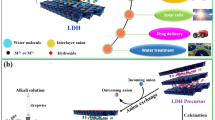
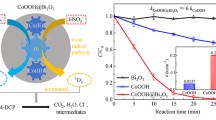
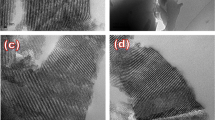
Abstract
The sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes (SR-AOPs) is a promising method for the degradation of pollutants, with the development of highly efficient catalysts for persulfate activation has been widely concerned. The novel BiCoFe-LDH (BCF-x) was synthesized successfully by coprecipitation method, which can activate peroxydisulfate (PDS) efficiently to degrade aniline. Comparative analysis with pure CoFe-LDH revealed a remarkable increase in reaction rate constant by approximately 14.66 times; the degradation rate of aniline (10 mg/L) was 100% in 60 min with the condition of 0.5 g/L BCF-1.5 and 0.5 g/L PDS, due to BCF-1.5 which was characterized as a complex of CoFe-LDH and Bi2O2CO3, promoting electron transport to improve the efficiency of activated PDS. In the reaction system, SO4•−, ·OH, and 1O2 were responsible for the aniline degradation and ·OH was the primary one. Furthermore, this work proposes a reaction electron transfer catalytic mechanism, which provided a new insight and good application prospect for efficient activation of PDS for pollutant degradation.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Akdağ S, Sadeghi Rad T, Keyikoğlu R, Orooji Y, Yoon Y, Khataee A (2022) Peroxydisulfate-assisted sonocatalytic degradation of metribuzin by La-doped ZnFe layered double hydroxide. Ultrason Sonochem 91:106236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106236
Ali Khan A, Tahir M, Khan N (2023) LDH-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic applications: a comprehensive review on the role of bi/trivalent cations, anions, morphology, defect engineering, memory effect, and heterojunction formation. J Energy Chem 84:242–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2023.04.049
An J, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Tang H (2013) Efficient visible light photo-Fenton-like degradation of organic pollutants using in situ surface-modified BiFeO3 as a catalyst. J Environ Sci 25:1213–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60172-7
Cao Y, Zheng D, Zhang F, Pan J, Lin C (2022) Layered double hydroxide (LDH) for multi-functionalized corrosion protection of metals: a review. J Mater Sci Technol 102:232–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.05.078
Chen X, Wang J, Guo Y et al (2023) Enhanced reduction of uranium (VI) in groundwater via regulation of heat-activated persulfate: the role of formate and its mechanisms. J Environ Chem Eng 11:110299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110299
Choi Y, Kim G, Kim J et al (2023) Anchoring catalytically active species on alumina via surface hydroxyl group for durable surface reaction. Appl Catal B 325:122325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122325
Daud M, Hai A, Banat F et al (2019) A review on the recent advances, challenges and future aspect of layered double hydroxides (LDH)—containing hybrids as promising adsorbents for dyes removal. J Mol Liq 288:110989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.110989
Fan Z, Feng T, Wu S et al (2023) Chitin-derived biochar with nitrogen doping to activate persulfate for phenol degradation: application potential and electron transfer pathway in system. Chemosphere 330:138641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138641
Fang HL, Liu J, Huang PW, Shi DW (2023) Tripling in coercivity (Hc) for the thermal and structural highly stabilized MnAlBi-C rare earth free permanent magnet via Bi doping. Mater Des 230:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111887
Gao S, Wang Z, Wang H et al (2022) Peroxydisulfate activation using B-doped biochar for the degradation of oxytetracycline in water. Appl Surf Sci 599:153917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153917
Ge L, Shao B, Liang Q et al (2022) Layered double hydroxide based materials applied in persulfate based advanced oxidation processes: property, mechanism, application and perspectives. J Hazard Mater 424:127612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127612
Giannakis S, Lin KA, Ghanbari F (2021) A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes (SR-AOPs). Chem Eng J 406:127083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127083
Guo J, Gao Q, Yang S et al (2021a) Degradation of pyrene in contaminated water and soil by Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation: performance, kinetics, and background electrolytes (Cl-, HCO3- and humic acid) effects. Process Saf Environ Prot 146:686–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.12.003
Guo J, Wei Z, Wang K, Zhang H (2021b) Synergistic coupling of CoFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheet arrays with reduced graphene oxide modified Ni foam for highly efficient oxygen evolution reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:27529–27542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.06.013
Guo J, Chen Y, Chen W et al (2023) CoFe2O4/MWCNTs as peroxymonosulfate activator for sulfadiazine degradation in wastewater: performance, mechanisms, degradation pathway, and products toxicity assessment. J Alloys Compd 960:170868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170868
He A, Wang C, Zhang N et al (2023) Oxygen vacancy-rich CeOx-Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets for enhancing electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formate. Appl Surf Sci 638:158140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158140
Hou J, He X, Zhang S, Yu J, Feng M, Li X (2021) Recent advances in cobalt-activated sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes for water remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 770:145311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145311
Huang X, Zhou X, Han S, Zhou J, Qian G, Gao N (2020) Cycle of Ni(II)-Ni(III)-Ni(II) in Ni-doped layered double hydroxides for activation of intercalated peroxydisulfate. Chem Eng J 386:123937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123937
Hussain I, Zhang Y, Li M et al (2018) Heterogeneously degradation of aniline in aqueous solution using persulfate catalyzed by magnetic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Catal Today 310:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.02.017
Li X, Hou T, Yan L, Shan L, Meng X, Zhao Y (2020) Efficient degradation of tetracycline by CoFeLa-layered double hydroxides catalyzed peroxymonosulfate: synergistic effect of radical and nonradical pathways. J Hazard Mater 398:122884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122884
Li J, Yang L, Lai B et al (2021) Recent progress on heterogeneous Fe-based materials induced persulfate activation for organics removal. Chem Eng J 414:128674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128674
Li X, Song C, Sun B, Gao J, Liu Y, Zhu J (2022) Kinetics of zero-valent iron-activated persulfate for methylparaben degradation and the promotion of Cl−. J Environ Manage 321:115973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115973
Li X, Chen Y, Xiao C et al (2023a) Manipulating the morphology of self-assembly broccoli-like cobalt nickel spinel for enhancing the peroxydisulfate activation towards highly-effective ciprofloxacin degradation: radical and non-radical pathways, mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Appl Surf Sci 617:156593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156593
Li X, Shao X, Wang Z, Ma J, He H (2023b) Regulating the chemical state of silver via surface hydroxyl groups to enhance ozone decomposition performance of Ag/Fe2O3 catalyst. Catal Today 410:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2022.04.011
Liu Y, Ren H, Lv H, Guang J, Cao Y (2018) Synthesis of magnetic Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 composite with improved photocatalytic activity and easy recyclability. Appl Surf Sci 433:610–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.081
Liu B, Wang Y, Hao X, Wang J, Yang Z, Yang Q (2022a) Green synthesis of stable structure spindle FeCo-LDH through Fe-MOF template for efficient degradation of 2,4-D. J Water Process Eng 46:102602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102602
Liu J, Wang S, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Kong D (2022b) Synergistic mechanism and decopperization kinetics for copper anode slime via an integrated ultrasound-sodium persulfate process. Appl Surf Sci 589:153032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153032
Liu Z, Pan S, Xu F et al (2022c) Revealing the fundamental role of MoO2 in promoting efficient and stable activation of persulfate by iron carbon based catalysts: efficient Fe2+/Fe3+ cycling to generate reactive species. Water Res 225:119142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119142
Liu B, Huang B, Wang Z et al (2023) Homogeneous/heterogeneous metal-catalyzed persulfate oxidation technology for organic pollutants elimination: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109586
Luo Y, Zheng A, Li J et al (2023) Integrated adsorption and photodegradation of tetracycline by bismuth oxycarbonate/biochar nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 457:141228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.141228
Ma Q, Nengzi L, Li B, Wang Z, Liu L, Cheng X (2020) Heterogeneously catalyzed persulfate with activated carbon coated with CoFe layered double hydroxide (AC@CoFe-LDH) for the degradation of lomefloxacin. Sep Purif Technol 235:116204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116204
Muttakin M, Mitra S, Thu K, Ito K, Saha BB (2018) Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int J Heat Mass Transf 122:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.01.107
Oyekunle DT, Cai J, Gendy EA, Chen Z (2021) Impact of chloride ions on activated persulfates based advanced oxidation process (AOPs): a mini review. Chemosphere (oxford) 280:130949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130949
Pelalak R, Hassani A, Heidari Z, Zhou M (2023) State-of-the-art recent applications of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) material in Fenton-based oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J:145511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145511.
Plubphon N, Thongtem S, Phuruangrat A, Randorn C, Kaowphong S, Thongtem T (2022) Rapid preparation of g-C3N4/Bi2O2CO3 composites and their enhanced photocatalytic performance. Diam Relat Mater 130:109488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109488
Ramesh AM, Purushotham D, Kodandaram A et al (2023) Visible light driven photocatalytic and competent antioxidant properties of phyto-fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) from Borreria hispida. J Mol Struct 1293:136152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136152
Ren T, Ma X, Wu X, Yuan L, Lai Y, Tong Z (2021) Degradation of imidazolium ionic liquids in a thermally activated persulfate system. Chem Eng J 412:128624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128624
Saleh R, AndianeHidayat S, Yose Rizal M, Taufik A, Yin S (2022) Synthesis and characterization of BiFeO3/LaFeO3/graphene composites as persulfate activator for removal of 4-nitrophenol. Adv Powder Technol 33:103752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2022.103752
Schilling M, Braig M, Köble K, Zeis R (2022) Investigating the V(IV)/V(V) electrode reaction in a vanadium redox flow battery – a distribution of relaxation times analysis. Electrochim Acta 430:141058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141058
Shen Y, Martín De Vidales MJ, Gorni G, Gómez-Herrero A, Fernández-Martínez F, Dos Santos-García AJ (2022) Enhanced performance and recyclability for peroxymonosulfate activation via g-C3N4 supported CoFe layer double oxide. Chem Eng J 444:136610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136610
Steuer L, Kaifer E, Himmel HJ (2022) Redox-active dendrimer-like oligoguanidines and their use in a proton-coupled electron transfer reaction. European J Org Chem 2022:41–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202101360
Wang R, Su S, Ren X, Guo W (2021a) Polyoxometalate intercalated La-doped NiFe-LDH for efficient removal of tetracycline via peroxymonosulfate activation. Sep Purif Technol 274:119113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119113
Wang Z, Fu Y, Peng Y, Wang S, Liu Y (2021b) HCO3-/CO32- enhanced degradation of diclofenac by Cu(II)-activated peracetic acid: efficiency and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 277:119434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119434
Wang Y, Wang L, Cao Y, Bai S, Ma F (2022) Phase transformation-driven persulfate activation by coupled Fe/N–biochar for bisphenol a degradation: pyrolysis temperature-dependent catalytic mechanisms and effect of water matrix components. Environ Pollut 314:120296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120296
Wang S, Li T, Cheng X, Zhu R, Xu Y (2023a) Regulating the concentration of dissolved oxygen to achieve the directional transformation of reactive oxygen species: a controllable oxidation process for ciprofloxacin degradation by calcined CuCoFe-LDH. Water Res 233:119744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119744
Wang S, Yin H, Ding J et al (2023b) One-pot preparation of novel Bi/BiOBr/Bi2O2CO3 heterojunction for pollutant degradation under visible light: catalyst generation insights, reaction mechanism, degradation pathways, and toxicological effects. Surf Interfaces 37:102642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2023.102642
Wang Z, Tan Y, Duan X et al (2023c) Pretreatment of membrane dye wastewater by CoFe-LDH-activated peroxymonosulfate: performance, degradation pathway, and mechanism. Chemosphere 313:137346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137346
Wu L, Hong J, Zhang Q, Chen B, Wang J, Dong Z (2020) Deciphering highly resistant characteristics to different pHs of oxygen vacancy-rich Fe2Co1-LDH/PS system for bisphenol A degradation. Chem Eng J 385:123620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123620
Wu J, Xu Z, Yao K et al (2023) Efficient degradation and detoxification of antibiotic fosfomycin by UV irradiation in the presence of persulfate. Sci Total Environ 905:167249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167249
Xin Q, Liu S, Lu S et al (2023) Surface-bound sulfate radical-dominated degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the CuFeAl-LDH/peroxymonosulfate system: the abundant hydroxyl groups enhancing efficiency mechanism. Chem Eng J 471:144453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.144453
Yang R, Zhou Y, Xing Y et al (2019) Synergistic coupling of CoFe-LDH arrays with NiFe-LDH nanosheet for highly efficient overall water splitting in alkaline media. Appl Catal B 253:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.054
Yang W, Li J, Wang M et al (2020) A colorimetric strategy for ascorbic acid sensing based on the peroxidase-like activity of core-shell Fe3O4/CoFe-LDH hybrid. Colloids Surf, B 188:110742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110742
Yang C, Zhang G, Meng Y, Pan G, Ni Z, Xia S (2021) Direct Z-scheme CeO2@LDH core–shell heterostructure for photodegradation of rhodamine B by synergistic persulfate activation. J Hazard Mater 408:124908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124908
Yao Y, Ma Z, Zhang Y et al (2023) N-doped carbon nanotubes encapsulated FeNi alloy in persulfate activation for nonradical reaction: confined metal redox. Appl Surf Sci 624:157069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157069
Ye Q, Wu J, Wu P, Rehman S, Ahmed Z, Zhu N (2021) Enhancing peroxymonosulfate activation by Co-Fe layered double hydroxide catalysts via compositing with biochar. Chem Eng J 417:129111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129111
Yuan X, Zheng W, Feng S et al (2021) Degradation of bisphenol A through Ti–BiOI/ZIF-8/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): catalyst preparation, experimental design and catalytic mechanism. J Solid State Chem 304:122596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122596
Zakaria SA, Ahmadi SH, Amini MH (2022) Chemiresistive gas sensors based on layered double hydroxides (LDHs) structures: a review. Sens Actuators, A 346:113827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113827
Zhang G, Wang J, Shen X, Wang J, Wang B, Gao D (2019) Br-doped Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets with improved electronic structure and accelerated charge migration for outstanding photocatalytic behavior. Appl Surf Sci 470:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.103
Zhang H, Nengzi L, Wang Z, Zhang X, Li B, Cheng X (2020a) Construction of Bi2O3/CuNiFe LDHs composite and its enhanced photocatalytic degradation of lomefloxacin with persulfate under simulated sunlight. J Hazard Mater 383:121236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121236
Zhang H, Song Y, Nengzi L, Gou J, Li B, Cheng X (2020b) Activation of persulfate by a novel magnetic CuFe2O4/Bi2O3 composite for lomefloxacin degradation. Chem Eng J 379:122362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122362
Zhang Y, Lou J, Wu L et al (2021) Minute Cu2+ coupling with HCO3- for efficient degradation of acetaminophen via H2O2 activation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 221:112422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112422
Zhang C, Ni X, Xu W et al (2023a) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalyst Ag/Ag3PO4/Bi2O2CO3 enabled by the synergistic effect of heterojunction and surface plasma resonance. Mater Sci Semicond Process 166:107704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107704
Zhang L, Xiao C, Li Z et al (2023b) Degradation of methyl orange using persulfate activated by magnetic CuS/Fe3O4 catalyst: Catalytic performance and mechanisms. Appl Surf Sci 618:156595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156595
Zhang M, Xing M, Dong B et al (2023c) Preparation of BiVO4/CO32–Bi2O2CO3 heterojunctions for enhanced photocatalytic activity in the degradation of levofloxacin under visible light. J Alloys Compd 965:171471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171471
Zhang R, Cai L, Yu J et al (2023d) Construction of CoS/Bi2O2CO3 micro-flowers: efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride over a wide concentration range. Appl Surf Sci 610:155492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155492
Zhou Y, Wang Z, Yin H et al (2023) One-pot synthesis of 2D Ag/BiOCl/Bi2O2CO3 S-scheme heterojunction with oxygen vacancy for photocatalytic disinfection of Fusarium graminearum in vitro and in vivo. Chemosphere 331:138768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138768
Zuo H, Wu C, Du H, Guo Z, Cheng Y, Yan Q (2023) Interfacial coupling of 3D nanoflower-like Bi2O2CO3 with PANI for tetracycline photocatalytic degradation and intermediate toxicity analysis. Appl Surf Sci 633:157600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157600
Funding
This work was supported by the financial supports from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Z20230005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Yutong Li analyzed and interpreted the data and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. Buying Qi performed writing—review and editing, validation, and supervision. Xinglong Jin performed supervision, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable in this paper.
Consent to participate
Not applicable in this paper.
Consent for publication
Not applicable in this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The BiCoFe-LDH showed excellent PDS activation properties for aniline removal.
• The Bi2O2CO3 serves as an electron transfer mediator to promote Co2+/Co3+ and Fe2+/Fe3+ cycles.
• SO4•−, ·OH, and 1O2 play a significant role in the degradation of aniline.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Jin, X. & Qi, B. Activation of peroxydisulfate via BiCoFe-layered double hydroxide for effective degradation of aniline. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 23979–23994 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32735-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32735-x