Abstract
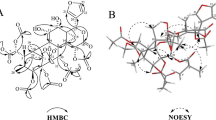
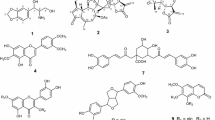
A bioassay-guided fractionation of the roots and stems of Litsea cubeba led to the isolation of 14 constituents, including three new compounds, cubebanone (1), N-cis-3,4-methylenedioxycinnamoyl-3-methoxytyramine (2), and 9,9′-O-di-(E)-feruloyl-(+)-secoisolariciresinol (3), together with 11 known ones (4–14). Compounds 1, 4, and 8–11 showed obvious in vitro anti-inflammatory activities against NO production in LPS-induced murine microglial (BV-2) cell line and RAW 264.7 macrophages. A cytotoxic evaluation showed that 2, 3, and 5–8 exhibited considerable inhibition against the growth of hepatocyte carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. These findings are evidence, to some extent, for the traditional medicinal application of L. cubeba, especially as folk medicine in the treatment of inflammation-related diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang SY, Guo Q, Gao XL, Guo ZQ, Zhao YF, Chai XY, Tu PF (2014) A phytochemical and pharmacological advance on medicinal plant Litsea cubeba (Lauraceae). Chin J Chin Mater Med 39:769–776
Lin B, Zhang H, Zhao XX, Rahman K, Wang Y, Ma XQ, Zheng CJ, Zhang QY, Han T, Qin LP (2013) Inhibitory effects of the root extract of Litsea cubeba (Lour.) per. on adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 147:327–334
Zhang SY, Guo Q, Cao Y, Zhang YF, Gao XL, Tu PF, Chai XY (2014) Alkaloids from the roots and stems of Litsea cubeba. Chin J Chin Mater Med 39:51–55
Chen CY, Chang FR, Yen HF, Wu YC (1998) Amides from stems of Annona cherimola. Phytochemistry 49:1443–1447
Jiang M, Lin S, Guo QL, Jiang ZB, Wang SJ, Yang YC, Lin PC (2013) Chemical constituents from Litsea greenmaniana. Chin J Chin Mater Med 38:1004–1007
Fuchino H, Satoh T, Tanaka N (1995) Chemical evaluation of Betula species in Japan. I. Constituents of Betula ermanii. Chem Pharm Bull 43:1937–1942
Xie LH, Akao T, Hamasaki K, Deyama T, Hattori M (2003) Biotransformation of pinoresinol diglucoside to mammalian lignans by human intestinal microflora, and isolation of Enterococcus faecalis strain PDG-1 responsible for the transformation of (+)-pinoresinol to (+)-lariciresinol. Chem Pharm Bull 51:508–515
Kuroda M, Sakurai K, Mimaki Y (2011) Chemical constituents of the stems and twigs of Lindera umbellata. J Nat Med 65:198–201
Chen TH, Huang YH, Lin JJ, Liau BC, Wang SY, Wu YC, Jong TT (2010) Cytotoxic lignan esters from Cinnamomum osmophloeum. Planta Med 76:613–619
Lee TH, Kuo YC, Wang GJ, Kuo YH, Chang CI, Lu CK, Lee CK (2002) Five new phenolics from the roots of Ficus beecheyana. J Nat Prod 65:1497–1500
Jang DS, Park EJ, Kang YH, Vigo JS, Graham JG, Cabieses F, Fong HHS, Pezzuto JM, Kinghorn AD (2004) Phenolic compounds obtained from stems of Couepia ulei with the potential to induce quinone reductase. Arch Pharm Res 27:169–172
Youssef D, Frahm AW (1995) Constituents of the Egyptian Centaurea scoparia; III. Phenolic constituents of the aerial parts. Planta Med 61:570–573
Ma GX, Wu HF, Yuan JQ, Wu LZ, Zheng QX, Sun ZC, Fan XR, Wei H, Yang JS, Xu XD (2013) Phenylpropanoid constituents from the seeds of Lithocarpus pachylepis. Phytochem Lett 6:152–155
Wang M, Liang JY, Liu XT, Qiu W (2006) Chemical constituents from Serissa serissoides. Chin J Nat Med 4:198–201
Chen ZJ, Bi HP, Fang CJ, Bao CY (2013) Chemical constituents from the branch of Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers. Chem Ind Forest Prod 33:133–136
Tanaka H, Yatsuhashi S, Yasuda T, Sato M, Sakai E, Xiao C, Murata H, Murata J (2009) A new amide from the leaves and twigs of Litsea auriculata. J Nat Med 63:331–334
Williamson EM (2001) Synergy and other interactions in phytomedicines. Phytomedicine 8:401–409
Wagner H, Ulrich-Merzenich G (2009) Synergy research: approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 16:97–110
Chen D, Xu Z, Chai X, Zeng K, Jia Y, Bi D, Ma Z, Tu P (2012) Nine 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone derivative from the resinous wood of Aquilaria sinensis and their inhibition of LPS-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. Eur J Org Chem 27:5389–5397
Li N, Zhang JY, Zeng KW, Zhang L, Che YY, Tu PF (2012) Anti-inflammatory homoisoflavonoids from the tuberous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus. Fitoterapia 83:1042–1045
Chen HY, Ye XL, Cui XL, He K, Jin YN, Chen Z, Li XG (2012) Cytotoxicity and antihyperglycemic effect of minor constituents from Rhizoma Coptis in HepG2 cells. Fitoterapia 83:67–73
Acknowledgments
This paper was financially support by the China Pharmacopeia Commission. The authors thank Dr. Yuan Zhang (School of Chinese Materia Medica, BUCM) for her authentication of the material medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Zeng, K., Gao, X. et al. Chemical constituents with NO production inhibitory and cytotoxic activities from Litsea cubeba . J Nat Med 69, 94–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0872-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0872-6