Abstract
The study aims to examine the relationship between carbon emissions and ecological footprints with economic complexity, core pollution indicators, urbanization, globalization, and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption in eight emerging Asian economies from 1971 to 2020. A panel data framework that considers cross-sectional dependence and heterogeneity was used for analysis. The Pedroni and Johnsen Fisher cointegration showed that carbon emission, ecological footprint, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, globalization, and urbanization confirmed the presence of cointegration. Moreover, fully modified ordinary least squares (FMOLS) and dynamic ordinary least squares (DLOS) indicated that globalization, non-renewable energy consumption, and economic complexity increase emission and ecological footprint in the long run, whereas renewable energy generated through biomass, solar, and wind decreases environmental degradation. Furthermore, urbanization also negatively affects the environment. From a policy perspective, policymakers in these countries may manage their natural resources efficiently by escalating the share of renewables in total energy production, offering tax holidays, incentives and encouraging companies to install clean energy plant, and providing support to research and development-oriented companies to engage in research activities to reduce the cost of production of renewable energy.

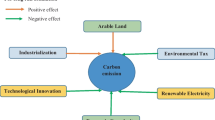
Source: author’s own contribution
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided upon request.
Abbreviations
- ECI :
-
Ecological foot print index
- CO2 :
-
Carbon emission
- FMLOS :
-
Fully modified ordinary least squares
- DLOS :
-
Dynamic ordinary least squares
- GDP :
-
Gross domestic product
- NREC :
-
Non-renewable energy consumption
- REC :
-
Renewable energy consumption
- Ln :
-
Natural log
References
Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environ Dev Sustain 23(11):16057–16082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01322-2
Adeola O, Evans O (2017) Financial inclusion, financial development, and economic diversification in Nigeria. J Dev Areas 51(3):1–15
Ahmad A, Zhao Y, Shahbaz M, Bano S, Zhang Z, Wang S, Liu Y (2016) Carbon emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth: an aggregate and disaggregate analysis of the Indian economy. Energy Policy 96:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.05.032
Ahmed C, Mohammed A, Saboonchi A (2020) ArcGIS mapping, characterizations and modelling the physical and mechanical properties of the Sulaimani City soils, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Geomech Geoeng 1–14
Ahmed MM, Shimada K (2019) The effect of renewable energy consumption on sustainable economic development: evidence from emerging and developing economies. Energies 12(15):2954
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Lean HH (2016) The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat Hazards 79(1):621–644
Ali G, Pumijumnong N, Cui S (2017) Decarbonization action plans using hybrid modeling for a low-carbon society: the case of Bangkok Metropolitan Area. J Clean Prod 168:940–951
Ali A, Kamarulzaman R, Soetrisno FK, Razimi MSA (2020a) Wavelet analysis of renewable, non-renewable energy consumption and environmental degradation as a precursor to economic Growth: evidence from Malaysia. Int J Energy Econ Policy 10(3):182
Ali HS, Nathaniel SP, Uzuner G, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2020b) Trivariate modelling of the nexus between electricity consumption, urbanization and economic growth in Nigeria: fresh insights from Maki Cointegration and causality tests. Heliyon 6(2):e03400
Alola AA, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2019) Dynamic impact of trade policy, economic growth, fertility rate, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in Europe. Sci Total Environ 685:702–709
Alper A, Oguz O (2016) The role of renewable energy consumption in economic growth: evidence from asymmetric causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:953–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.123
Ang JB (2008) A survey of recent developments in the literature of finance and growth. J Econ Surv 22(3):536–576
Ansari MA, Haider S, Khan N (2020) Environmental Kuznets curve revisited: an analysis using ecological and material footprint. Ecol Ind 115:106416
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Ind 52:16–22
Apergis N, Christou C, Gupta R (2017) Are there environmental Kuznets curves for US state-level CO2 emissions? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69(October 2015):551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.219
Arain H, Sharif A, Akbar B, Younis MY (2020) Dynamic connection between inward foreign direct investment, renewable energy, economic growth and carbon emission in China: evidence from partial and multiple wavelet coherence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(32):40456–40474
Aslan A, Destek MA, Okumus I (2018) Bootstrap rolling window estimation approach to analysis of the environment Kuznets curve hypothesis: evidence from the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(3):2402–2408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0548-3
Aye GC, Edoja PE (2017) Effect of economic growth on CO2 emission in developing countries: evidence from a dynamic panel threshold model. Cogent Econ Finance 5(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2017.1379239
Azizalrahman H (2019) A model for urban sector drivers of carbon emissions. Sustain Cities Soc 44:46–55
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113:356–367
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Sinha A (2020) The dynamic effects of globalization process in analysing N-shaped tourism led growth hypothesis. J Hosp Tour Manag 43(February):42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2020.02.005
Battaglini E (2012) Coalition formation and endogenous strategic timing. Rev Econ Stud 79(4):1227–1257
Baz K, Xu D, Ali H, Ali I, Khan I, Khan MM, Cheng J (2020) Asymmetric impact of energy consumption and economic growth on ecological footprint: using asymmetric and nonlinear approach. Sci Total Environ 718:137364
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019a) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Bekun FV, Emir F, Sarkodie SA (2019b) Another look at the relationship between energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth in South Africa. Sci Total Environ 655:759–765
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S, Ozturk I (2013) The environmental Kuznets curve: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade openness
Bhat JA (2018) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption—impact on economic growth and CO2 emissions in five emerging market economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(35):35515–35530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3523-8
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü (2016) The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: a revisited environmental Kuznets curve approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:838–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.080
Bölük G, Mert M (2014) Fossil & renewable energy consumption, GHGs (greenhouse gases) and economic growth: evidence from a panel of EU (European Union) countries. Energy 74:439–446
Boutabba MA (2014) The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: evidence from the Indian economy. Econ Model 40:33–41
Can M, Gozgor G (2017) The impact of economic complexity on carbon emissions: evidence from France. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(19):16364–16370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9219-7
Caviglia-Harris JL, Chambers D, Kahn JR (2009) Taking the “U” out of Kuznets: a comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation. Ecol Econ 68(4):1149–1159
Charfeddine L, Ben Khediri K (2016) Financial development and environmental quality in UAE: cointegration with structural breaks. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:1322–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.059
Charfeddine L, Mrabet Z (2017) The impact of economic development and social-political factors on ecological footprint: a panel data analysis for 15 MENA countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:138–154
Chen C-Z, Lin Z-S (2008) Multiple timescale analysis and factor analysis of energy ecological footprint growth in China 1953–2006. Energy Policy 36(5):1666–1678
Chen B, Chen G, Yang Z, Jiang M (2007) Ecological footprint accounting for energy and resource in China. Energy Policy 35(3):1599–1609
Chen DD, Gao WS, Chen YQ, Zhang Q (2010) Ecological footprint analysis of food consumption of rural residents in China in the latest 30 years. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 1:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2010.09.013
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhong Z (2019) CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy production and foreign trade in China. Renew Energy 131:208–216
Chin AW, Chu JT, Perera MR, Hui KP, Yen H-L, Chan MC, Peiris M, Poon LL (2020) Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe 1(1):e10
Cho C-H, Chu Y-P, Yang H-Y (2014) An environment Kuznets curve for GHG emissions: a panel cointegration analysis. Energy Sources Part B: Econ Plan Policy 9(2):120–129
Christmann P, Taylor G (2001) Globalization and the environment: determinants of firm self-regulation in China. J Int Bus Stud 32(3):439–458
Danish, Hassan ST, Baloch MA, Mahmood N, Zhang JW (2019) Linking economic growth and ecological footprint through human capital and biocapacity. Sustain Cities Soc 47(January):101516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101516
Danish S, Zafar-ul-Hye M, Mohsin F, Hussain M (2020) ACC-deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and biochar mitigate adverse effects of drought stress on maize growth. PLoS One 15(4):e0230615
Dauvergne P, Lister J (2012) Big brand sustainability: governance prospects and environmental limits. Glob Environ Chang 22(1):36–45
Dean JM (2002) Does trade liberalization harm the environment? A new test. Can. J. Econ/Revue canadienne d’économique 35(4):819–842
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489
Destek MA, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2018) Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: the role of ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29387–29396
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1074–1085
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5323-8
Dogan E, Taspinar N, Gokmenoglu KK (2019) Determinants of ecological footprint in MINT countries. Energy Environ 30(6):1065–1086
Doğan B, Saboori B, Can M (2019) Does economic complexity matter for environmental degradation? An empirical analysis for different stages of development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(31):31900–31912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06333-1
Dong K, Sun R, Jiang H, Zeng X (2018) CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: what roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J Clean Prod 196:51–63
Du K, Li P, Yan Z (2019) Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 146:297–303
Engle RF, Granger CW (1987) Co-integration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 251–276
Eren BM, Taspinar N, Gokmenoglu KK (2019) The impact of financial development and economic growth on renewable energy consumption: empirical analysis of India. Sci Total Environ 663:189–197
Evans O (2019) Repositioning for increased digital dividends: Internet usage and economic well-being in sub-Saharan Africa. J Glob Inf Technol Manag 22(1):47–70
Fan J, Zhou L (2019) Impact of urbanization and real estate investment on carbon emissions: evidence from China’s provincial regions. J Clean Prod 209:309–323
Fan Y, Liu LC, Wu G, Wei YM (2006) Analyzing impact factors of CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model. Environ Impact Assess Rev 26(4):377–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2005.11.007
Faria WR, Almeida AN (2016) Relationship between openness to trade and deforestation: empirical evidence from the Brazilian Amazon. Ecol Econ 121:85–97
Fiala N (2008) Measuring sustainability: Why the ecological footprint is bad economics and bad environmental science. Ecol Econ 67(4):519–525
Gasimli O, Naradda Gamage SK, Shihadeh F, Rajapakshe PSK, Shafiq M (2019) Energy, trade, urbanization and environmental degradation nexus in Sri Lanka: bounds testing approach. Energies 12(9):1655
Gokmenoglu KK, Sadeghieh M (2019) Financial development, CO2 emissions, fossil fuel consumption and economic growth: the case of Turkey. Strateg Plan Energy Environ 38(4):7–28
Gökmenolu S, Taspinar N (2016) FDI, energy consumption, and environmental pollution: A comparative study of Turkey and Mexico. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):12214–12228
Gorus MS, Aydin M (2019) The effect of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: A case study of emerging economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(15):15032–15043
Gozgor G (2017) Does trade matter for carbon emissions in OECD countries? Evidence from a new trade openness measure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(36):27813–27821
Hanif I, Raza SMF, Gago-de-Santos P, Abbas Q (2019) Fossil fuels, foreign direct investment, and economic growth have triggered CO2 emissions in emerging Asian economies: some empirical evidence. Energy 171:493–501
Haseeb A, Xia E, Baloch MA, Abbas K (2018) Financial development, globalization, and CO 2 emission in the presence of EKC: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(31):31283–31296
Hassan ST, Xia E, Khan NH, Shah SMA (2019) Economic growth, natural resources, and ecological footprints: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2929–2938
Hidalgo CAHR (2009) The building blocks of quality. Proc Natl Acad Sci 06(26):10570–10575
Hidalgo CAHR (2021) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, CO2 emissions, and ecological footprint in the USA: testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):846–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10446-3
Hidalgo CA, Hausmann R (2009) The building blocks of economic complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(26):10570–10575
Ho S-Y, Iyke BN (2019) Trade openness and carbon emissions: evidence from central and eastern European countries. Rev Econ 70(1):41–67
Hossain MS (2011) Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 39(11):6991–6999
Hu A, Li S, Zhang L, Wang H, Yang J, Luo Z, Rashid A, Chen S, Huang W, Yu C-P (2018) Prokaryotic footprints in urban water ecosystems: a case study of urban landscape ponds in a coastal city, China. Environ Pollut 242:1729–1739
Hurlin C, Mignon V (2007) Second generation panel unit root tests
Ike GN, Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020) Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries. Sci Total Environ 721:137813
International Energy Agency (2019) World Energy Outlook 2019. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/worldenergy-outlook-2019
International Monetary Fund (2021) World Economic Outlook Database, October 2021. Retrieved from https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO
Jalil A, Mahmud SF (2009) Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy 37(12):5167–5172
Jiang Y, Khaskheli A, Raza SA, Qureshi MA, Ahmed M (2021) Threshold non-linear relationship between globalization, renewable energy consumption, and environmental degradation: evidence from smooth transition models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:13323–13339
Jinke L, Hualing S, Dianming G (2008) Causality relationship between coal consumption and GDP: difference of major OECD and non-OECD countries. Appl Energy 85(6):421–429
Kalmaz DB, Kirikkaleli D (2019) Modeling CO 2 emissions in an emerging market: empirical finding from ARDL-based bounds and wavelet coherence approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(5):5210–5220
Kaltenegger O, Löschel A, Pothen F (2017) The effect of globalisation on energy footprints: disentangling the links of global value chains. Energy Econ 68:148–168
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econ 90(1):1–44
Katircioglu S, Gokmenoglu KK, Eren BM (2018) Testing the role of tourism development in ecological footprint quality: evidence from top 10 tourist destinations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(33):33611–33619
Kennedy C, Pincetl S, Bunje P (2011) The study of urban metabolism and its applications to urban planning and Design. Environ Pollut 159(8–9):1965–1973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.10.022
Khan MA, Khan MZ, Zaman K, Ahmad M (2019) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and environmental degradation: a panel data analysis of selected Asian countries. Renew Energy 139:1291–1297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.02.066
Khan MK, Khan MI, Rehan M (2020) The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan. Financ Innov 6(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-019-0162-0
Khan Z, Ali S, Dong K, Li RYM (2021) How does fiscal decentralization affect CO2 emissions? The roles of institutions and human capital. Energy Econ 94:105060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2020.105060
Kim S-H, Han S-K, Shin H-S (2004) Kinetics of LCFA inhibition on acetoclastic methanogenesis, propionate degradation and β-oxidation. J Environ Sci Health Part A 39(4):1025–1037
Kirikkaleli D, Alper A, Delen D (2021) Exploring the dynamics of renewable energy consumption, real GDP, and carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from G7 countries. Renew Energ 165:1176–1185
Kissinger M, Gottlieb D (2012) From global to place oriented hectares—the case of Israel’s wheat ecological footprint and its implications for sustainable resource supply. Ecol Ind 16:51–57
Koçak E, Ulucak R, Dedeoğlu M, Ulucak ZŞ (2019) Is there a trade-off between sustainable society targets in sub-Saharan Africa? Sustain Cities Soc 51:101705
Lapatinas A, Garas A, Boleti E, Kyriakou A (2019) Economic complexity and environmental performance: evidence from a world sample
Lee C-C, Chang C-P (2005) Structural breaks, energy consumption, and economic growth revisited: evidence from Taiwan. Energy Econ 27(6):857–872
Lee KH, Min B (2014) Globalization and carbon constrained global economy: a fad or a trend? J Asia-Pac Bus 15(2):105–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/10599231.2014.904181
Li P, Yang G (2007) Ecological footprint study on tourism itinerary products in Shangri-La, Yunnan Province, China. Acta Ecol Sin 27(7):2954–2963
Li S, Zhou C, Wang S (2019) Does modernization affect carbon dioxide emissions? A panel data analysis. Sci Total Environ 663:426–435
Liddle B, Lung S (2010) Age-structure, urbanization, and climate change in developed countries: revisiting STIRPAT for disaggregated population and consumption-related environmental impacts. Popul Environ 31(5):317–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11111-010-0101-5
Ling CH, Ho HS, Ding X (2015) Nexus between carbon dioxide emissions, foreign direct investment, and economic growth: Fresh evidence from dynamic simultaneous-equation models. Sustainability 7(12):15670–15688
Lv Z, Xu T (2018) Is economic globalization good or bad for the environmental quality? New evidence from dynamic heterogeneous panel models. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 137(August):340–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.08.004
Magani F (2004) Fish echo classification using an a priori physical model: advantaines ani) limitations. 133
Maji IK, Abdul-Rahim A, Ndawayo AB, Ofozor CA, Basiru HA, Mubarak SMB (2017) The relationship between income, energy consumption, population and deforestation for environmental quality in Nigeria. Int J Green Econ 11(3–4):204–216
McAusland C (2010) Globalisation’s direct and indirect effects on the environment
Mesagan EP, Olunkwa CN (2020) Energy consumption, capital investment and environmental degradation: the African experience. AGDI Working Paper
Nathaniel S, Khan SAR (2020) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy, trade, and ecological footprint in ASEAN countries. J Clean Prod 272:122709
Neagu O (2019) The link between economic complexity and carbon emissions in the European Union countries: a model based on the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) approach. Sustainability (Switzerland) 11(17). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174753
Neagu O, Teodoru MC (2019) The relationship between economic complexity, energy consumption structure and greenhouse gas emission: heterogeneous panel evidence from the EU countries. Sustainability 11(2):497
Nikolova M (2015) The need to evaluate ecosystem benefits. Bus Manag 02:09
Nkengfack H, Fotio HK (2019) Energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: evidence from the top three emitters in Africa. Mod Econ 10(1):52–71
Omri A, Daly S, Rault C, Chaibi A (2015) Financial development, environmental quality, trade and economic growth: what causes what in MENA countries. Energy Econ 48:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2015.01.008
Owusu PA, Asumadu-Sarkodie S (2016) A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng 3(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2016.1167990
Paramati SR, Mo D, Gupta R (2017) The effects of stock market growth and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Energy Econ 66:360–371
Pata UK (2021) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic complexity, CO 2 emissions, and ecological footprint in the USA: testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):846–861
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):653–670
Pedroni P (2001) Purchasing power parity tests in cointegrated panels. Rev Econ Stat 83(4):727–731
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theor 20(3):597–625
Pesaran MH (2015) Testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels. Economet Rev 34(6–10):1089–1117
Pham H, Ho VT, Maani KE (2020) Sustainable development, FDI and environmental quality: New evidence from Asian economies. J Clean Prod 252:119848
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manage 244:265–275
Rahman S (2020) Renewable energy. ISEAS Publishing, In Renewable energy
Raza N, Jawad S, Shahzad H, Kumar A, Shahbaz M (2016) Asymmetric impact of gold, oil prices and their volatilities on stock prices of emerging markets. Resour Policy 49:290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2016.06.011
Raza S, Qamar S, Ahmed M (2021) Asymmetric role of non-renewable energy consumption, ICT, and financial development on ecological footprints: evidence from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(23):29909–29922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14208-1
Raza AS, Shah N, Sharif A, Shahbaz M (2022) A revisit of the globalization and carbon dioxide emission nexus. Energy-Growth Nexus Era Glob 383–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-824440-1.00002-3
Rees W, Wackernagel M (2012) Urban ecological footprints: why cities cannot be sustainable–and why they are a key to sustainability. In The urban sociology reader (pp. 171–180). Routledge
Saidi K, Mbarek MB (2016) Nuclear energy, renewable energy, CO2 emissions, and economic growth for nine developed countries: evidence from panel Granger causality tests. Prog Nucl Energy 88:364–374
Saint Akadiri S, Alkawfi MM, Uğural S, Akadiri AC (2019) Towards achieving environmental sustainability target in Italy. The role of energy, real income and globalization. Sci Total Environ 671:1293–1301
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I, Sohag K (2018) The effects of electricity consumption, economic growth, financial development and foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Kuwait. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:2002–2010
Salahuddin M, Ali MI, Vink N, Gow J (2019) The effects of urbanization and globalization on CO 2 emissions: evidence from the sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2699–2709
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V, Weldekidan H, Asamoah EF, Owusu PA, Doyi INY (2019) Environmental sustainability assessment using dynamic autoregressive-distributed lag simulations—nexus between greenhouse gas emissions, biomass energy, food and economic growth. Sci Total Environ 668:318–332
Sassen S (1991) The global city. Princeton University Press
Saud S, Chen S, Haseeb A (2020a) The role of financial development and globalization in the environment: accounting ecological footprint indicators for selected one-belt-one-road initiative countries. J Clean Prod 250:119518
Saud S, Chen S, Haseeb A, Sumayya (2020b) The role of financial development and globalization in the environment: accounting ecological footprint indicators for selected one-belt-one-road initiative countries. J Clean Prod 250:119518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119518
Saudi MHM (2019) The role of renewable, non-renewable energy consumption and technology innovation in testing environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia
Shafiei S, Salim RA (2014) Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 66:547–556
Shafik N (1994) Economic development and environmental quality: an econometric analysis. Oxf Econ Pap 46:757–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/oep/46.Supplement_1.757
Shahbaz M, Loganathan N, Zeshan M, Zaman K (2015a) Does renewable energy consumption add in economic growth? An application of auto-regressive distributed lag model in Pakistan. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 44:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.01.017
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015b) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Ind 52:379–393
Shahbaz M, Zakaria M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018) The energy consumption and economic growth nexus in top ten energy-consuming countries: Fresh evidence from using the quantile-on-quantile approach. Energy Econ 71:282–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.02.023
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017) The impact of globalization on co 2 emissions in China. 62(3). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217590817400331
Sharif A, Ali Raza SA (2016) The impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on economic growth: Evidence from low-, middle- and high-income countries. Renew Energ 91:370–381
Shujah-ur-Rahman, Chen S, Saud S, Saleem N, Bari MW (2019) Nexus between financial development, energy consumption, income level, and ecological footprint in CEE countries: do human capital and biocapacity matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(31):31856–31872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06343-z
Solarin SA, Bello MO (2018) Persistence of policy shocks to an environmental degradation index: the case of ecological footprint in 128 developed and developing countries. Ecol Indic 89(December 2017):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.01.064
Stern DI (1993) Energy use and economic growth. Energy Econ 15(2):137–150
Swart J, Brinkmann L (2020) Economic complexity and the environment: evidence from Brazil. 3–45
TemizDinç D, Akdoğan EC (2019) Renewable energy production, energy consumption and sustainable economic growth in Turkey: a VECM approach. Sustainability 11(5):1273
Thomakos DD, Alexopoulos TA (2016) Carbon intensity as a proxy for environmental performance and the informational content of the EPI. Energy Policy 94(2016):179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.03.030
Tietenberg T, Folmer H (2005) The international yearbook of environmental and resource economics 2005/2006: a survey of current issues. Edward Elgar Publishing
Topcu M, Tugcu CT (2020) The impact of renewable energy consumption on income inequality: evidence from developed countries. Renew Energy 151:1134–1140
Udemba EN (2020) A sustainable study of economic growth and development amidst ecological footprint: new insight from Nigerian Perspective. Sci Total Environ 732:139270
Ullah A, Ahmed M, Raza SA, Ali S (2021) A threshold approach to sustainable development: nonlinear relationship between renewable energy consumption, natural resource rent, and ecological footprint. J Environ Manage 295:113073
Usman O, Akadiri SS, Adeshola I (2020) Role of renewable energy and globalization on ecological footprint in the USA: implications for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:30681–30693
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1998) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth (Vol. 9). New society publishers
Wang J, Dong K (2019) What drives environmental degradation? Evidence from 14 sub-Saharan African countries. Sci Total Environ 656:165–173
Yilanci V, Pata UK (2020) Investigating the EKC hypothesis for China: the role of economic complexity on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32683–32694
Zafar MW, Shahbaz M, Hou F, Sinha A (2019a) From nonrenewable to renewable energy and its impact on economic growth: the role of research & development expenditures in Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. J Clean Prod 212:1166–1178
Zafar MW, Zaidi SAH, Khan NR, Mirza FM, Hou F, Kirmani SAA (2019b) The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: the case of the United States. Resour Policy 63(May):101428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101428
Zhang Y, Huang K, Yu Y, Yang B (2017) Mapping of water footprint research: a bibliometric analysis during 2006–2015. J Clean Prod 149:70–79
Zhao S, Li Z, Li W (2005) A modified method of ecological footprint calculation and its application. Ecol Model 185(1):65–75
Zhao J, Jiang Q, Dong X, Dong K, Jiang H (2022) How does industrial structure adjustment reduce CO2 emissions? Spatial and mediation effects analysis for China. Energy Econ 105:105704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105704
Funding
The study is supported by the Startup Foundation (Grant No. 2020R068) for Introducing Talent of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (NUIST), People’s Republic of China, and the Key Program of National Social Science Fund of China (No. 21AZD067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Asim Rafiq and Abdul Rauf: conceptualization, data curation, and writing—original draft. Ameer Muhammad Aamir Abbas and Saifullah Shakir: formal analysis, data handling, and methodology. Abdul Rauf and Saira Abid: writing—review and editing and variable construction. T. Guo: writing—review and editing. Muhammad Asim Rafiq: supervision. Huaping Sun: funding acquisition. Ameer Muhammad Aamir Abbas: writing—review and editing. These authors contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rafiq, M.A., Rauf, A., Shakir, S. et al. Exploring the Intertwined Nexus between Globalization, Energy Usage, Economic Complexity, and Environmental Quality in Emerging Asian Economies: A Pathway Towards a Greener Future. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 100431–100449 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29330-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29330-x