Abstract
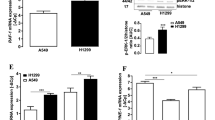
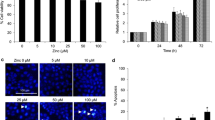
To determine that p38 MAPK activation contributes to the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells caused by cadmium (Cd). A549 lung cancer cell migration and invasion were assessed using a transwell plate system, and the role of p38 was determined by knocking down p38 activity with two different inhibitors of p38. The activity of p38 was measured by western blot analysis using phospho-specific p38 antibodies and normalized to blots using antibodies directed to total p38 proteins. Snail transcripts were measured using qRT-PCR. The inhibition of p38 blocked Cd-induced migration and invasion, which correlated with an increased activation of p38 as a function of dose and time. Furthermore, Cd-induced activation of p38 MAPK controlled the increase of snail mRNA expression. The p38 MAPK/snail signaling axis was involved in Cd-induced lung cancer cell migration and invasion.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated or analyzed during the present study are included in this article.
References
Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Alhadlaq HA (2022) Combined effect of single-walled carbon nanotubes and cadmium on human lung cancer cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:87844–87857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21933-0
Anwar T, Arellano-Garcia C, Ropa J, Chen YC, Kim HS, Yoon E, Grigsby S, Basrur V, Nesvizhskii AI, Muntean A, Gonzalez ME, Kidwell KM, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, Kleer CG (2018) p38-mediated phosphorylation at T367 induces EZH2 cytoplasmic localization to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nat Commun 9:2801. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05078-8
Aramjoo H, Arab-Zozani M, Feyzi A, Naghizadeh A, Aschner M, Naimabadi A, Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S (2022) The association between environmental cadmium exposure, blood pressure, and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:35682–35706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17777-9
Bi SS, Talukder M, Sun XT, Lv MW, Ge J, Zhang C, Li JL (2023) Cerebellar injury induced by cadmium via disrupting the heat-shock response. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:22550–22559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23771-6
Brey C, Consonni D, Sarquis LMM, Miranda FMD (2022) Lung cancer and occupational exposure: hospital-based case-control study. Rev Gaucha Enferm 43:e20210043. https://doi.org/10.1590/1983-1447.2022.20210043.en
Castro MV, Barbero GA, Máscolo P, Villanueva MB, Nsengimana J, Newton-Bishop J, Illescas E, Quezada MJ, Lopez-Bergami P (2023) ROR2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by hyperactivating ERK in melanoma. J Cell Commun Signal 17:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00683-1
Chen F, Aye L, Yu L, Liu L, Liu Y, Lin Y, Gao D, Gao Q, Zhang S (2023) SSH1 promotes progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via p38 MAPK-CXCL8 axis. Carcinogenesis 44:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgad009
Chiou JT, Wu YY, Lee YC, Chang LS (2023a) BCL2L1 inhibitor A-1331852 inhibits MCL1 transcription and triggers apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Biochem Pharmacol 215:115738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115738
Chiou JT, Hsu CC, Hong YC, Lee YC, Chang LS (2023b) Cytarabine-induced destabilization of MCL1 mRNA and protein triggers apoptosis in leukemia cells. Biochem Pharmacol 211:115494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115494
Chiou J T, Wang L J, Lee Y C, Chang L S (2021) Naja atra cardiotoxin 1 induces the FasL/Fas death pathway in human leukemia cells. Cells 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082073
Chiu WC, Fang PT, Lee YC, Wang YY, Su YH, Hu SC, Chen YK, Tsui YT, Kao YH, Huang MY, Yuan SF (2020) DNA repair protein Rad51 induces tumor growth and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via a p38/Akt-dependent pathway. Ann Surg Oncol 27:2090–2101. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-08043-x
Cui ZG, Ahmed K, Zaidi SF, Muhammad JS (2021) Ins and outs of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis: mechanism and prevention. Cancer Treat Res Commun 27:100372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100372
Dong ZY, Zhou YR, Wang LX (2018) HDAC1 is indirectly involved in the epigenetic regulation of p38 MAPK that drive the lung cancer progression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:5980–5986. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201809_15932
Feki-Tounsi M, Hamza-Chaffai A (2014) Cadmium as a possible cause of bladder cancer: a review of accumulated evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:10561–10573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2970-0
Fujiki K, Inamura H, Miyayama T, Matsuoka M (2017) Involvement of Notch1 signaling in malignant progression of A549 cells subjected to prolonged cadmium exposure. J Biol Chem 292:7942–7953. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.759134
Furuta M, Kikuchi H, Shoji T, Takashima Y, Kikuchi E, Kikuchi J, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, Sakakibara-Konishi J (2019) DLL3 regulates the migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer by modulating Snail. Cancer Sci 110:1599–1608. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13997
Gan P, Gao Z, Zhao X, Qi G (2016) Surfactin inducing mitochondria-dependent ROS to activate MAPKs, NF-κB and inflammasomes in macrophages for adjuvant activity. Sci Rep 6:39303. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39303
García-Esquinas E, Pollan M, Tellez-Plaza M, Francesconi KA, Goessler W, Guallar E, Umans JG, Yeh J, Best LG, Navas-Acien A (2014) Cadmium exposure and cancer mortality in a prospective cohort: the strong heart study. Environ Health Perspect 122:363–370. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1306587
Genchi G, Sinicropi M S, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113782
Huang Q, Lan F, Wang X, Yu Y, Ouyang X, Zheng F, Han J, Lin Y, Xie Y, Xie F, Liu W, Yang X, Wang H, Dong L, Wang L, Tan J (2014) IL-1β-induced activation of p38 promotes metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma via upregulation of AP-1/c-fos, MMP2 and MMP9. Mol Cancer 13:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-18
Idrees N, Tabassum B, Abd Allah EF, Hashem A, Sarah R, Hashim M (2018) Groundwater contamination with cadmium concentrations in some West U.P. Regions. India Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1365–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.07.005
Jallal B, Mossie K, Vasiloudis G, Knyazev P, Zachwieja J, Clairvoyant F, Schilling J, Ullrich A (1997) The receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase DEP-1 is constitutively associated with a 64-kDa protein serine/threonine kinase. J Biol Chem 272:12158–12163. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.18.12158
Jiang A, Gong L, Ding H, Wang M (2021a) Cancer mortality and long-term environmental exposure of cadmium in contaminated community based on a third retrospective cause of death investigation of residents living in the Guangdong Province from 2004 to 2005. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:4504–4515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02599-0
Jiang Y, Zhan H, Zhang Y, Yang J, Liu M, Xu C, Fan X, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Shi X, Ramesh R, Li M (2021b) ZIP4 promotes non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by activating snail-N-cadherin signaling axis. Cancer Lett 521:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.08.025
Kato S, Yokoyama S, Hayakawa Y, Li L, Iwakami Y, Sakurai H, Saiki I (2016) P38 pathway as a key downstream signal of connective tissue growth factor to regulate metastatic potential in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci 107:1416–1421. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13009
Kim TH, Kim JH, Le Kim MD, Suh WD, Kim JE, Yeon HJ, Park YS, Kim SH, Oh YH, Jo GH (2020) Exposure assessment and safe intake guidelines for heavy metals in consumed fishery products in the Republic of Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:33042–33051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09624-0
Kondoh K, Sunadome K, Nishida E (2007) Notch signaling suppresses p38 MAPK activity via induction of MKP-1 in myogenesis. J Biol Chem 282:3058–3065. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607630200
Krewski D, Rice JM, Bird M, Milton B, Collins B, Lajoie P, Billard M, Grosse Y, Cogliano VJ, Caldwell JC, Rusyn II, Portier CJ, Melnick RL, Baan RA, Little J, Zielinski JM (2019) Concordance between sites of tumor development in humans and in experimental animals for 111 agents that are carcinogenic to humans. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 22:203–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2019.1642586
Kumar S, Jiang MS, Adams JL, Lee JC (1999) Pyridinylimidazole compound SB 203580 inhibits the activity but not the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:825–831. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.1454
Lee NW, Wang HY, Du CL, Yuan TH, Chen CY, Yu CJ, Chan CC (2022) Air-polluted environmental heavy metal exposure increase lung cancer incidence and mortality: a population-based longitudinal cohort study. Sci Total Environ 810:152186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152186
Lee SW, Kim B, Seong JB, Park YH, Lee HJ, Lee DS (2023) ATF6 is a critical regulator of cadmium-mediated apoptosis in spermatocytes. Toxicol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfad055
Li P, Lin Z, Liu Q, Chen S, Gao X, Guo W, Gong F, Wei J, Lin H (2021a) Enhancer RNA SLIT2 inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer through regulating P38 MAPK/c-Fos signaling pathway. Front Oncol 11:743840. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.743840
Li X, Cao X, Zhao H, Guo M, Fang X, Li K, Qin L, He Y, Liu X (2021b) Hypoxia activates Notch4 via ERK/JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathways to promote lung adenocarcinoma progression and metastasis. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:780121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.780121
Li Y, Ren BX, Li HM, Lu T, Fu R, Wu ZQ (2022) Omeprazole suppresses aggressive cancer growth and metastasis in mice through promoting Snail degradation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43:1816–1828. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00787-1
Li Y, Yuan T, Zhang H, Liu S, Lun J, Guo J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Fang J (2023) PHD3 inhibits colon cancer cell metastasis through the occludin-p38 pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 55:1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.3724/abbs.2023103
Lin Y, Mallen-St Clair J, Wang G, Luo J, Palma-Diaz F, Lai C, Elashoff DA, Sharma S, Dubinett SM, St John M (2016) p38 MAPK mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating p38IP and Snail in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 60:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.06.010
Lin X, Peng L, Xu X, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Huo X (2018) Connecting gastrointestinal cancer risk to cadmium and lead exposure in the Chaoshan population of Southeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:17611–17619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1914-5
Liu YH, Yuan M, Xu BX, Gao R, You YJ, Wang ZX, Zhang YC, Guo M, Chen ZY, Yu BF, Wang QW, Wang HL, Pang M (2022b) ANKRD49 promotes the invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma via a P38/ATF-2 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 26:4401–4415. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17464
Liu C, Jiang S, Xie H, Jia H, , Li R, Zhang K, Wang N, Lin P, Yu X (2022a) Long non-coding RNA AC245100.4 contributes to prostate cancer migration via regulating PAR2 and activating p38-MAPK pathway. Med Oncol 39:94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01689-w
Lorenzo-Gonzalez M, Ruano-Ravina A, Torres-Duran M, Kelsey KT, Provencio M, Parente-Lamelas I, Piñeiro-Lamas M, Varela-Lema L, Perez-Rios M, Fernandez-Villar A, Barros-Dios JM (2020) Lung cancer risk and residential radon exposure: a pooling of case-control studies in northwestern Spain. Environ Res 189:109968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109968
Luevano J, Damodaran C (2014) A review of molecular events of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 33:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.2014011075
Luo H, Li Z, Ge H, Mei D, Zhao L, Jiang L, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X, Cao J (2017) HMGA2 upregulation mediates Cd-induced migration and invasion in A549 cells and in lung tissues of mice. Chem Biol Interact 277:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.08.012
Lv W, Sui L, Yan X, Xie H, Jiang L, Geng C, Li Q, Yao X, Kong Y, Cao J (2018) ROS-dependent Atg4 upregulation mediated autophagy plays an important role in Cd-induced proliferation and invasion in A549 cells. Chem Biol Interact 279:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.11.013
Meng H, Li G, Wei W, Bai Y, Feng Y, Fu M, Guan X, Li M, Li H, Wang C, Jie J, Wu X, He M, Zhang X, Wei S, Li Y, Guo H (2021) Epigenome-wide DNA methylation signature of benzo[a]pyrene exposure and their mediation roles in benzo[a]pyrene-associated lung cancer development. J Hazard Mater 416:125839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125839
Peana M, Pelucelli A, Chasapis C T, Perlepes S P, Bekiari V, Medici S, Zoroddu M A (2022) Biological effects of human exposure to environmental cadmium. Biomolecules 13.https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036
Peng L, Huang Y, Zhang J, Peng Y, Lin X, Wu K, Huo X (2015a) Cadmium exposure and the risk of breast cancer in Chaoshan population of southeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:19870–19878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5212-1
Peng L, Wang X, Huo X, Xu X, Lin K, Zhang J, Huang Y, Wu K (2015b) Blood cadmium burden and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a case-control study in Chinese Chaoshan population. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:12323–12331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4533-4
Ryu KJ, Park SM, Park SH, Kim IK, Han H, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Hong KS, Kim H, Kim M, Yoon SJ, Asaithambi K, Lee KH, Park JY, Hah YS, Cho HJ, Yook JI, Yang JW, Ko GH, Lee G, Kang YJ, Hwangbo C, Kim KD, Park YJ, Yoo J (2019) p38 Stabilizes Snail by suppressing DYRK2-mediated phosphorylation that is required for GSK3β-βTrCP-induced Snail degradation. Cancer Res 79:4135–4148. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0049
Shao K, Zhou Z, Xun P, Cohen SM (2021) Bayesian benchmark dose analysis for inorganic arsenic in drinking water associated with bladder and lung cancer using epidemiological data. Toxicology 455:152752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2021.152752
Song Y, Wang Y, Mao W, Sui H, Yong L, Yang D, Jiang D, Zhang L, Gong Y (2017) Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 12:e0177978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177978
Sun XL, Phuc HD, Okamoto R, Kido T, Oanh NTP, Manh HD, Anh LT, Ichimori A, Nogawa K, Suwazono Y, Nakagawa H (2023) A 30-year follow-up study in a former cadmium-polluted area of Japan: the relationship between cadmium exposure and β(2)-microglobulin in the urine of Japanese people. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:23079–23085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23818-8
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tan H W, Liang Z L, Yao Y, Wu D D, Mo H Y, Gu J, Chiu J F, Xu Y M, Lau A T Y (2019) Lasting DNA damage and aberrant DNA repair gene expression profile are associated with post-chronic cadmium exposure in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cells 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080842
Wang Y, Pan T, Wang H, Li L, Li J, Zhang C, Yang H (2016) Silencing of TGIF attenuates the tumorigenicity of A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol 37:12725–12730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5222-8
Wang Y, Pan T, Li L, Wang H, Zhang D, Yang H (2018a) Benzo(a)pyrene promotes Hep-G2 cell migration and invasion by upregulating phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase expression. Oncol Lett 15:8325–8332. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8379
Wang Y, Mandal AK, Son YO, Pratheeshkumar P, Wise JTF, Wang L, Zhang Z, Shi X, Chen Z (2018b) Roles of ROS, Nrf2, and autophagy in cadmium-carcinogenesis and its prevention by sulforaphane. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 353:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.003
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Wang H, Yang H (2019a) The roles of TG-interacting factor in cadmium exposure-promoted invasion and migration of lung cancer cells. Toxicol in Vitro 61:104630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104630
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Li L, Wang H, Yang H (2019b) Involvement of p38 MAPK pathway in benzo(a)pyrene-induced human hepatoma cell migration and invasion. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:35838–35845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06733-3
Wang Y, Shi L, Li J, Li L, Wang H, Yang H (2019c) Long-term cadmium exposure promoted breast cancer cell migration and invasion by up-regulating TGIF. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 175:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.046
Wei L, Wu T, He P, Zhang JL, Wu W (2018) LncRNA ATB promotes the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer via activation of the p38 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 16:3907–3912. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9117
Wu Z, He D, Zhao S, Wang H (2019) IL-17A/IL-17RA promotes invasion and activates MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 455:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3483-9
Xing W, Wang L, Gu W, Liang M, Wang Z, Fan D, Zhang B (2023) Association of blood cadmium and metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017–2020. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30:27150–27162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24177-0
Yang Y, Li Y, Wang K, Wang Y, Yin W, Li L (2013) P38/NF-κB/snail pathway is involved in caffeic acid-induced inhibition of cancer stem cells-like properties and migratory capacity in malignant human keratinocyte. PLoS ONE 8:e58915. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058915
Yang X, Han M, Han H, Wang B, Li S, Zhang Z, Zhao W (2017) Silencing Snail suppresses tumor cell proliferation and invasion by reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and arresting G2/M phase in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol 50:1251–1260. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3888
Yang H, Zhang H, Pan T, Wang H, Wang Y (2018) Benzo(a)pyrene promotes migration, invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells by upregulating TGIF. Toxicol Lett 294:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.05.005
Yang MC, Huang YY, Hsieh SH, Sun JH, Wang CC, Lin CH (2021) Ankle-Brachial Index is independently associated with cardiovascular outcomes and foot ulcers in asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 12:752995. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.752995
Yao W, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Li G, Xu X, Zou K, Xu Y, Zou L (2015) ALX1 promotes migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through increasing snail expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:12129–12139
Young JL, Cai L (2020) Implications for prenatal cadmium exposure and adverse health outcomes in adulthood. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 403:115161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2020.115161
Yu R, Zhong J, Zhou Q, Ren W, Liu Z, Bian Y (2022) Kaempferol prevents angiogenesis of rat intestinal microvascular endothelial cells induced by LPS and TNF-α via inhibiting VEGF/Akt/p38 signaling pathways and maintaining gut-vascular barrier integrity. Chem Biol Interact 366:110135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110135
Zhai H, Pan T, Yang H, Wang H, Wang Y (2019) Cadmium induces A549 cell migration and invasion by activating ERK. Exp Ther Med 18:1793–1799. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7750
Zhang C, Liu T, Wang G, Wang H, Che X, Gao X, Liu H (2017a) Rac3 regulates cell invasion, migration and EMT in lung adenocarcinoma through p38 MAPK Pathway. J Cancer 8:2511–2522. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.18161
Zhang K, Li XY, Wang ZM, Han ZF, Zhao YH (2017b) MiR-22 inhibits lung cancer cell EMT and invasion through targeting Snail. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:3598–3604
Zhang Y, Liao Y, Chen C, Sun W, Sun X, Liu Y, Xu E, Lai M, Zhang H (2020) p38-regulated FOXC1 stability is required for colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol 250:217–230. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5362
Zhou Z, Huang Z, Chen B, Lu Q, Cao L, Chen W (2020) LncRNA-ENST00000446135 is a novel biomarker of cadmium toxicity in 16HBE cells, rats, and Cd-exposed workers and regulates DNA damage and repair. Toxicol Res (camb) 9:823–834. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxres/tfaa088
Zou X, Ma L, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Xu C, Zhang D, Chu Y, Zhang J, Li M, Zhang H, Wang J, Peng C, Wei G, Wu Y, Hou Z, Jia H (2023) GATA zinc finger protein p66β promotes breast cancer cell migration by acting as a co-activator of Snail. Cell Death Dis 14:382. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05887-w
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Prof. Weiguo Zhang for his kind help in editing the English language of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by a grant from Henan Young and Middle-aged Health Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project (no. YXKC2021005). The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yadong Wang and Haiyan Yang designed this study. Mengke Hu, Liqin Shi, Jie Xu, Li Shi, and Yadong Wang done the experiments and analyzed the data. Yadong Wang and Mengke Hu wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, M., Xu, J., Shi, L. et al. The p38 MAPK/snail signaling axis participates in cadmium-induced lung cancer cell migration and invasiveness. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 24042–24050 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32746-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32746-8