y., Jiang, S., Wan, Z., Tao, L., Chen, J., Lin, C., et al. (2020). LXR activation potentiates sorafenib sensitivity in HCC by activating microRNA-378a transcription. Theranostics 10, 8834–8850.
Liu, J., Song, T., Zhou, W., Xing, L., Wang, S., Ho, M., Peng, Z., Tai, Y.T., Hideshima, T., Anderson, K.C., et al. (2019). A genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screening in myeloma cells identifies regulators of immunomodulatory drug sensitivity. Leukemia 33, 171–180.
Llovet, J.M., Montal, R., Sia, D., and Finn, R.S. (2018). Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15, 599–616.
Llovet, J.M., Montal, R., and Villanueva, A. (2019). Randomized trials and endpoints in advanced HCC: role of PFS as a surrogate of survival. J Hepatol 70, 1262–1277.
Marrero, J.A., Kulik, L.M., Sirlin, C.B., Zhu, A.X., Finn, R.S., Abecassis, M.M., Roberts, L.R., and Heimbach, J.K. (2018). Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 68, 723–750.
Ouyang, Q., Liu, Y., Tan, J., Li, J., Yang, D., Zeng, F., Huang, W., Kong, Y., Liu, Z., Zhou, H., et al. (2019). Loss of ZNF587B and SULF1 contributed to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cell lines based on Genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 screening. Am J Cancer Res 9, 988–998.
Robledinos-Antón, N., Fernández-Ginés, R., Manda, G., and Cuadrado, A. (2019). Activators and inhibitors of NRF2: a review of their potential for clinical development. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 1–20.
Rojo de la Vega, M., Chapman, E., and Zhang, D.D. (2018). NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell 34, 21–43.
Rudalska, R., Dauch, D., Longerich, T., McJunkin, K., Wuestefeld, T., Kang, T.W., Hohmeyer, A., Pesic, M., Leibold, J., von Thun, A., et al. (2014). In vivo RNAi screening identifies a mechanism of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer. Nat Med 20, 1138–1146.
Saber, A., Liu, B., Ebrahimi, P., and Haisma, H.J. (2020). CRISPR/Cas9 for overcoming drug resistance in solid tumors. Daru 28, 295–304.
Sánchez-Rivera, F.J., and Jacks, T. (2015). Applications of the CRISPR-Cas9 system in cancer biology. Nat Rev Cancer 15, 387–393.
Sanghvi, V.R., Leibold, J., Mina, M., Mohan, P., Berishaj, M., Li, Z., Miele, M.M., Lailler, N., Zhao, C., de Stanchina, E., et al. (2019). The oncogenic action of NRF2 depends on de-glycation by fructosamine-3-kinase. Cell 178, 807–819.e21.
Shalem, O., Sanjana, N.E., Hartenian, E., Shi, X., Scott, D.A., Mikkelsen, T.S., Heckl, D., Ebert, B.L., Root, D.E., Doench, J.G., et al. (2014). Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 343, 84–87.
Singh, A., Venkannagari, S., Oh, K.H., Zhang, Y.Q., Rohde, J.M., Liu, L., Nimmagadda, S., Sudini, K., Brimacombe, K.R., Gajghate, S., et al. (2016). Small molecule inhibitor of NRF2 selectively intervenes therapeutic resistance in KEAP1-deficient NSCLC tumors. ACS Chem Biol 11, 3214–3225.
Song, C.Q., Li, Y., Mou, H., Moore, J., Park, A., Pomyen, Y., Hough, S., Kennedy, Z., Fischer, A., Yin, H., et al. (2017). Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies regulators of mitogen-activated protein kinase as suppressors of liver tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 152, 1161–1173.e1.
Sun, X., Niu, X., Chen, R., He, W., Chen, D., Kang, R., and Tang, D. (2016a). Metallothionein-1G facilitates sorafenib resistance through inhibition of ferroptosis. Hepatology 64, 488–500.
Sun, X., Ou, Z., Chen, R., Niu, X., Chen, D., Kang, R., and Tang, D. (2016b). Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 63, 173–184.
Teng, Y., Zhao, H., Gao, L., Zhang, W., Shull, A.Y., and Shay, C. (2017). FGF19 protects hepatocellular carcinoma cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress via activation of FGFR4-GSK3β-Nrf2 signaling. Cancer Res 77, 6215–6225.
Torre, L.A., Bray, F., Siegel, R.L., Ferlay, J., Lortet-Tieulent, J., and Jemal, A. (2015). Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65, 87–108.
Wei, L., Lee, D., Law, C.T., Zhang, M.S., Shen, J., Chin, D.W.C., Zhang, A., Tsang, F.H.C., Wong, C.L.S., Ng, I.O.L., et al. (2019). Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screening identified PHGDH as a critical driver for Sorafenib resistance in HCC. Nat Commun 10, 4681.
Wu, A., Feng, B., Yu, J., Yan, L., Che, L., Zhuo, Y., Luo, Y., Yu, B., Wu, D., and Chen, D. (2021). Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates iron overload-induced liver injury and fibrosis by inhibiting ferroptosis. Redox Biol 46, 102131.
Xia, S., Pan, Y., Liang, Y., Xu, J., and Cai, X. (2020). The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ebiomedicine 51, 102610.
Xu, J., Ji, L., Liang, Y., Wan, Z., Zheng, W., Song, X., Gorshkov, K., Sun, Q., Lin, H., Zheng, X., et al. (2020a). CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5, 298.
Xu, J., Ji, L., Ruan, Y., Wan, Z., Lin, Z., Xia, S., Tao, L., Zheng, J., Cai, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). UBQLN1 mediates sorafenib resistance through regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and ROS homeostasis by targeting PGC1β in hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6, 190.
Xu, J., Stanislaus, S., Chinookoswong, N., Lau, Y.Y., Hager, T., Patel, J., Ge, H., Weiszmann, J., Lu, S.C., Graham, M., et al. (2009). Acute glucose-lowering and insulin-sensitizing action of FGF21 in insulin-resistant mouse models—association with liver and adipose tissue effects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297, E1105–E1114.
Xu, J., Wan, Z., Tang, M., Lin, Z., Jiang, S., Ji, L., Gorshkov, K., Mao, Q., Xia, S., Cen, D., et al. (2020b). N6-methyladenosine-modified circRNA-SORE sustains sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating β-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer 19, 163.
Yamamoto, M., Kensler, T.W., and Motohashi, H. (2018). The KEAP1-NRF2 system: a thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev 98, 1169–1203.
Yau, T., Hsu, C., Kim, T.Y., Choo, S.P., Kang, Y.K., Hou, M.M., Numata, K., Yeo, W., Chopra, A., Ikeda, M., et al. (2019). Nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: sorafenib-experienced Asian cohort analysis. J Hepatol 71, 543–552.
Yeh, W.L., Shioda, K., Coser, K.R., Rivizzigno, D., McSweeney, K.R., and Shioda, T. (2013). Fulvestrant-induced cell death and proteasomal degradation of estrogen receptor a protein in MCF-1 cells require the CSK c-Src tyrosine kinase. PLoS ONE 8, e60889.
Yu, Y., Bai, F., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Yuan, Q., Zou, D., Qu, S., Tian, G., Song, L., Zhang, T., et al. (2015). Fibroblast growth factor (FGF21) protects mouse liver against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 403, 287–299.
Yu, Y., He, J., Li, S., Song, L., Guo, X., Yao, W., Zou, D., Gao, X., Liu, Y., Bai, F., et al. (2016). Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 38, 144–152.
Yu, Z., Lin, L., Jiang, Y., Chin, I., Wang, X., Li, X., Lo, E.H., and Wang, X. (2019). Recombinant FGF21 protects against blood-brain barrier leakage through Nrf2 upregulation in type 2 diabetes mice. Mol Neurobiol 56, 2314–2327.
Yuan, Y., Li, H., Pu, W., Chen, L., Guo, D., Jiang, H., He, B., Qin, S., Wang, K., Li, N., et al. (2022). Cancer metabolism and tumor microenvironment: fostering each other? Sci China Life Sci 65, 236–279.
Zhang, B.C., Luo, B.Y., Zou, J.J., Wu, P.Y., Jiang, J.L., Le, J.Q., Zhao, R. R., Chen, L., and Shao, J.W. (2020). Co-delivery of sorafenib and CRISPR/Cas9 based on targeted core-shell hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for synergistic HCC therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12, 57362–57312.
Zhang, C., Liu, Z., Bunker, E., Ramirez, A., Lee, S., Peng, Y., Tan, A.C., Eckhardt, S.G., Chapnick, D.A., and Liu, X. (2017). Sorafenib targets the mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes and ATP synthase to activate the PINK1-Parkin pathway and modulate cellular drug response. J Biol Chem 292, 15105–15120.
Zhang, S., Yu, D., Wang, M., Huang, T., Wu, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., Wang, W., Yin, J., Ren, G., et al. (2018). FGF21 attenuates pulmonary fibrogenesis through ameliorating oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother 103, 1516–1525.
Zheng, A., Chevalier, N., Calderoni, M., Dubuis, G., Dormond, O., Ziros, P. G., Sykiotis, G.P., and Widmann, C. (2019). CRISPR/Cas9 genome-wide screening identifies KEAP1 as a sorafenib, lenvatinib, and regorafenib sensitivity gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 10, 7058–7070.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81702981, 81827804, 81902367, 81772546 and LQ18H160010), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY20H160021 and Y15H160052), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020T130584 and 2020M671755), Health Innovation Talent Support Project of Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan (2021447581). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We thank Yong Cang for giving comments and suggestions to this study. We also thank the Genome Center of WuXi AppTec Inc. for the initial data analysis of the CRISPR screening. We thank J. Iacona, Ph.D., from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (https://www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Jiang, S., Shao, H. et al. CRISPR-Cas9-based genome-wide screening identified novel targets for treating sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma: a cross-talk between FGF21 and the NRF2 pathway. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 1998–2016 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2067-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2067-7