Abstract
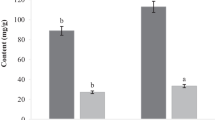
The present study is devoted to evaluate in vitro the chemical composition and the antioxidant and antibacterial properties of essential oils (Eo) extracted by hydrodistillation (HD) and microwave (MW) from the plant peels of Citrus sinensis. The extraction provided yields of 0.26% and 0.02%, respectively. The essential oils were analyzed by GC–MS whose major component is limonene that has a remarkable percentage (78.192% and 58.6%, respectively) for the essential oil extracted by HD and MW. The results of the antioxidant potential were noticeable in each of the essential oils with a higher priority to that extracted by hydrodistillation. The evaluation of the antioxidant power by the free radical scavenging method (DPPH) showed that the essential oils studied have good antioxidant activity, especially for the oil extracted by HD having presented an IC50 of (13.07 ± 0.169) mg/ml, while BHT and ascorbic acid showed very potent and effective anti-free radical activity with IC50 of the order of (19.54 ± 0.32) µg/ml and (1.17 ± 0.05) µg/ml respectively. According to the β-carotene/linoleic acid test, the oxidation of β-carotene was effectively inhibited by the two essential oils of Citrus sinensis peels with a percentage of inhibition of (56.46 ± 0.76) % and (31.39 ± 1.49) % respectively for HD and MW. Eo extracted by HD is more active than ascorbic acid (15.43%). In the antibacterial test, the activity was evaluated by the disc-diffusion method, the two types of sweet orange essential oils inhibited the growth of five bacterial strains out of six: The best activity was obtained against E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Agrobacterium with a diameter of the zone of inhibition between 70 and 84 mm, with the exception of the strain of Bacillus subtilis, there is no zone of inhibition has been observed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Amiri H (2010) Antioxidant activity of the essential oil and methanolic extract of Teucrium orientale (L.) subsp. taylori (Boiss.) Rech. f. Iran J Pharm Res 9(4):417–423
Belletti N, Nidagijimana M, Sisto C, Guerzoni ME, Lanciotti R, Gardini F (2004) Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of Citrus essences on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Agric Food Chem 52(23):6932–6938. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf049444v
Betoret E, Betoret N, Carbonell JV, Fito P (2009) Effects of pressure homogenization on particle size and the functional properties of citrus juices. J Food Eng 92(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.10.028
Bousbia N (2011) Extraction des huiles essentielles riches en anti-oxydants à partir de produits naturels et de co-produits agroalimentaires. Doctoral dissertation. Universitéd’Avignon et des Pays de Vaucluse & Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique (ENSA/ UAPV), p 128
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94(3):223–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022
Delaquis PJ, Stanich K, Girard B, Mazza G (2002) Antimicrobial activity of individual and mixed fraction of dill, cilantro, coriander and eucalyptus essential oil. Int J Food Microbiol 74(1–2):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(01)00734-6
Essawi T, Srour M (2000) Screening of some Palestinian medicinal plants for antibactérial activity. J Ethnopharmacol 70(3):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(99)00187-7
Favela-Hernández J, González-Santiago O, Ramírez-Cabrera E-F, Camacho-Corona M (2016) Chemistry and pharmacology of Citrus sinensis. Molecules 21(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020247
Ferhat MA, Boukhatem MN, Hazzit M, Chemat F (2018) Rapid extraction of volatile compounds from Citrus fruits using a microwave dry distillation. J Fundam Appl Sci 8(3):753. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfas.v8i3.6
Inouye S, Takizawa T, Yamaguchi H (2001) Antibacterial activity of essential oils and their major constituents against respiratory tract pathogens by gaseous contact. J Antimicrob Chemother 47(5):565–573. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/47.5.565
Jridi M, Boughriba S, Abdelhedi O, Nciri H, Nasri R, Kchaou H, Kaya M, Sebai H, Zouari N (2019) Nasri M (2019) Investigation of physicochemical and antioxidant properties of gelatin edible film mixed with blood orange (Citrus sinensis) peel extract. Food Packag Shelf Life 21:100342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100342
Kalemba D, Kunicka A (2003) Antibacterial and antifungal proerties of essential oils. Curr Med Chem 10:813–829. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867033457719
Kubola J, Siriamornpun S (2008) Phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) leaf, stem and fruit fraction extracts in vitro. Food Chem 110(4):881–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.076
Labiad MH, Harhar H, Ghanimi A, Tabyaoui M (2017) Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Moroccan Thymus satureioïdes extracts. J Mater Environ Sci 8(6):2132–2139 (ISSN: 2028-2508)
Makuba TS, Taba KM, Rosillon F, Wathelet B (2016) Contribution à l’étude de la désinfection de l’eau par photosensibilisation avec des extraits de plantes. C R Chim 19(7):827–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2016.01.012
McLafferty FW, Wesdemiotis C (1989) Isomeric characterization via ion neutralization and dissociation. Experimental variables Organic Mass Spectrometry 24:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/Oms.1210240824
Miraliakbari H, Shahidi F (2008) Oxidative stability of tree nut oils. J Agric Food Chem 56(12):4751–4759. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8000982
Mutai C, Bii C, Vagias C, Abatis D, Roussis V (2009) Antimicrobial activity of Acacia mellifera extracts and lupane triterpenes. J Ethnopharmacol 123(1):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2009.02.007
Nicholson WL, Munakata N, Horneck G, Melosh HJ, Setlow P (2000) Resistance of Bacillus Endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(3). https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.64.3.548-572.2000
Oussalah M, Caillet S, Saucier L, Lacroix M (2007) Inhibitory effects of selected plant essential oils on the growth of four pathogenic bacteria: E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 18:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2005.11.009
Rapisarda P, Bianco ML, Pannuzzo P, Timpanaro N (2008) Effect of cold storage on vitamin C, phenolics and antioxidant activity of five orange genotypes [Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck]. Postharvest Biol Technol 49(3):348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.02.002
Svoboda KP, Hampson JB (1999) Bioactivity of essential oils of selected temperate aromatic plants: antibacterial, antioxidant, antiinflammatory and other related pharmacological activities. Plant Biology Department, SAC Auchincruive, Ayr, Scotland, UK., KA65HW
Valko M, Rhodes CJB, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Yamaguchi T, Takamura H, Matoba T, Terao J (1998) HPLC Method for evaluation of the free radical-scavenging activity of foods by using 1,1-Diphenyl-2- picrylhydrazyl. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62(6):1201–1204. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.62.1201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Hinda HACIB, Zineb LAKACHE, Hamza ALIBOUDHAR, Affaf LAASSAMI, Hassina TOUNSSI, Somia HAMIL, and Abdelkrim KAMELI. First draft of the manuscript was written by Hinda HACIB, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. HH: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hacib, H., Lakache, Z., Aliboudhar, H. et al. Chemical composition and antioxidant and antibacterial properties of the essential oils extracted from Citrus sinensis peels by hydrodistillation and microwave methods. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31526-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31526-0