Abstract
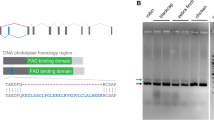
Magnetoreception is a hallmark ability of animals for orientation and migration via sensing and utilizing geomagnetic fields. Magnetoreceptor (MagR) and cryptochromes (Cry) have recently been identified as the basis for magnetoreception in Drosophila. However, it has remained unknown whether MagR and Cry have conserved roles in diverse animals. Here we report the identification and expression of magr and cry genes in the fish medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cloning and sequencing identified a single magr gene, four cry genes and one cry-like gene in medaka. By sequence alignment, chromosomal synteny and gene structure analysis, medaka cry2 and magr were found to be the orthologs of human Cry2 and Magr, with cry1aa and cry1ab being coorthologs of human Cry1. Therefore, magr and cry2 have remained as single copy genes, whereas cry1 has undergone two rounds of gene duplication in medaka. Interestingly, magr and cry genes were detected in various stages throughout embryogenesis and displayed ubiquitous expression in adult organs rather than specific or preferential expression in neural organs such as brain and eye. Importantly, magr knockdown by morpholino did not produce visible abnormality in developing embryos, pointing to the possibility of producing viable magr knockouts in medaka as a vertebrate model for magnet biology.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Aizawa, K., Shimada, A., Naruse, K., Mitani, H., and Shima, A. (2003). The medaka midblastula transition as revealed by the expression of the paternal genome. Gene Expr Patterns 3, 43–47.
Amores, A., Force, A., Yan, Y.L., Joly, L., Amemiya, C., Fritz, A., Ho, R.K., Langeland, J., Prince, V., Wang, Y.L., Westerfield, M., Ekker, M., and Postlethwait, J.H. (1998). Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 282, 1711–1714.
Bazalova, O., Kvicalova, M., Valkova, T., Slaby, P., Bartos, P., Netusil, R., Tomanova, K., Braeunig, P., Lee, H.J., Sauman, I., Damulewicz, M., Provaznik, J., Pokorny, R., Dolezel, D., and Vacha, M. (2016). Cryptochrome 2 mediates directional magnetoreception in cockroaches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 1660–1665.
Cai, J., and Plenio, M.B. (2013). Chemical compass model for avian magnetoreception as a quantum coherent device. Phys Rev Lett 111, 2305031304.4143.
Cashmore, A.R., Jarillo, J.A., Wu, Y.J., and Liu, D. (1999). Cryptochromes: blue light receptors for plants and animals. Science 284, 760–765.
Ceriani, M.F., Darlington, T.K., Staknis, D., Más, P., Petti, A.A., Weitz, C.J., and Kay, S.A. (1999). Light-dependent sequestration of timeless by cryptochrome. Science 285, 553–556.
Chaves, I., Pokorny, R., Byrdin, M., Hoang, N., Ritz, T., Brettel, K., Essen, L.O., van der Horst, G.T.J., Batschauer, A., and Ahmad, M. (2011). The cryptochromes: blue light photoreceptors in plants and animals. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62, 335–364.
Etoc, F., Lisse, D., Bellaiche, Y., Piehler, J., Coppey, M., and Dahan, M. (2013). Subcellular control of Rac-GTPase signalling by magnetogenetic manipulation inside living cells. Nat Nanotech 8, 193–198.
Etoc, F., Vicario, C., Lisse, D., Siaugue, J.M., Piehler, J., Coppey, M., and Dahan, M. (2015). Magnetogenetic control of protein gradients inside living cells with high spatial and temporal resolution. Nano Lett 15, 3487–3494.
Foley, L.E., Gegear, R.J., and Reppert, S.M. (2011). Human cryptochrome exhibits light-dependent magnetosensitivity. Nat Commun 2, 356.
Gegear, R.J., Casselman, A., Waddell, S., and Reppert, S.M. (2008). Cryptochrome mediates light-dependent magnetosensitivity in Drosophila. Nature 454, 1014–1018.
Gegear, R.J., Foley, L.E., Casselman, A., and Reppert, S.M. (2010). Animal cryptochromes mediate magnetoreception by an unconventional photochemical mechanism. Nature 463, 804–807.
Griffin, E.A., Staknis, D. and Weitz, C.J. (1999). Light-independent role of CRY1 and CRY2 in the mammalian circadian clock. Science 286, 768–771.
Haug, M.F., Gesemann, M., Lazovic, V., and Neuhauss, S.C.F. (2015). Eumetazoan cryptochrome phylogeny and evolution. Genome Biol Evol 7, 601–619.
Häusser, M. (2014). Optogenetics: the age of light. Nat Meth 11, 1012–1014.
Heasman, J. (2002). Morpholino oligos: making sense of antisense? Dev Biol 243, 209–214.
Hong, N., Li, Z. and Hong, Y. (2011). Fish stem cell cultures. Int J Biol Sci 7, 392–402.
Hong, Y., Liu, T., Zhao, H., Xu, H., Wang, W., Liu, R., Chen, T., Deng, J., and Gui, J. (2004). Establishment of a normal medakafish spermatogonial cell line capable of sperm production in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 8011–8016.
Iwamatsu, T. (2004). Stages of normal development in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Mechan Dev 121, 605–618.
Johnsen, S., and Lohmann, K.J. (2008). Magnetoreception in animals feature article. Physics Today 61, 29.
Kobayashi, Y., Ishikawa, T., Hirayama, J., Daiyasu, H., Kanai, S., Toh, H., Fukuda, I., Tsujimura, T., Terada, N., Kamei, Y., Yuba, S., Iwai, S., and Todo, T. (2000). Molecular analysis of zebrafish photolyase/cryptochrome family: two types of cryptochromes present in zebrafish. Genes Cells 5, 725–738.
Kringelbach, M.L., Jenkinson, N., Owen, S.L.F., and Aziz, T.Z. (2007). Translational principles of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 8, 623–635.
Kume, K., Zylka, M.J., Sriram, S., Shearman, L.P., Weaver, D.R., Jin, X., Maywood, E.S., Hastings, M.H., and Reppert, S.M. (1999). mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop. Cell 98, 193–205.
Liedvogel, M., and Mouritsen, H. (2010). Cryptochromes—a potential magnetoreceptor: what do we know and what do we want to know? J R Soc Interface 7, S147–S162.
Liu, C., Hu, J., Qu, C., Wang, L., Huang, G., Niu, P., Zhong, Z., Hong, F., Wang, G., Postlethwait, J.H., and Wang, H. (2015). Molecular evolution and functional divergence of zebrafish (Danio rerio) cryptochrome genes. Sci Rep 5, 8113.
Long, X., Ye, J., Zhao, D., and Zhang, S.J. (2015). Magnetogenetics: remote non-invasive magnetic activation of neuronal activity with a magnetoreceptor. Sci Bull 60, 2107–2119.
Möller, A., Sagasser, S., Wiltschko, W., and Schierwater, B. (2004). Retinal cryptochrome in a migratory passerine bird: a possible transducer for the avian magnetic compass. Naturwissenschaften 91, 585–588.
Maeda, K., Henbest, K.B., Cintolesi, F., Kuprov, I., Rodgers, C.T., Liddell, P.A., Gust, D., Timmel, C.R., and Hore, P.J. (2008). Chemical compass model of avian magnetoreception. Nature 453, 387–390.
Mandilaras, K., and Missirlis, F. (2012). Genes for iron metabolism influence circadian rhythms in Drosophila melanogaster. Metallomics 4, 928–936.
Mohseni, M., Omar, Y., Engel, G.S. and Plenio, M.B. (2014). Quantum Effects in Biology. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Nilsson, R., Schultz, I.J., Pierce, E.L., Soltis, K.A., Naranuntarat, A., Ward, D.M., Baughman, J.M., Paradkar, P.N., Kingsley, P.D., Culotta, V.C., Kaplan, J., Palis, J., Paw, B.H., and Mootha, V.K. (2009). Discovery of genes essential for heme biosynthesis through large-scale gene expression analysis. Cell Metab 10, 119–130.
Oliveri, P., Fortunato, A.E., Petrone, L., Ishikawa-Fujiwara, T., Kobayashi, Y., Todo, T., Antonova, O., Arboleda, E., Zantke, J., Tessmar-Raible, K., and Falciatore, A. (2014). The cryptochrome/photolyase family in aquatic organisms. Mar Genomics 14, 23–37.
Phillips, J.B., Muheim, R., and Jorge, P.E. (2010). A behavioral perspective on the biophysics of the light-dependent magnetic compass: a link between directional and spatial perception? J Exp Biol 213, 3247–3255.
Qin, S., Yin, H., Yang, C., Dou, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, P., Yu, H., Huang, Y., Feng, J., Hao, J., Hao, J., Deng, L., Yan, X., Dong, X., Zhao, Z., Jiang, T., Wang, H.W., Luo, S.J., and Xie, C. (2016). A magnetic protein biocompass. Nat Mater 15, 217–226.
Ritz, T., Adem, S., and Schulten, K. (2000). A model for photoreceptorbased magnetoreception in birds. Biophysical J 78, 707–718.
Schulten, K., and Weller, A. (1978). Exploring fast electron transfer processes by magnetic fields.
Biophys J 24, 295–305.
Schwartz, C.J., Giel, J.L., Patschkowski, T., Luther, C., Ruzicka, F.J., Beinert, H., and Kiley, P.J. (2001). IscR, an Fe-S cluster-containing transcription factor, represses expression of Escherichia coli genes encoding Fe-S cluster assembly proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 14895–14900.
Soderlund, C., Bomhoff, M., and Nelson, W.M. (2011). SyMAP v3.4: a turnkey synteny system with application to plant genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 39, e68–e68.
Stanley, S.A., Kelly, L., Latcha, K.N., Schmidt, S.F., Yu, X., Nectow, A.R., Sauer, J., Dyke, J.P., Dordick, J.S., and Friedman, J.M. (2016). Bidirectional electromagnetic control of the hypothalamus regulates feeding and metabolism. Nature 531, 647–650.
Stanley, S.A., Sauer, J., Kane, R.S., Dordick, J.S., and Friedman, J.M. (2015). Remote regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice using genetically encoded nanoparticles. Nat Med 21, 92–98.
Thoss, F., Bartsch, B., Fritzsche, B., Tellschaft, D., and Thoss, M. (2000). The magnetic field sensitivity of the human visual system shows resonance and compass characteristic. J Comp Physiol A 186, 1007–1010.
Thoss, F., Bartsch, B., Tellschaft, D., and Thoss, M. (2002). The light sensitivity of the human visual system depends on the direction of view. J Comp Physiol A 188, 235–237.
Todo, T. (1999). Functional diversity of the DNA photolyase/blue light receptor family. Mutation Res/DNA Repair 434, 89–97.
Todo, T., Ryo, H., Yamamoto, K., Toh, H., Inui, T., Ayaki, H., Nomura, T., and Ikenaga, M. (1996). Similarity among the Drosophila (6-4)photolyase, a human photolyase homolog, and the DNA photolyase-bluelight photoreceptor family. Science 272, 109–112.
Todo, T., Takemori, H., Ryo, H., Ihara, M., Matsunaga, T., Nikaido, O., Sato, K., and Nomura, T. (1993). A new photoreactivating enzyme that specifically repairs ultraviolet light-induced (6-4)photoproducts. Nature 361, 371–374.
Vinella, D., Brochier-Armanet, C., Loiseau, L., Talla, E., and Barras, F. (2009). Iron-sulfur (Fe/S) protein biogenesis: phylogenomic and genetic studies of A-Type carriers. PLoS Genet 5, e1000497.
Wheeler, M.A., Smith, C.J., Ottolini, M., Barker, B.S., Purohit, A.M., Grippo, R.M., Gaykema, R.P., Spano, A.J., Beenhakker, M.P., Kucenas, S., Patel, M.K., Deppmann, C.D., and Güler, A.D. (2016). Genetically targeted magnetic control of the nervous system. Nat Neurosci 19, 756–761.
Wichmann, T., and Delong, M.R. (2006). Deep brain stimulation for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuron 52, 197–204.
Wiltschko, W., and Wiltschko, R. (1988). Magnetic orientation in birds. In: R.F. Johnston, ed. Current Ornithology. (Berlin: Springer), pp. 67–121.
Wiltschko, W., and Wiltschko, R. (2005). Magnetic orientation and magnetoreception in birds and other animals. J Comp Physiol A 191, 675–693.
Yuan, Q., Metterville, D., Briscoe, A.D., and Reppert, S.M. (2007). Insect cryptochromes: gene duplication and loss define diverse ways to construct insect circadian clocks. Mol Biol Evol 24, 948–955.
Zhang, F., Vierock, J., Yizhar, O., Fenno, L.E., Tsunoda, S., Kianianmomeni, A., Prigge, M., Berndt, A., Cushman, J., Polle, J., Magnuson, J., Hegemann, P., and Deisseroth, K. (2011). The microbial opsin family of optogenetic tools. Cell 147, 1446–1457.
Zheng, L., Cash, V.L., Flint, D.H. and Dean, D.R. (1998). Assembly of iron-sulfur clusters. Identification of an iscSUA-hscBA-fdx gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem 273, 13264–13272.
Zhou, Z., Peng, X., Chen, J., Wu, X., Wang, Y., and Hong, Y. (2016). Identification of zebrafish magnetoreceptor and cryptochrome homologs. Sci China Life Sci doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0195-x.
Zhu, H., Sauman, I., Yuan, Q., Casselman, A., Emery-Le, M., Emery, P., and Reppert, S.M. (2008). Cryptochromes define a novel circadian clock mechanism in monarch butterflies that may underlie sun compass navigation. PLoS Biol 6, e4.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Singapore (NRF-CRP7-2010-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published with open access at link.springer.com
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chen, J., Zhu, F. et al. Identification of medaka magnetoreceptor and cryptochromes. Sci. China Life Sci. 60, 271–278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0266-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0266-5