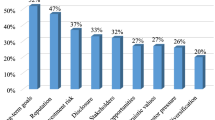
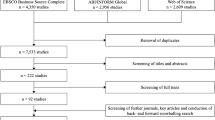
Abstract
Government-led green governance, as a crucial tool for achieving green and sustainable development, has garnered significant attention among researchers worldwide. Nevertheless, research on incentive-based green governance and green orientation remains insufficient. This study adopts an evolutionary game theory framework to elucidate the mechanisms underlying incentive-based green governance and green orientation in facilitating green innovation. The effectiveness of this framework is then verified through the utilization of propensity score matching (PSM) and difference-in-differences (DID) methods using data from Chinese companies. The main findings include the following: (1) Government incentive-based green governance exhibits a compensatory effect on green innovation, which is validated through robustness testing. (2) Internal green orientation serves as an intermediary factor between incentive-based green governance and green innovation, while external green orientation exerts a positive regulatory effect. (3) Heterogeneity analysis demonstrates that the impact of incentive-based green governance on green innovation is more pronounced in non-high-pollution industries, high-tech corporations, and companies operating in areas with lower governance intensity. This study is conducive to illustrate the compensatory effect of government incentive-based green governance on green innovation and also provides reference for the government to issue targeted green governance policies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Albort-Morant G, Leal-Millán A, Cepeda-Carrión G (2016) The antecedents of green innovation performance: a model of learning and capabilities. J Bus Res 69:4912–4917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.052
Bai Y, Song S, Jiao J, Yang R (2019) The impacts of government R&D subsidies on green innovation: evidence from Chinese energy-intensive firms. J Clean Prod 233:819–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.107
Banerjee SB (2002) Corporate environmentalism: the construct and its measurement. J Bus Res 55:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-2963(00)00135-1
Boeing P (2016) The allocation and effectiveness of China’s R&D subsidies - evidence from listed firms. Res Policy 45:1774–1789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2016.05.007
Borsatto JMLS, Bazani CL (2021) Green innovation and environmental regulations: a systematic review of international academic works. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:63751–63768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11379-7
Cek K, Eyupoglu S (2020) Does environmental, social and governance performance influence economic performance? J Bus Econ Manag 21:1165–1184. https://doi.org/10.3846/jbem.2020.12725
Chan RYK (2010) Corporate environmentalism pursuit by foreign firms competing in China. J World Bus 45:80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2009.04.010
Chan RYK, He H, Chan HK, Wang WYC (2012) Environmental orientation and corporate performance: the mediation mechanism of green supply chain management and moderating effect of competitive intensity. Ind Mark Manag 41:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2012.04.009
Chen Y, Chang C, Wu F (2012) Origins of green innovations: the differences between proactive and reactive green innovations. Manag Decis 50:368–398. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251741211216197
Chen X, Liu X, Zhu Q (2022) Comparative analysis of total factor productivity in China’s high-tech industries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 175:121332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121332
Dangelico RM, Pujari D, Pontrandolfo P (2017) Green product innovation in manufacturing firms: a sustainability-oriented dynamic capability perspective. Bus Strateg Environ 26:490–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.1932
Darnall N, Jolley GJ, Handfield R (2008) Environmental management systems and green supply chain management: complements for sustainability? Bus Strateg Environ 17:30–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.557
Debbarma J, Choi Y (2022) A taxonomy of green governance: a qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustain Cities Soc 79:103693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103693
Du J, Mickiewicz T (2016) Subsidies, rent seeking and performance: being young, small or private in China. J Bus Ventur 31:22–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2015.09.001
Du K, Cheng Y, Yao X (2021) Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: the road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Econ 98:105247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105247
Fatoki O (2021) Environmental orientation and green competitive advantage of hospitality firms in South Africa: mediating effect of green innovation. J Open Innov Technol Mark Complex 7:223. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7040223
Fei J, Wang Y, Yang Y et al (2016) Towards eco-city: the role of green innovation. Energy Procedia 104:165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2016.12.029
Feng L, Zhao W, Li H, Song Y (2018) The effect of environmental orientation on green innovation: do political ties matter? Sustainability 10:4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124674
Fraj E, Martínez E, Matute J (2011) Green marketing strategy and the firm’s performance: the moderating role of environmental culture. J Strateg Mark 19:339–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/0965254X.2011.581382
Guinot J, Barghouti Z, Chiva R (2022) Understanding green innovation: a conceptual framework. Sustainability 14:5787. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14105787
Hong J, Hong S, Wang L et al (2015) Government grants, private R&D funding and innovation efficiency in transition economy. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 27:1068–1096. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2015.1060310
Hu D, Qiu L, She M, Wang Y (2021) Sustaining the sustainable development: how do firms turn government green subsidies into financial performance through green innovation? Bus Strateg Environ 30:2271–2292. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2746
Huang Z, Liao G, Li Z (2019) Loaning scale and government subsidy for promoting green innovation. Technol Forecast Soc Change 144:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.04.023
Humphrey JE, Lee DD, Shen Y (2012) The independent effects of environmental, social and governance initiatives on the performance of UK firms. Aust J Manag 37:135–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/0312896211410081
Jabbour CJC, de Freitas TP, Soubihia DF et al (2015) Green and competitive: empirical evidence from ISO 9001 certified Brazilian companies. TQM J 27:22–41. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-01-2013-0013
Jiang L, Bai Y (2022) Strategic or substantive innovation? -the impact of institutional investors’ site visits on green innovation evidence from China. Technol Soc 68:101904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101904
KarimiTakalo S, SayyadiTooranloo H, ShahabaldiniParizi Z (2021) Green innovation: a systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 279:122474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122474
Keszey T (2020) Environmental orientation, sustainable behaviour at the firm-market interface and performance. J Clean Prod 243:118524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118524
Kuo L, Yu HC, Chang BG (2015) The signals of green governance on mitigation of climate change–evidence from Chinese firms. Int J Clim Chang Strateg Manag 7:154–171. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCCSM-07-2013-0083
Lanoie P, Laurent-Lucchetti J, Johnstone N, Ambec S (2011) Environmental policy, innovation and performance: new insights on the porter hypothesis. J Econ Manag Strateg 20:803–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9134.2011.00301.x
Larrán Jorge M, Herrera Madueño J, Martínez-Martínez D, Lechuga Sancho MP (2015) Competitiveness and environmental performance in Spanish small and medium enterprises: is there a direct link? J Clean Prod 101:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.016
Li W, Xu J, Zheng M (2018a) Green governance: new perspective from open innovation. Sustainability 10:3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10113845
Li Z, Liao G, Wang Z, Huang Z (2018b) Green loan and subsidy for promoting clean production innovation. J Clean Prod 187:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.066
Li G, Wang X, Su S, Su Y (2019) How green technological innovation ability influences enterprise competitiveness: green technological innovation ability, product differentiation and enterprise competitiveness. Technol Soc 59:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.04.012
Li Y, Tong Y, Ye F, Song J (2020) The choice of the government green subsidy scheme: innovation subsidy vs. product subsidy. Int J Prod Res 58:4932–4946. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1730466
Li X, Hu Z, Cao J, Xu X (2022) The impact of environmental accountability on air pollution: a public attention perspective. Energy Policy 161:112733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112733
Liu M, Lo K (2021) Governing eco-cities in China: Urban climate experimentation, international cooperation, and multilevel governance. Geoforum 121:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2021.02.017
Liu Q, Dong B (2022) How does China’s green credit policy affect the green innovation of heavily polluting enterprises? The perspective of substantive and strategic innovations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:77113–77130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21199-6
Liu X, Li X, Li H (2016) R&D subsidies and business R&D: evidence from high-tech manufacturing firms in Jiangsu. China Econ Rev 41:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2016.08.003
Liu J, Zhao M, Wang Y (2020) Impacts of government subsidies and environmental regulations on green process innovation: a nonlinear approach. Technol Soc 63:101417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101417
Lokshin B, Mohnenb P (2012) How effective are level-based R&D tax credits? Evidence from the Netherlands. Appl Econ 44:1527–1538. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2010.543083
Ma W, Zhang R, Chai S (2019) What drives green innovation? A game theoretic analysis of government subsidy and cooperation contract. Sustainability 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205584
Mankiw NG (2016) Principles of economics. Cengage Learning, Boston
Martinelli A, Midttun A (2012) Introduction: towards green growth and multilevel governance. Energy Policy 48:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.04.048
Olson M (1971) The logic of collective action. Harvard University Press, Boston
Pane Haden S, Oyler J, Humphreys J (2009) Historical, practical and theoretical perspective on green management: an exploratory analysis. Manag Decis 47:1041–1055. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740910978287
Peng B, Zheng C, Wei G, Elahi E (2020) The cultivation mechanism of green technology innovation in manufacturing industry: from the perspective of ecological niche. J Clean Prod 252:119711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119711
Rennings K (2000) Redefining innovation - eco-innovation research and the contribution from ecological economics. Ecol Econ 32:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00112-3
Rubashkina Y, Galeotti M, Verdolini E (2015) Environmental regulation and competitiveness: empirical evidence on the Porter Hypothesis from European manufacturing sectors. Energy Policy 83:288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.02.014
Siew RYJ, Balatbat MCA, Carmichael DG (2016) The impact of ESG disclosures and institutional ownership on market information asymmetry. Asia-Pacific J Account Econ 23:432–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/16081625.2016.1170100
Tan Y, Tian X, Zhang X, Zhao H (2020) The real effect of partial privatization on corporate innovation: evidence from China’s split share structure reform. J Corp Financ 64:101661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2020.101661
Tang Y, Yang R, Chen Y, Miao X (2022) Assessment of China’s green governance performance based on integrative perspective of technology utilization and actor management. Int J Sustain Dev WORLD Ecol 29:827–839. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2022.2107105
Tian M, Xu GH, Zhang LZ (2019) Does environmental inspection led by central government undermine Chinese heavy-polluting firms’ stock value? The buffer role of political connection. J Clean Prod 236:117695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117695
Wang F, Sun Z (2022) Does the environmental regulation intensity and ESG performance have a substitution effect on the impact of enterprise green innovation: evidence from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148558
Wang C, Nie PY, Peng DH, Li ZH (2017) Green insurance subsidy for promoting clean production innovation. J Clean Prod 148:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.145
Wang G, Li Y, Zuo J et al (2021) Who drives green innovations? Characteristics and policy implications for green building collaborative innovation networks in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 143:110875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110875
Wang JX, Ma MD, Dong TY, Zhang ZY (2023) Do ESG ratings promote corporate green innovation? A quasi-natural experiment based on SynTao Green Finance’s ESG ratings. Int Rev Financ Anal 87:102623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102623
Xie X, Zhu Q, Wang R (2019) Turning green subsidies into sustainability: how green process innovation improves firms’ green image. Bus Strateg Environ 28:1416–1433. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2323
Xinle T, Zhen W, Xinting L (2022) The influence of government subsidy on enterprise innovation: based on Chinese high-tech enterprises. Econ Res Istraz 35:1481–1499. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1972818
Xu JH, Ng CP, Sam TH et al (2023) Fiscal and tax policies, access to external financing and green innovation efficiency: an evaluation of chinese listed firms. Sustainability 15:11567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511567
Yu Y, Huo B (2019) The impact of environmental orientation on supplier green management and financial performance: the moderating role of relational capital. J Clean Prod 211:628–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.198
Zhai Y, Cai Z, Lin H et al (2022) Does better environmental, social, and governance induce better corporate green innovation: the mediating role of financing constraints. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag 29:1513–1526. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.2288
Zhang SZ, Yu YM, Zhu QH et al (2020a) Green innovation mode under carbon tax and innovation subsidy: an evolutionary game analysis for portfolio policies. Sustainability 12:1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041385
Zhang Y, Sun J, Yang Z, Wang Y (2020b) Critical success factors of green innovation: technology, organization and environment readiness. J Clean Prod 264:121701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121701
Zhao X, Zhao Y, Zeng S, Zhang S (2015) Corporate behavior and competitiveness: impact of environmental regulation on Chinese firms. J Clean Prod 86:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.074
Zheng S, Ward MR (2011) The effects of market liberalization and privatization on Chinese telecommunications. China Econ Rev 22:210–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2011.01.003
Zheng M, Feng G-F, Jiang R-A, Chang C-P (2023) Does environmental, social, and governance performance move together with corporate green innovation in China? Bus Strateg Environ 32:1670–1679. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3211
Zhou X, Du J (2021) Does environmental regulation induce improved financial development for green technological innovation in China? J Environ Manage 300:113685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113685
Zhou C, Xia W, Feng T et al (2020a) How environmental orientation influences firm performance: the missing link of green supply chain integration. Sustain Dev 28:685–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2019
Zhou M, Govindan K, Xie X (2020b) How fairness perceptions, embeddedness, and knowledge sharing drive green innovation in sustainable supply chains: an equity theory and network perspective to achieve sustainable development goals. J Clean Prod 260:120950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120950
Zhou M, Govindan K, Xie X, Yan L (2021) How to drive green innovation in China’s mining enterprises? Under the perspective of environmental legitimacy and green absorptive capacity. Resour Policy 72:102038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102038
Funding
This research was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (grant No. 18BGL094), Shandong Social Science Planning Research Project (grant No. 21CGLJ30), Shandong Social Science Planning Research Project (grant No. 22CGLJ33) and Shandong Social Science Planning Research Project (grant No. 23CGLJ36).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FW: literature, methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing original draft, visualization. HF: writing, review and editing, guidance, funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Feng, H. Does incentive-based green governance compensate for green innovation in enterprises? The role of green orientation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 7443–7464 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31671-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31671-6