Abstract
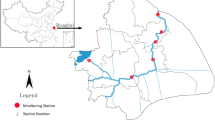
In this study, we employed the random forest model to identify the riparian buffer zone in the upper and middle reaches of the Ziwu River, used the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to simulate and calculate the nonpoint source pollution load in the riparian buffer zone, and used empirical formulas to estimate the pollutant concentration when surface runoff passes the edge of the riparian buffer zone. Moreover, through correlation analysis, we identified the main factors that affect the safe width of the riparian buffer zone. By combining these factors with the characteristic parameters of the riparian buffer zone and the water quality demand, we analyzed and calculated the safe width of the riparian buffer zone. Our findings are as follows: ① the simulated values of the SWAT model were highly consistent with the measured values. Specifically, the calibration and verification results of the hydrological station achieved Ens ≥ 0.65, RE < ± 15%, and R2 ≥ 0.85, while the overall total nitrogen and total phosphorus loads achieved Ens ≥ 0.65, RE < ± 15%, and R2 > 0.65. ② We found that the total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) loads in the riparian buffer zone gradually increased from upstream to downstream. Among these loads, the normal season had the largest TN and TP concentrations reaching the edge of the riparian buffer zone, while the dry season had the minimum concentrations. ③ The factors affecting the safe width of the riparian buffer zone included the connectivity, slope of the buffer zone, cultivated land area, and regional population density. For the effective protection of water quality, it is recommended that the upstream, midstream, and downstream buffer zones be at least 77.9 m, 33.37 m, and 60.25 m wide, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aguiar TR, Bortolozo FR, Hansel FA, Rasera K, Ferreira MT (2015) Riparian Buffer zones as pesticide filters of no-till crops. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(14):10618–10626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4281-5
Azimi S, Dariane AB, Modanesi S, Bauer-Marschallinger B, Bindlish R, Wagner W, Massari C (2020) Assimilation of Sentinel 1 and Smap – based satellite soil moisture retrievals into swat hydrological model: the impact of satellite revisit time and product spatial resolution on flood simulations in small basins. J Hydrol 581:124367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124367
Bai X, Shen W, Wang P, Chen X, He Y (2020) Response of non-point source pollution loads to land use change under different precipitation scenarios from a future perspective. Water Resour Manag 34(13):3987–4002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02626-0
Bentrup G (2008) Conservation buffers: design guidelines for buffers, corridors, and greenways. Washington, D.C: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Southern Research Station Asheville, NC. pp. 32–37. https://doi.org/10.2737/SRS-GTR-109
Brezonik PL, Stadelmann TH (2002) Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area, Minnesota, USA. Water Res 36(7):1743–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00375-X
Busico G, Colombani N, Fronzi D, Pellegrini M, Tazioli A, Mastrocicco M (2020) Evaluating swat model performance, considering different soils data input, to quantify actual and future runoff susceptibility in a highly urbanized basin. J Environ Manag 266:110625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110625
Chen HT, Chen J, Liu YY, He J (2021) Study of nitrogen pollution simulation and management measures on swat model in typhoon period of Shanxi Reservoir Watershed, Zhejiang Province, China. Pol J Environ Stud 30(3):2499–2507. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/130038
China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization (2019) Code for design of building water supply and drainage (GB 50015–2019). China Construction Industry Press, Beijing
Dakhlalla AO, Parajuli PB (2019) Assessing model parameters sensitivity and uncertainty of streamflow, sediment, and nutrient transport using swat. Inf Process Agric 6(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2018.08.007
Department of rural socio - economic investigation, National Bureau of Statistics (2020) Agricultural Statistics of China (1949–2019). China Statistics Press, Beijing
Deval C, Brooks ES, Dobre M, Lew R, Robichaud PR, Fowler A, Boll J, Easton ZM, Collick AS (2022) Pi-Vat: a web-based visualization tool for decision support using spatially complex water quality model outputs. J Hydro 607:127529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127529
Gene SM, Hoekstra PF, Hannam C, White M, Truman C, Hanson ML, Prosser RS (2019) The role of vegetated buffers in agriculture and their regulation across Canada and the United States. J Environ Manag 243:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.003
Graziano MP, Deguire AK, Surasinghe TD (2022) Riparian buffers as a critical landscape feature: insights for riverscape conservation and policy renovations. Diversity 14(3):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14030172
Han X, Xiao J, Wang L, Tian S, Liang T, Liu Y (2021) Identification of areas vulnerable to soil erosion and risk assessment of phosphorus transport in a typical watershed in the Loess Plateau. Sci Total Enviro 758:143661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143661
Hilary B, Chris B, North BE, Angelica Maria AZ, Sandra Lucia AZ, Carlos Alberto QG, Beatriz LG, Rachael E, Andrew W (2021) Riparian buffer length is more influential than width on river water quality: a case study in Southern Costa Rica. J Environ Manag 286:112132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112132
Hou G, Zheng J, Cui X, He F, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li X, Fan C, Tan B (2022) Suitable coverage and slope guided by soil and water conservation can prevent non-point source pollution diffusion: a case study of grassland. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 241:113804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113804
Jiang K, Li Z, Luo C, Wu M, Chao L, Zhou Q, Zhao H (2019) The reduction effects of riparian reforestation on runoff and nutrient export based on Annagnps model in a small typical watershed, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5934–5943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4030-7
Jou MHH, Khojasteh DN, Besalatpour AA (2019) Land use planning based on soil and water assessment tool model in a mountainous watershed to reduce runoff and sediment load. Can J Soil Sci 99(3):305–320. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjss-2018-0109
King SE, Osmond DL, Smith J, Burchell MR, Dukes M, Evans RO, Knies S, Kunickis S (2016) Effects of riparian buffer vegetation and width: a 12-Year longitudinal study. J Environ Qual 45(4):1243–1251. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2015.06.0321
Koycegiz C, Buyukyildiz M (2019) Calibration of Swat and two data-driven models for a data-scarce mountainous headwater in Semi-Arid Konya Closed Basin. Water 11(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010147
Lai Q, Ma J, He F, Wei G (2022) Response model for urban area source pollution and water environmental quality in a river network region. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(17):10546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710546
Lee D, Dillaha TA, Sherrard JH (1989) Modeling phosphorus transport in grass buffer strips. J Environ Eng 115(2):409–427. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1989)115:2(409)
Li K, Xie Y, Sun W, Wang X, Li Z, Wang L (2020) Spatial response of lake water quality to multi-scale landscape pattern of lakeside zone in agricultural watershed. J Appl Ecol 31(6):2057–2066. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202006.036
Li R, Xu M, Chen Z, Gao B, Cai J, Shen F, He X, Zhuang Y, Chen D (2021a) Phenology-based classification of crop species and rotation types using fused Modis and Landsat data: the comparison of a random-forest-based model and a decision-rule-based model. Soil Tillage Res 206:104838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104838
Li S, Li J, Xia J, Hao G (2021b) Optimal control of nonpoint source pollution in the Bahe River Basin, Northwest China, based on the Swat model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(39):55330–55343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14869-4
Li H, Zhou X, Huang K, Hao G, Li J (2022) Research on optimal control of non-point source pollution: a case study from the Danjiang River Basin in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):15582–15602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16740-y
Lind L, Hasselquist EM, Laudon H (2019) Towards ecologically functional riparian zones: a meta-analysis to develop guidelines for protecting ecosystem functions and biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. J Environ Manag 249:109391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109391
Malik MA, Dar AQ, Jain MK (2022) Modelling streamflow using the Swat model and multi-site calibration utilizing Sufi-2 of Swat-cup model for high altitude catchments, Nw Himalaya’s. Model Earth Syst Environ 8(1):1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01145-0
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (2002) Environmental quality standard for surface water (GB 3838–2002). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Ndhlovu GZ, Woyessa YE (2021) Use of gridded climate data for hydrological modelling in the Zambezi River Basin, Southern Africa. J Hydrol 602:126749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126749
Nie Z, Li J, Liu H, Liu S, Wang D, Zhao P, Liu H (2020) Adsorption kinetic characteristics of molybdenum in yellow-brown soil in response to Ph and phosphate. Open Chem 18(1):663–668. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2020-0501
Peak S, Gil K (2015) Correlation analysis of factors affecting removal efficiency in vegetative filter strips. Environ Earth Sci 75(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4834-4
Phillips JD (1989) An evaluation of the factors determining the effectiveness of water quality buffer zones. J Hydrol 107(1):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(89)90054-1
Ruan S, Zhuang Y, Hong S, Zhang L, Wang Z, Tang X, Wen W (2020) Cooperative identification for critical periods and critical source areas of nonpoint source pollution in a typical watershed in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(10):10472–10483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07630-w
Sao D, Kato T, Tu LH, Thouk P, Fitriyah A, Oeurng C (2020) Evaluation of different objective functions used in the Sufi-2 calibration process of swat-cup on water balance analysis: a case study of the Pursat River Basin, Cambodia. Water 12(10):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102901
Shrestha NK, Rudra RP, Daggupati P, Goel PK, Shukla R (2021) A comparative evaluation of the continuous and event-based modelling approaches for identifying critical source areas for sediment and phosphorus losses. J Enviro Manag 277:111427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111427
Sirabahenda Z, St-Hilaire A, Courtenay SC, van den Heuvel MR (2020) Assessment of the effective width of riparian buffer strips to reduce suspended sediment in an agricultural landscape using Anfis and Swat models. CATENA 195:104762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104762
Stahl AT, Fremier AK, Cosens BA (2020) Mapping legal authority for terrestrial conservation corridors along streams. Conserv Biol 34(4):943–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13484
Stott TA (2021) Do Riparian buffer zones and new forest management practices reduce stream suspended sediment loads?: Re-Visiting the Afon Tanllwyth in Hafren Forest, Plynlimon, 20 Years On. Soil Use Manag 37(4):921–935. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12670
Taghvaye Salimi E, Nohegar A, Malekian A, Hosseini M, Holisaz A (2016) Runoff simulation using Swat model and Sufi-2 algorithm (case study: Shafaroud Watershed, Guilan Province, Iran). Casp J Environ Sci (CJES) 14:69–80
Tejaswini V, Sathian KK (2018) Calibration and validation of Swat model for Kunthipuzha Basin using Sufi-2 algorithm. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7(1):2162–2172. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.260
Tufa FG, Sime CH (2021) Stream flow modeling using Swat model and the model performance evaluation in Toba sub-watershed, Ethiopia. Model Earth Syst Environ 7(4):2653–2665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01039-7
Wang M, Duan L, Wang J, Peng J, Zheng B (2020) Determining the width of lake riparian buffer zones for improving water quality base on adjustment of land use structure. Ecol Eng 158:106001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.106001
Xia JH, Yan ZM (2009) Comprehensive evaluation theory and restoration technology of ecological riparian zone. China water resources and Hydropower Press, Beijing, pp 31–38
Xu H, Cai C, Du H, Guo Y (2021) Responses of water quality to land use in riparian buffers: a case study of Huangpu River, China. Geojournal 86(4):1657–1669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10150-2
Xu L, Ouyang XZ, Pan P, Zang H, Liu J, Yang K (2022) Identification of forest vegetation types in Southern China based on spatio-temporal fusion of Gf-1 Wfv and Modis data. J Appl Ecol 33(7):1948–1956. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202207.022
Xue J, Wang Q, Zhang M (2022) A review of non-point source water pollution modeling for the urban–rural transitional areas of China: research status and prospect. Sci Total Environ 826:154146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154146
Yang D, Fan DY, Xie ZQ, Zhang AY, Xiong GM, Zhao CM, Xu WT (2016) Research progress on the mechanisms and influence factors of nitrogen retention and transformation in riparian ecosystems. J Appl Ecol 27(3):973–980. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201603.040
Yuan Y, Koropeckyj-Cox (2022) Swat model application for evaluating agricultural conservation practice effectiveness in reducing phosphorous loss from the Western Lake Erie Basin. J Environ Manag 302:114000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114000
Zhang H, Wang B, Liu DL, Zhang M, Leslie LM, Yu Q (2020) Using an improved swat model to simulate hydrological responses to land use change: a case study of a catchment in tropical Australia. J Hydrol 585:124822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124822
Zhang X, Chen P, Han Y, Chang X, Dai S (2022) Quantitative analysis of self-purification capacity of non-point source pollutants in watersheds based on Swat model. Ecol Indic 143:109425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109425
Zuo D, Han Y, Gao X, Ma G, Xu Z, Bi Y, Abbaspour KC, Yang H (2022) Identification of priority management areas for non-point source pollution based on critical source areas in an agricultural watershed of Northeast China. Environ Res 214:113892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113892
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the editors and reviewers who have put considerable time and effort into their comments on this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation (grant number 2019JLM-63); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51979222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hang Chen: conceptualization, data curation, methodology, formal analysis, software, validation, visualization, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing; Xiaode Zhou: data curation and formal analysis; Ying Wang: software and visualization; Wei Wu: funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing; Cao Li: data curation and formal analysis; Zhang Xin: investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zhou, X., Wang, Y. et al. Study on the planning and influential factors of the safe width of riparian buffer zones in the upper and middle reaches of the Ziwu River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 103703–103717 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29154-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29154-9