Abstract
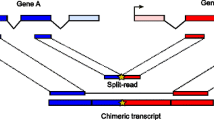
Fusion transcripts are commonly found in eukaryotes, and many aberrant fusions are associated with severe diseases, including cancer. One class of fusion transcripts is generated by joining separate transcripts through trans-splicing. However, the mechanism of trans-splicing in mammals remains largely elusive. Here we showed evidence to support an intuitive hypothesis that attributes trans-sphcing to the spatial proximity between premature transcripts. A novel trans-splicing detection tool (TSD) was developed to reliably identify intra-chromosomal trans-splicing events (iTSEs) from RNA-seq data. TSD can maintain a remarkable balance between sensitivity and accuracy, thus distinguishing it from most state-of-the-art tools. The accuracy of TSD was experimentally demonstrated by excluding potential false discovery from mosaic genome or template switching during PCR. We showed that iTSEs identified by TSD were frequently found between genomic regulatory elements, which are known to be more prone to interact with each other. Moreover, iTSE sites may be more physically adjacent to each other than random control in the tested human lymphoblastoid cell line according to Hi-C data. Our results suggest that trans-splicing and 3D genome architecture may be coupled in mammals and that our pipeline, TSD, may facilitate investigations of trans-splicing on a systematic and accurate level previously thought impossible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akers, N.K., Schadt, E.E., and Losic, B. (2018). STAR Chimeric Post for rapid detection of circular RNA and fusion transcripts. Bioinformatics 34, 2364–2370.
Allen, M.A., Hillier, L.D.W., Waterston, R.H., and Blumenthal, T. (2011). A global analysis of C. eleganstrans-splicing. Genome Res 21, 255–264.
Berlivet, S., Paquette, D., Dumouchel, A., Langlais, D., Dostie, J., and Kmita, M. (2013). Clustering of tissue-specific sub-TADs accompanies the regulation of HoxA genes in developing limbs. PLoS Genet 9, e 1004018.
Brockdorff, N., Ashworth, A., Kay, G.F., McCabe, V.M., Norris, D.P., Cooper, P.J., Swift, S., and Rastan, S. (1992). The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell 71, 515–526.
Brugiolo, M., Herzel, L., and Neugebauer, K.M. (2013). Counting on co-transcriptional splicing. FlooPrime Rep 5, 9.
Buck, M.J., Nobel, A.B., and Lieb, J.D. (2005). ChlPOTle: A user-friendly tool for the analysis of ChlP-chip data. Genome Biol 6, R97.
Carninci, P., Kasukawa, T., Katayama, S., Gough, J., Frith, M.C., Maeda, N., Oyama, R., Ravasi, T., Lenhard, B., Wells, C., et al. (2005). The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 309, 1559–1563.
Carrara, M., Beccuti, M., Cavallo, F., Donatelli, S., Lazzarato, F., Cordero, F., and Calogero, R.A. (2013). State of art fusion-finder algorithms are suitable to detect transcription-induced chimeras in normal tissues? BMC Bioinformatics 14, S2.
Cho, W.K., Jayanth, N., English, B.P., Inoue, T., Andrews, J.O., Conway, W., Grimm, J.B., Spille, J.H., Lavis, L.D., Lionnet, T., et al. RNA polymerase II cluster dynamics predict mRNA output in living cells. eLife, 2016, 5.
Chuang, T.J., Wu, C.S., Chen, C.Y., Hung, L.Y., Chiang, T.W., and Yang, M.Y (2016). NCLscan: Accurate identification of non-co-linear transcripts (fusion, trans-splicing and circular RNA) with a good balance between sensitivity and precision. Nucleic Acids Res 44, e29.
Chuang, T.J., Chen, Y.J., Chen, C.Y., Mai, T.L., Wang, Y.D., Yeh, C.S., Yang, M.Y., Hsiao, Y.T., Chang, T.H., Kuo, T.C., et al. (2018). Integrative transcriptome sequencing reveals extensive alternative trans-splicing and cis-backsplicing in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 3671–3691.
Conrad, R., Thomas, J., Spieth, J., and Blumenthal, T. (1991). Insertion of part of an intron into the 5’ untranslated region of a Caenorhabditis elegans gene converts it into a trans-spliced gene. Mol Cell Biol 11, 1921–1926.
Cremer, T., and Cremer, M. (2010). Chromosome territories. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2, a003889.
Davidson, N.M., Majewski, I.J., and Oshlack, A. (2015). JAFFA: High sensitivity transcriptome-focused fusion gene detection. Genome Med 7, 43.
Dekker, J., Rippe, K., Dekker, M., and Kleckner, N. (2002). Capturing chromosome conformation. Science 295, 1306–1311.
Dixon, J.R., Selvaraj, S., Yue, F., Kim, A., Li, Y., Shen, Y., Hu, M., Liu, J. S., and Ren, B. (2012). Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature 485, 376–380.
Djebali, S., Davis, C.A., Merkel, A., Dobin, A., Lassmann, T., Mortazavi, A., Tanzer, A., Lagarde, J., Lin, W., Schlesinger, F., et al. (2012). Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489, 101–108.
Duan, Z., Andronescu, M., Schutz, K., Mcllwain, S., Kim, Y.J., Lee, C., Shendure, J., Fields, S., Blau, C.A., and Noble, W.S. (2010). A three-dimensional model of the yeast genome. Nature 465, 363–367.
Dunham, I., Aldred, S.F., Collins, P.J., Davis, C.A., Doyle, F., Epstein, C. B., Frietze, S., Harrow, J., and Kaul, R. (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489, 57–74.
Edgren, H., Murumagi, A., Kangaspeska, S., Nicorici, D., Hongisto, V., Kleivi, K., Rye, I.H., Nyberg, S., Wolf, M., Borresen-Dale, A.L., et al. (2011). Identification of fusion genes in breast cancer by paired-end RNA-sequencing. Genome Biol 12, R6.
Engreitz, J.M., Agarwala, V., and Mirny, L.A. (2012). Three-dimensional genome architecture influences partner selection for chromosomal translocations in human disease. PLoS ONE 7, e44196.
Fullwood, M.J., Liu, M.H., Pan, Y.F., Liu, J., Xu, H., Mohamed, Y.B., Orlov, Y.L., Velkov, S., Ho, A., Mei, P.H., et al. (2009). An oestrogen-receptor-a-bound human chromatin interactome. Nature 462, 58–64.
Gao, T., He, B., Liu, S., Zhu, H., Tan, K., and Qian, J. (2016). Enhancer Atlas: A resource for enhancer annotation and analysis in 105 human cell/tissue types. Bioinformatics btw495.
Ge, H., Liu, K., Juan, T., Fang, F., Newman, M., and Hoeck, W. (2011). FusionMap: Detecting fusion genes from next-generation sequencing data at base-pair resolution. Bioinformatics 27, 1922–1928.
Gingeras, T.R. (2009). Implications of chimaeric non-co-linear transcripts. Nature 461, 206–211.
Haas, B., Dobin, A., Stransky, N., Li, B., Yang, X., Tickle, T., Bankapur, A., Ganote, C., Doak, T., Pochet, N., et al. (2017). STAR-Fusion: Fast and accurate fusion transcript detection from RNA-seq. BioRxiv.
Hannon, G.J., Maroney, P.A., and Nilsen, T.W. U small nuclear ribonu- cleoprotein requirements for nematode cis- and trans-splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem, 1991, 266: 22792–22795.
Harrow, J., Frankish, A., Gonzalez, J.M., Tapanari, E., Diekhans, M., Kokocinski, F., Aken, B.L., Barrell, D., Zadissa, A., Searle, S., et al. (2012). GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res 22, 1760–1774.
Hastings, K.E.M. (2005). SL trans-splicing: Easy come or easy go? Trends Genets 21, 240–247.
Hoffmann, S., Otto, C., Doose, G., Tanzer, A., Langenberger, D., Christ, S., Kunz, M., Holdt, L.M., Teupser, D., Hackermüller, J., et al. (2014). A multi-split mapping algorithm for circular RNA, splicing, trans-splicing and fusion detection. Genome Biol 15, R34.
Houseley, J., and Tollervey, D. (2010). Apparent non-canonical trans-splicing is generated by reverse transcriptase in vitro. PLoS ONE 5, el2271.
Horton, M., Bodenhausen, N., and Bergelson, J. (2010). MARTA: A suite of Java-based tools for assigning taxonomic status to DNA sequences. Bioinformatics 26, 568–569.
Huang, W., Li, L., Myers, J.R., and Marth, G.T. (2012). ART: A next-generation sequencing read simulator. Bioinformatics 28, 593–594.
Iyer, M.K., Chinnaiyan, A.M., and Maher, C.A. (2011). ChimeraScan: A tool for identifying chimeric transcription in sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27, 2903–2904.
Jia, W., Qiu, K., He, M., Song, P., Zhou, Q., Zhou, F., Yu, Y., Zhu, D., Nickerson, M.L., Wan, S., et al. (2013). SOAPfuse: An algorithm for identifying fusion transcripts from paired-end RNA-Seq data. Genome Biol 14, R12.
Jia, Y., Xie, Z., and Li, H. (2016). Intergenically spliced chimeric RNAs in cancer. Trends Cancer 2, 475–484.
Kangaspeska, S., Hultsch, S., Edgren, H., Nicorici, D., Murumagi, A., and Kallioniemi, O. (2012). Reanalysis of RNA-sequencing data reveals several additional fusion genes with multiple isoforms. PLoS ONE 7, e48745.
Kaufmann, S., Fuchs, C., Gonik, M., Khrameeva, E.E., Mironov, A.A., and Frishman, D. (2015). Inter-chromosomal contact networks provide insights into Mammalian chromatin organization. PLoS ONE 10, e0126125.
Kent, W.J. (2002). BLAT-The BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res 12, 656–664.
Kim, D., and Salzberg, S.L. (2011). TopHat-Fusion: An algorithm for discovery of novel fusion transcripts. Genome Biol 12, R72.
Kumar, S., Razzaq, S.K., Vo, A.D., Gautam, M., and Li, H. (2016a). Identifying fusion transcripts using next generation sequencing. WIREs RNA 7, 811–823.
Kumar, S., Vo, A.D., Qin, F., and Li, H. (2016b). Comparative assessment of methods for the fusion transcripts detection from RNA-Seq data. Sci Rep 6, 21597.
Lasda, E.L., and Blumenthal, T. (2011). Tram-splicing. WIREs RNA 2, 417–434.
Lei, Q., Li, C., Zuo, Z., Huang, C., Cheng, H., and Zhou, R. (2016). Evolutionary insights into RNA trans-splicing in vertebrates. Genome Biol Evol 8, 562–577.
Li, H., Wang, J., Mor, G., and Sklar, J. (2008). A neoplastic gene fusion mimics trans-splicing of RNAs in normal human cells. Science 321, 1357–1361.
Li, W., Freudenberg, J., and Miramontes, P. (2014). Diminishing return for increased mappability with longer sequencing reads: Implications of the k-mer distributions in the human genome. BMC Bioinformatics 15, 2.
Lieberman-Aiden, E., van Berkum, N.L., Williams, L., Imakaev, M., Ragoczy, T., Telling, A., Amit, I., Lajoie, B.R., Sabo, P.J., Dorschner, M.O, et al. (2009). Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 326, 289–293.
Liu, S., Tsai, W.H., Ding, Y., Chen, R., Fang, Z., Huo, Z., Kim, S.H., Ma, T., Chang, T.Y., Priedigkeit, N.M., et al. (2016). Comprehensive evaluation of fusion transcript detection algorithms and a meta-caller to combine top performing methods in paired-end RNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 44, e47.
Mao, Y.S., Zhang, B., and Spector, D.L. (2011). Biogenesis and function of nuclear bodies. Trends Genets 27, 295–306.
McCord, R.P, and Balajee, A. (2018). 3D genome organization influences the chromosome translocation pattern. In: Zhang, Y, ed. Chromosome Translocation. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Singapore: Springer, 113–133.
McManus, C.J., Duff, M.O, Eipper-Mains, J., and Graveley, B.R. (2010). Global analysis of trans-splicing in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 12975–12979.
McPherson, A., Hormozdiari, F., Zayed, A., Giuliany, R., Ha, G., Sun, M. G.F., Griffith, M., Heravi Moussavi, A., Senz, J., Melnyk, N., et al. (2011). deFuse: An algorithm for gene fusion discovery in tumor RNA-Seq data. PLoS Comput Biol 7, el001138.
Mifsud, B., Tavares-Cadete, F., Young, A.N., Sugar, R., Schoenfelder, S., Ferreira, L., Wingett, S.W., Andrews, S., Grey, W., Ewels, P.A., et al. (2015). Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C. Nat Genet 47, 598–606.
Mignone, F., Gissi, C., Liuni, S., and Pesole, G. (2002). Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol 3, reviews0004.1.
Murtagh, F., and Legendre, P. (2014). Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement ward’s criterion? J Classif 31, 274–295.
Nicorici, D., Šatalan, M., Edgren, H., Kangaspeska, S., Murumagi, A., Kallioniemi, O., Virtanen, S., Kilkku, O (2014). FusionCatcher-A tool for finding somatic fusion genes in paired-end RNA-sequencing data. bioRxiv.
Nowotny, J., Wells, A., Oluwadare, O., Xu, L., Cao, R., Trieu, T., He, C., and Cheng, J. (2016). GMOL: An interactive tool for 3D genome structure visualization. Sci Rep 6, 20802.
Peng, Z., Yuan, C., Zellmer, L., Liu, S., Xu, N., and Liao, D.J. (2015). Hypothesis: Artifacts, including spurious chimeric RNAs with a short homologous sequence, caused by consecutive reverse transcriptions and endogenous random primers. J Cancer 6, 555–567.
Philippe, N., Salson, M., Commes, T., and Rivals, E. (2013). CRAC: An integrated approach to the analysis of RNA-seq reads. Genome Biol 14, R30.
Piazza, R., Pirola, A., Spinelli, R., Valletta, S., Redaelli, S., Magistroni, V., and Gambacorti-Passerini, C. (2012). FusionAnalyser: A new graphical, event-driven tool for fusion rearrangements discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 40, el23.
Rao, S.S.P, Huntley, M.H., Durand, N.C, Stamenova, E.K., Bochkov, I.D., Robinson, J.T., Sanborn, A.L., Machol, I., Omer, A.D., Lander, E.S., et al. (2014). A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 159, 1665–1680.
Rickman, D.S., Pflueger, D., Moss, B., VanDoren, V.E., Chen, C.X., de la Taille, A., Kuefer, R., Tewari, A.K., Setlur, S.R., Demichelis, F., et al. (2009). SLC45A3-ELK4 is a novel and frequent erythroblast transformation-specific fusion transcript in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 69, 2734–2738.
Rodriguez-Martin, B., Palumbo, E., Marco-Sola, S., Griebel, T, Ribeca, P., Alonso, G., Rastrojo, A., Aguado, B., Guigo, R., and Djebali, S. (2017). ChimPipe: Accurate detection of fusion genes and transcription-induced chimeras from RNA-seq data. BMC Genomics 18, 7.
Roix, J.J., McQueen, P.G., Munson, P.J., Parada, L.A., and Misteli, T. (2003). Spatial proximity of translocation-prone gene loci in human lymphomas. Nat Genet 34, 287–291.
Sexton, T., Yaffe, E., Kenigsberg, E., Bantignies, F., Leblanc, B., Hoichman, M., Parrinello, H., Tanay, A., and Cavalli, G. (2012). Three-dimensional folding and functional organization principles of the Drosophila genome. Cell 148, 458–472.
Sutherland, H., and Bickmore, W.A. (2009). Transcription factories: Gene expression in unions? Nat Rev Genet 10, 457–466.
Sutton, R.E., and Boothroyd, J.C. (1986). Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell 47, 527–535.
Tang, Z., Luo, O.J., Li, X., Zheng, M., Zhu, J.J., Szalaj, P., Trzaskoma, P., Magalska, A., Wlodarczyk, J., Ruszczycki, B., et al. (2015). CTCF- mediated human 3D genome architecture reveals chromatin topology for transcription. Cell 163, 1611–1627.
Torres-Garcia, W., Zheng, S., Sivachenko, A., Vegesna, R., Wang, Q., Yao, R., Berger, M.F., Weinstein, J.N., Getz, G., and Verhaak, R.G.W. (2014). PRADA: Pipeline for RNA sequencing data analysis. Bioinformatics 30, 2224–2226.
Trieu, T, Oluwadare, O., and Cheng, J. (2019). Hierarchical reconstruction of high-resolution 3D models of large chromosomes. Sci Rep 9, 4971.
Wahl, M.C, Will, C.L., and Luhrmann, R. (2009). The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 136, 701–718.
Wang, K., Singh, D., Zeng, Z., Coleman, S.J., Huang, Y, Savich, G.L., He, X., Mieczkowski, P., Grimm, S.A., Perou, CM., et al. (2010). MapSplice: Accurate mapping of RNA-seq reads for splice junction discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 38, el78.
Wu, C.S., Yu, C.Y., Chuang, C.Y., Hsiao, M., Kao, C.F., Kuo, H.C, and Chuang, T.J. (2014). Integrative transcriptome sequencing identifies trans-splicing events with important roles in human embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Genome Res 24, 25–36.
Xie, B., Yang, W., Ouyang, Y, Chen, L., Jiang, H, Liao, Y, and Liao, D.J. (2016). Two RNAs or DNAs may artificially fuse together at a short homologous sequence (SHS) during reverse transcription or polymerase chain reactions, and thus reporting an SHS-containing chimeric RNA requires extra caution. PLoS ONE 11, e0154855.
Yan, Z., Huang, N, Wu, W., Chen, W., Jiang, Y, Chen, J., Huang, X., Wen, X., Xu, J., Jin, Q., et al. (2019). Genome-wide colocalization of RNA-DNA interactions and fusion RNA pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 3328–3337.
Yates, B., Braschi, B., Gray, K.A., Seal, R.L., Tweedie, S., and Bruford, E. A. (2017). Genenames.org: The HGNC and VGNC resources in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res 45, D619–D625.
Zhang, H, Li, E, Jia, Y, Xu, B., Zhang, Y, Li, X., and Zhang, Z. (2017). Characteristic arrangement of nucleosomes is predictive of chromatin interactions at kilobase resolution. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 12739–12751.
Zhang, Y, McCord, R.P, Ho, Y.J., Lajoie, B.R., Hildebrand, D.G., Simon, A.C., Becker, M.S., Alt, F.W., and Dekker, J. (2012). Spatial organization of the mouse genome and its role in recurrent chromosomal translocations. Cell 148, 908–921.
Zhang, Y, Wong, C.H., Birnbaum, R.Y, Li, G., Favaro, R., Ngan, C.Y., Lim, J., Tai, E., Poh, H.M., Wong, E., et al. (2013). Chromatin connectivity maps reveal dynamic promoter-enhancer long-range associations. Nature 504, 306–310.
Zhao, Z.W., Roy, R., Gebhardt, J.C.M., Suter, D.M., Chapman, A.R., and Xie, X.S. (2014). Spatial organization of RNA polymerase II inside a mammalian cell nucleus revealed by reflected light-sheet superresolution microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 681–686.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671342, 31871331, 91540114, and 31401112). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Thanks to David Martin for English language editorial services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Li, X. et al. Evidence of constraint in the 3D genome for trans-splicing in human cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 63, 1380–1393 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1609-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1609-6