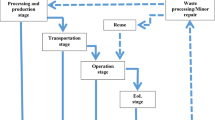
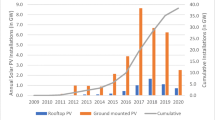
Abstract
The global surge in photovoltaic (PV) installations and the resulting increase in PV waste are a growing concern. The aims of this study include predicting the volume of photovoltaic waste in Canada. The forecasting of solar waste volume employed linear regression, 2nd order polynomial regression, and power regression models. The study’s results indicate that Canada is on the verge of facing challenges related to the end-of-life treatment of photovoltaic modules in the coming years due to the significant growth in PV capacity over recent decades. According to the analysis, for early loss, the PV waste volume in 2045 could range from 180,000 MT to 270,000 MT, and for regular loss, it could range from 160,000 MT to 180,000 MT. This research is anticipated to assist relevant government agencies in assessing the prospective volume of PV waste to establish a sustainable and resilient PV waste management plan for Canada. These findings may shed light on the feasibility of a circular economy and advocate for the involvement of all stakeholders in a carefully coordinated strategy to mitigate potential environmental impacts and optimize resource utilization efficiency.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) (2017) Investing in Australia’s renewable energy future. Australian Renewable Energy Agency. https://arena.gov.au/assets/2017/05/AU21397_ARENA_IP_Document_FA_Single_Pages_LORES.pdf. Accessed 30 June 2021
Behi Z, Ng KTW, Richter A, Karimi N, Ghosh A, Zhang L (2022) Exploring the untapped potential of solar photovoltaic energy at a smart campus: shadow and cloud analyses. Energy Environ 33(3):511–526. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X211008998
Bevir M (2012) Global market outlook. Encyclopedia of Governance. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412952613.n215
Bolingbroke D, Ng KTW, Vu HL, Richter A (2021) Quantification of solid waste management system efficiency using input–output indices. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 23(3):1015–1025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01187-7
Bruce N, Asha AZ, Ng KTW (2016) Analysis of solid waste management systems in Alberta and British Columbia using provincial comparison. Can J Civ Eng 43(4):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2015-0414
Canada Energy Regulator, C (2019) Canada Energy Regulator (2019). https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-markets/provincial-territorial-energy-profiles/provincial-territorial-energy-profiles-canada.html. More than half of the electricity in Canada,electricity sector occurs primarily at the provincial l. Accessed 30 June 2021
Canada Energy Regulator, C. E (2021) Canada’s energy future 2021 (macro indicators, electricity capacity). Canada Energy Regulator website. https://apps.cer-rec.gc.ca/ftrppndc/dflt.aspx?GoCTemplateCulture=en-CA. Accessed 30 May 2022
Canadian Energy Regulator (2021) CER – Canada’s energy future 2021 - key findings. https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/canada-energy-future/2021/key-findings.html. Accessed 30 May 2022
Canadian Institute for Climate Choices CICC (2021) Canada’s net zero future: finding our way in the global transition. Canadian Institute for Climate Choices, 131
CanREA (2021) Powering Canada’s journey to net-zero. Canadian Renewable Energy Association
Chowdhury A, Vu HL, Ng KTW, Richter A, Bruce N (2017) An investigation on Ontario’s non-hazardous municipal solid waste diversion using trend analysis. Can J Civ Eng 44(11):861–870. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2017-0168
D’Adamo I, Miliacca M, Rosa P (2017) Economic feasibility for recycling of waste crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules. Int J Photoenergy 2017:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4184676
DeGraaff D, Lacerda R, Campeau Z (2011) Degradation mechanisms in Si module technologies observed in the field; their analysis and statistics. NREL 2011 Photovoltaic Module Reliability Workshop
Domínguez A, Geyer R (2019) Photovoltaic waste assessment of major photovoltaic installations in the United States of America. Renew Energy:1188–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.063
Eghbali H, Arkat J, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2022) Sustainable supply chain network design for municipal solid waste management: a case study. J Clean Prod 381:135211
Faircloth CC, Wagner KH, Woodward KE, Rakkwamsuk P, Gheewala SH (2019) The environmental and economic impacts of photovoltaic waste management in Thailand. Resour Conserv Recycl 143:260–272
Farrell CC, Osman AI, Doherty R, Saad M, Zhang X, Murphy A, Harrison J, Vennard ASM, Kumaravel V, Al-Muhtaseb AH, Rooney DW (2020) Technical challenges and opportunities in realising a circular economy for waste photovoltaic modules. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 128(February):109911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109911
Guerard JB (2013) Introduction to financial forecasting in investment analysis. Intro Financ Forecast Invest Anal 2007:1–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5239-3
Heelan J, Gratz E, Zheng Z, Wang Q, Chen M, Apelian D, Wang Y (2016) Current and prospective Li-Ion battery recycling and recovery processes. Jom 68(10):2632–2638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-1994-y
Hyndman RJ, Khandakar Y (2008) Automatic time series forecasting: the forecast package for R. J Stat Softw 27(3):22. http://www.jstatsoft.org/%0Ahttp://www.jstatsoft.org/v27/i03/paper
International Energy Agency, I. (2021). Canada 2022 - energy policy review. International Energy Agency. https://www.iea.org/t&c/. Accessed 30 May 2022
IRENA (2016) End of life management solar PV panels. In International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and the International Energy Agency (IEA)
IRENA: Weckend S (2016) End-of-life photovoltaic modules: a systematic quantitative literature review. Resour Conserv Recycl 146(March):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.018
Jain S, Sharma T, Gupta AK (2022) End-of-life management of solar PV waste in India: situation analysis and proposed policy framework. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 153:111774
Karimi N, Ng KTW, Richter A (2022b) Integrating geographic information system network analysis and nighttime light satellite imagery to optimize landfill regionalization on a regional level. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21462-w
Karimi N, Ng KTW, Richter A (2022a) Development of a regional solid waste management framework and its application to a prairie province in central Canada. Sustain Cities Soc 82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103904
Lovekin D, Moorhouse J, Morales V, Salek B (2020) Diesel reduction progress in remote communities modelling approach and methodology About the Pembina Institute. Pembina Institute, July
Mahmoudi S, Huda N, Behnia M (2019) Photovoltaic waste assessment: forecasting and screening of emerging waste in Australia. Resour Conserv Recycl 146(March):192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.039
Mahmoudi S, Huda N, Behnia M (2021) Critical assessment of renewable energy waste generation in OECD countries: decommissioned PV panels. Resour Conserv Recycl 164:105145
NRCan (2020) Natural Resources Canada
Oteng D, Zuo J, Sharifi E (2022a) Environmental emissions influencing solar photovoltaic waste management in Australia: an optimised system network of waste collection facilities. J Environ Manage 314:115007
Oteng D, Zuo J, Sharifi E (2022b) An expert-based evaluation on end-of-life solar photovoltaic management: an application of Fuzzy Delphi Technique. Sustain Horiz 4:100036
Richter A, Bruce N, Ng KTW, Chowdhury A, Vu HL (2017) Comparison between Canadian and Nova Scotian waste management and diversion models—a Canadian case study. Sustain Cities Soc 30:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.01.013
Richter A, Ng KTW, Fallah B (2019) Bibliometric and text mining approaches to evaluate landfill design standards. Scientometrics 118(3):1027–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03011-4
Richter A, Ng KTW, Karimi N (2021a) The role of compactness distribution on the development of regionalized waste management systems. J Clean Prod 296:126594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126594
Richter A, Ng KTW, Karimi N, Li RYM (2021b) An iterative tessellation-based analytical approach to the design and planning of waste management regions. Comput Environ Urb Syst 88(June 2020):101652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2021.101652
Romel M, Kabir G, Ng KTW (2023) Analysis of barriers to photovoltaic waste management to achieve net-zero goal of Canada. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(36):85772–85791
Sharma S, Kleinbaum DG, Kupper LL (1978) Applied regression analysis and other multivariate methods. J Mark Res 15(3):498. https://doi.org/10.2307/3150614
Vu HL, Ng KTW, Bolingbroke D (2018) Parameter interrelationships in a dual phase GIS-based municipal solid waste collection model. Waste Manage 78:258–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.050
Vu HL, Ng KTW, Richter A, Li J, Hosseinipooya SA (2022) Impacts of nested forward validation techniques on machine learning and regression waste disposal time series models. Ecol Inform 72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101897
Wang Y, Ng KTW, Asha AZ (2016) Non-hazardous waste generation characteristics and recycling practices in Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 18(4):715–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-015-0373-z
Weibull W (1951) A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J Appl Mech Am Soc Mech Eng 1951: 0–5
Xu Y, Li J, Tan Q, Peters AL, Yang C (2018) Global status of recycling waste solar panels: a review. Waste Manage 75:450–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.036
Yang Y (2015) Development of the regional freight transportation demand prediction models based on the regression analysis methods. Neurocomputing 158:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.01.069
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Monasib Romel contributed to the conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, result visualization, and preparing the initial draft. Golam Kabir and Kelvin Tsun Wai Ng contributed to the conceptualization, data curation, model validation, result visualization, drafting the final document, and project supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We declare that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
I, the undersigned, give my consent for the publication of identifiable details, which can include data, figures, and tables, and details within the text to be published in this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Table
Table
Table
Fig.
Weight-to-power ratio ((IRENA 2016)
Fig.
Weibull curve with two shape factors by Weibull (1951)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Romel, M., Kabir, G. & Ng, K.T.W. Prediction of photovoltaic waste generation in Canada using regression-based model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 8650–8665 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31628-9