Abstract
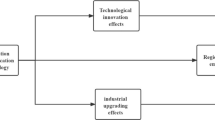
It is unidentified whether information communication technology (ICT) agglomeration can contribute to carbon reduction and to what extent it plays a role in energy conservation and emission reduction, and further exploration is urgently needed. Based on the panel data of 108 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2008 to 2019, the spatial panel Durbin model and intermediary effect model are employed to explore the effect of ICT agglomeration on carbon emissions and its pathways. It can be indicated from the results as below. (1) The local ICT agglomeration can reduce carbon emissions, but an increase in the level of ICT agglomeration in surrounding cities will increase local carbon emissions. (2) ICT agglomeration can reduce carbon emissions through reducing energy intensity and capital mismatch. (3) The effect of ICT agglomeration on carbon emissions is heterogeneous. ICT agglomeration can suppress carbon emissions in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, while it will increase carbon emissions in the upper reaches. ICT agglomeration increases carbon emissions in old industrial cities, reduces carbon emissions in non-old industrial cities, and has a more significant emission reduction effect in non-resource-based cities. We suggest promoting the formation of a coordinated linkage mechanism for ICT industry development and carbon emission reduction policies among regions, and implement differentiated ICT development strategies according to different industrial structure types.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the authors upon request.
References
Adedoyin FF, Bekun FV, Driha OM, Balsalobre LD (2020) The effects of air transportation, energy, ICT and FDI on economic growth in the industry 4.0 era: Evidence from the United States. Technol Forecast Soc 160:120297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120297
Amri F (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions, total factor productivity, ICT, trade, financial development, and energy consumption: testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia. Environ Sci Polluti R 25:33691–33701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3331-1
Antweiler W, Copeland B, Taylor M (2001) Is free trade good for the environment? Am Econ Rev 4:877–908. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.91.4.877
Arouri MEH, Youssef AB, M’henni H, Rault C (2012) Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energ Policy 45:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.02.042
Asongu S, Le Roux S, Nwachukwu J, Pyke C (2019) Reducing information asymmetry with ICT: a critical review of loan price and quantity effects in Africa. Int J Manag Financ. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMF-01-2018-0027
Bai JH, Liu YY (2018) Can outward foreign direct investment improve the resource misallocation of China. China Ind Econ 1:60–78. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.20180115.002
Batool Z, Ahmed N, Luqman M (2023) Examining the role of ict, transportation energy consumption, and urbanization in CO2 emissions in Asia: a threshold analysis. Environ Sci Pollut R 30(32):78482–78494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27995-y
Behrens K, Duranton G, Robert NF (2014) Productive cities: sorting, selection, and agglomeration. J Polit Econ 122(3):507–553. https://doi.org/10.1086/675534
Bosker M (2007) Growth, agglomeration and convergence: a space-time analysis for European regions. Spat Econ Anal 2(1):91–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/17421770701255237
Chen H, Hao Y, Li J, Song X (2018) The impact of environmental regulation, shadow economy, and corruption on environmental quality: theory and empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 9:200–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.206
Cheng S, Fan W, Meng F, Chen J, Cai B, Liu G, Yang Z (2020) Toward low-carbon development: assessing emissions-reduction pressure among Chinese cities. J Environ Manag 271:111036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111036
Ciccone A, Hall RE (1993) Productivity and the density of economic activity. NBER Work Pap. https://doi.org/10.3386/w4313
Cole MA, Elliott RJR, Okubo T (2010) Trade, environmental regulations and industrial mobility: an industry-level study of Japan. Ecol Econ 69(10):1995–2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2010.05.015
Combes PP (2000) Economic structure and local growth: France, 1984–1993. J Urban Econ 47(3):329–355. https://doi.org/10.1006/juec.1999.2143
Danish (2019) Effects of information and communication technology and real income on CO2 emissions: the experience of countries along Belt and Road. Telemat Inform 45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2019.101300
Dhakal S (2009) Urban energy use and carbon emissions from cities in China and policy implications. Energ Policy 37(11):4208–4219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.05.020
Dong F, Li Y, Zhang X, Zheng L (2021) How does industrial convergence affect the energy efficiency of manufacturing in newly industrialized countries? Fresh evidence from China. J Clean Prod 316:128316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128316
Duranton G, Overman HG (2005) Testing for localization using micro-geographic data. Rev Econ Stud 72(4):1077–1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/0034-6527.00362
Elhorst JP (2003) Specification and estimation of spatial panel data models. Int Regional Sci Rev 26(3):244–268. https://doi.org/10.1177/0160017603253791
Fong MWL (2009) Digital divide between urban and rural regions in China. Electron J Inf Syst Dev Countries 36(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1681-4835.2009
Fontagné L, Santoni G (2019) Agglomeration economies and firm-level labor misallocation. J Econ Geogr 19(1):251–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lby007
Geppert K, Gornig M, Werwatz A (2008) Economic growth of agglomerations and geographic concentration of industries: evidence for West Germany. Reg Stud 42(3):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343400701291518
Glaeser EL, Kahn ME (2010) The greenness of cities: carbon dioxide emissions and urban development. J Urban Econ 67(3):404–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2009.11.006
Glaeser EL, Kallal HD, Scheinkman JA, Shleifer A (1992) Growth in cities. J Polit Econ 100(6):1126–1152. https://doi.org/10.1086/261856
Goldfarb A, Tucker C (2019) Digital economics. J Econ Lit 57(1):3–43. https://doi.org/10.1257/jel.20171452
Guo S, Ma H (2023) Can urban digitalization significantly improve carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from 282 cities in China. Environ Sci Pollut R 30(19):55214–55236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26041-1
Han D, Ding Y, Shi Z, He Y (2022) The impact of digital economy on total factor carbon productivity: the threshold effect of technology accumulation. Env Sci Polluti R 29(37):55691–55706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19721-x
Heo PS, Lee DH (2019) Evolution of the linkage structure of ICT industry and its role in the economic system: the case of Korea. Inform Technol Dev 25(3):424–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/02681102.2018.1470486
Horner NC, Shehabi A, Azevedo IL (2016) Known unknowns: indirect energy effects of information and communication technology. Environ Res Lett 11(10):103001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/10/103001
Klimova A, Rondeau E, Andersson K, Zaslavsky A (2016) An international Master’ program in green ICT as a contribution to sustainable development. J Clean Prod 135:223–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/jclepro.2016.06.032
Koch T, Windsperger J (2017) Seeing through the network: competitive advantage in the digital economy. J Organ Des 6(1):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41469-017-0016-z
Lange S, Pohl J, Santarius T (2020) Digitalization and energy consumption. Does ICT reduce energy demand? Ecol Econ 176:106760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106760
Lee M, Zhang SZ, Ng H (2017) Development of an industrial Internet of things suite for smart factory towards re-industrialization. Adv Manuf 5:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-017-0197-2
Lee CC, Hussain J (2022) Optimal behavior of environmental regulations to reduce carbon emissions: a simulation-based dual green gaming model. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19710-0
Li Y, Yang X, Ran Q, Wu H, Irfan M, Ahmad M (2021) Energy structure, digital economy, and carbon emissions: evidence from China. Environ Sci Polluti R 28(45):64606–64629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15304-4
Liao G, Yao D, Hu Z (2020) The Spatial Effect of the Efficiency of Regional Financial Resource Allocation from the Perspective of Internet Finance: Evidence from Chinese Provinces. Emerg Mark Financ Tr 56(6):1211–1223. https://doi.org/10.1080/1540496X.2018.1564658
Lin X, Polenske KR (1995) Input–output anatomy of China’s energy use changes in the 1980s. Econ Syst Res 7(1):67–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/09535319500000011
Liobikienė G, Butkus M (2019) Scale, composition, and technique effects through which the economic growth, foreign direct investment, urbanization, and trade affect greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Energ 132:1310–1322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.09.032
Liu S, He N, Shi Y, Li G (2021) The roles logistics agglomeration and technological progress play in air pollution–new evidence in sub-regions of Chongqing. China J Clean Prod 317:128414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128414
Liu G, Wan S (2022) The impact of information and communication technology on carbon emissions in China: spatial effect and mechanism discussion. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23201-7
Luo K, Liu Y, Chen PF, Zeng M (2022) Assessing the impact of digital economy on green development efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energy Economics 112:106127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106127
Lyu W, Liu J (2021) Artificial Intelligence and emerging digital technologies in the energy sector. Appl Energ 303:117615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117615
Ma Q, Khan Z, Tariq M, Rjoub H (2022) Sustainable digital economy and trade adjusted carbon emissions: evidence from China’s provincial data. Econ Res-Ekon Istraz 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677x.2022.2028179
Mitra A, Sato H (2007) Agglomeration economies in Japan: technical efficiency, growth and unemployment. Review of Urban & Regional Development Studies: J Appl Reg Sci Conf. Melbourne, Australia: Blackwell Publishing Asia 19(3):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-940X.2007.00136.x
Moyer JD, Hughes BB (2021) ICTs: do they contribute to increased carbon emissions? Technol Forecast Soc 79(5):919–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2011.12.005
Obashi A, Kimura F (2021) New developments in international production networks: impact of digital technologies*. Asian Econ J 35(2):115–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/asej.12240
Pang QH, Li H, Yang TT (2019) Spatial correlation of carbon emissions in Yangze River economic zone and its influencing factors. Sci Technol Manag Res 39(15):246–251. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj202303008
Park C, Heo WG (2020) Review of the changing electricity industry value chain in the ICT convergence era. J Clean Prod 258:120743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120743
Porter ME (1998) Clusters and the new economics of competition[M]. Harvard Business Review, Boston
Shehzad K, Zaman U, Ahmad M, Liu X (2022) Asymmetric impact of information and communication technologies on environmental quality: analyzing the role of financial development and energy consumption. Env Develop Sus 24(2):1761–1780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01506-w
Shen Y, Hueng CJ, Hu W (2021) Measurement and spillover effect of digital financial inclusion: a cross-country analysis. Appl Econ Lett 28(20):1738–1743. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2020.1853663
Sun W, Huang C (2020) How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China J Clean Prod 272:122828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122828
Tao S, Wang Y, Zhai Y (2023) Can the application of artificial intelligence in industry cut china’s industrial carbon intensity? Environ Sci Pollut R 30(33):79571–79586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27964-5
Thompson P, Williams R, Thomas B (2013) Are UK SMEs with active web sites more likely to achieve both innovation and growth? J Small Bus Enterp D. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-05-2012-0067
Tveteras R, Battese GE (2006) Agglomeration externalities, productivity, and technical inefficiency. J Regional Sci 46(4):605–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2006.00470.x
Ulucak R, Khan D (2020) Does information and communication technology affect CO2 mitigation under the pathway of sustainable development during the mode of globalization? Sustain Dev 28(4):857–867. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2041
Ushifusa Y, Tomohara A (2013) Productivity and labor density: agglomeration effects over time. Atlantic Econ J 41:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11293-012-9354-y
Van AB, Inklaar R, McGuckin RH (2003) ICT and Productivity in Europe and the United States Where do the differences come from? Cesifo Econ Stud 49(3):295–318. https://doi.org/10.1093/cesifo/49.3.295
Wang B, Yu M, Zhu Y, Bao P (2021a) Unveiling the driving factors of carbon emissions from industrial resource allocation in China: a spatial econometric perspective. Energ Policy 158:112557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112557
Wang L, Chen Y, Ramsey TS, Hewings GJ (2021) Will researching digital technology really empower green development? Technol Soc 66:101638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101638
Wang J, Dong X, Dong K (2022a) How does ICT agglomeration affect carbon emissions? The case of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration in China. Energ Econ 111:106107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022b.106107
Wang J, Dong K, Dong X, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022b) Assessing the digital economy and its carbon-mitigation effects: the case of China. Energ Econ 113:106198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106198
Warner J, Zawahri N (2012) Hegemony and asymmetry: multiple-chessboard games on transboundary rivers. Int Environ Agreem-P 12:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10784-012-9177-y
Wu J, Guo Z (2016) Convergence analysis of carbon emissions in China based on continuous dynamic distribution method. Statistical Res 33:54–60. https://doi.org/10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2016.01.008
Wu L, Kaneko S, Matsuoka S (2005) Driving forces behind the stagnancy of China’s energy-related CO2 emissions from 1996 to 1999: the relative importance of structural change, intensity change and scale change. Energ Policy 33(3):319–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.08.003
Wu H, Xue Y, Hao Y, Ren S (2021a) How does internet development affect energy-saving and emission reduction? Evidence from China Energ Econ 103:105577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105577
Wu J, Xu H, Tang K (2021b) Industrial agglomeration, CO2 emissions and regional development programs: a decomposition analysis based on 286 Chinese cities. Energ 225:120239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120239
Wu L, Sun L, Qi P, Ren X, Sun X (2021c) Energy endowment, industrial structure upgrading, and CO2 emissions in China: revisiting resource curse in the context of carbon emissions. Resour Policy 74:102329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102329
Yang N, Yuan X, Qin F, Qian F (2022) Coagglomeration of manufacturing and producer services: how does it affect regional innovation in China? Appl Spat Anal Policy 15(4):1411–1432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12061-022-09463-1
Yi M, Liu Y, Sheng MS, Wen L (2022) Effects of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: New evidence from China. Energ Policy 171:113271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113271
Yu N, Roo G, Jong M, Storm S (2016) Does the expansion of a motorway network lead to economic agglomeration? Evidence from China Transport Policy 1:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2015.03.014
Yuan B, Li C, Yin H, Zeng M (2022) Green innovation and China’s CO2 emissions–the moderating effect of institutional quality. J Environ Plann Man 65(5):877–906. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2021.1915260
Zhang L, Mu R, Zhan Y, Yu J, Liu L, Yu Y, Zhang J (2022a) Digital economy, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions: evidence from provincial panel data in China. Sci Total Environ 852:158403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158403
Zhang W, Liu X, Wang D, Zhou J (2022b) Digital economy and carbon emission performance: evidence at China’s city level. Energ Policy 165:112927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112927
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 42201184) and the Project of Jiangxi Social Science Foundation in 2022 (22YJ30) and China Scholarship Council (202006825025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tianran Guo: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Ling Bai: conceptualization, data curation, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition. Huilin Chen: methodology, validation, and visualization. Kang Luo: data curation and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, T., Bai, L., Chen, H. et al. Effects of ICT agglomeration on carbon emission reduction: New evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110869–110887 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30104-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30104-8