Abstract
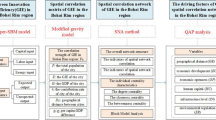
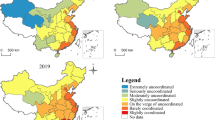
Against the background of increasing urbanization rate and intensifying global warming, conflicts between humans and the natural environment continue to arise, and regionalized forms of spatial organization have become an important research direction. This paper constructs a green innovation city network. It empirically tests the evolution process of the green innovation city network and its carbon emission effect by combining the social network approach and the spatial Durbin model. The conclusions are as follows: (1) the strong ties among green innovation city networks are mainly distributed in and around the provincial capital cities and the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin; the density of green innovation city networks has been strengthened, and the degree centrality and closeness centrality have been improved. (2) The carbon emissions of cities in the Yellow River Basin are generally increasing. Still, the rate of increase is slowing down. The carbon emissions from liquefied petroleum gas show a decreasing trend yearly, and the energy structure tends to improve. (3) The impact of the green innovation city network on carbon emissions mainly comes from its externality’s direct and indirect effects; the increase of degree centrality will reduce the total carbon emissions in the region and the network-associated regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All supplementary documents will be available upon request.
References
Barnett TP, Adam JC, Lettenmaier DP (2005) Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 438(7066):303–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04141
Chang N (2015) Changing industrial structure to reduce carbon dioxide emissions: a Chinese application. J Clean Prod 103:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.003
Chen YY, Yao ZY, Zhong K (2022) Do environmental regulations of carbon emissions and air pollution foster green technology innovation: evidence from China’s prefecture-level cities. J Clean Prod 350:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131537
Delgado BM, Cao SL, Hasan A, Siren K (2017) Multiobjective optimization for lifecycle cost, carbon dioxide emissions and exergy of residential heat and electricity prosumers. Energy Convers Manag 154:455–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.11.037
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1(2):277–300
Du KR, Li PZ, Yan ZM (2019) Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 146:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.010
Erdogan S (2021) Dynamic nexus between technological innovation and building sector carbon emissions in the BRICS countries. J Environ Manag 293:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112780
Fan JD, Xiao ZH (2021) Analysis of spatial correlation network of China’s green innovation. J Clean Prod 299:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126815
Goeppert A, Czaun M, Jones JP, Prakash GKS, Olah GA (2014) Recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol and derived products - closing the loop. Chem Soc Rev 43(23):7995–8048. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00122b
Guo Y, Li B, Han YL (2020) Dynamic network coupling between high-speed rail development and urban growth in emerging economies: evidence from China. Cities 105:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102845
He J, Li Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Dong W, Du E, Chang S, Ou X, Guo S, Tian Z, Gu A, Teng F, Hu B, Yang X, Chen S, Yao M, Yuan Z, Zhou L, Zhao X et al (2022) Towards carbon neutrality: a study on China’s long-term low-carbon transition pathways and strategies. Environ Sci Ecotechnol 9:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2021.100134
Hong QQ, Cui LH, Hong PH (2022) The impact of carbon emissions trading on energy efficiency: evidence from quasi-experiment in China?s carbon emissions trading pilot. Energy Econ 110:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106025
James K, Thompson-Fawcett M, Hansen CJ (2016) Transformations in identity, governance and planning: The case of the small city. Urban Stud 53(6):1162–1177. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098015571060
Jiao JJ, Wang JO, Jin FJ (2017) Impacts of high-speed rail lines on the city network in China. J Transp Geogr 60:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.03.010
Kaya B, Abubakar AM, Behravesh E, Yildiz H, Mert IS (2020) Antecedents of innovative performance: findings from PLS-SEM and fuzzy sets (fsQCA). J Bus Res 114:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.04.016
Li YY, Zhang YR, Lee CC, Li J (2021) Structural characteristics and determinants of an international green technological collaboration network. J Clean Prod 324:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129258
Lin BQ, Ma RY (2022) Green technology technology innovations, urban innovation environment and CO2 emission reduction in China: fresh evidence from a partially linear functional-coefficient panel model. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 176:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121434
Liu J, Yang QS, Ou SH, Liu J (2022) Factor decomposition and the decoupling effect of carbon emissions in China’s manufacturing high-emission subsectors. Energy 248:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123568
Liu YQ, Shao XY, Tang MP, Lan HX (2021) Spatio-temporal evolution of green innovation network and its multidimensional proximity analysis: empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 283:17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124649
Lu ZN, Chen HY, Hao Y, Wang JY, Song XJ, Mok TM (2017) The dynamic relationship between environmental pollution, economic development and public health: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 166:134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.010
Luan BJ, Huang JB, Zou H (2019) Domestic R&D, technology acquisition, technology assimilation and China’s industrial carbon intensity: evidence from a dynamic panel threshold model. Sci Total Environ 693:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.242
Mariotti F, Haider S (2020) Managing institutional diversity and structural holes: network configurations for recombinant innovation. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 160:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120237
Omer AM (2008) Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12(9):2265–2300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2007.05.001
Patil V, Shastry V, Himabindu M, Ravikrishna RV (2016) Life-cycle analysis of energy and greenhouse gas emissions of automotive fuels in India: part 2-well-to-wheels analysis. Energy 96:699–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.11.076
Qyyum MA, Qadeer K, Minh LQ, Haider J, Lee M (2019) Nitrogen self-recuperation expansion-based process for offshore coproduction of liquefied natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, and pentane plus. Appl Energy 235:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.127
Root TL, Price JT, Hall KR, Schneider SH, Rosenzweig C, Pounds JA (2003) Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants. Nature 421(6918):57–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01333
Saldanha TJV, Sahaym A, Mithas S, Andrade-Rojas MG, Kathuria A, Lee HH (2020) Turning liabilities of global operations into assets: IT-enabled social integration capacity and exploratory innovation. Inf Syst Res 31(2):361–382. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2019.0890
Salman M, Long XL, Dauda L, Mensah CN, Muhammad S (2019) Different impacts of export and import on carbon emissions across 7 ASEAN countries: a panel quantile regression approach. Sci Total Environ 686:1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.019
Sofi IB, Gupta A (2018) A survey on energy efficient 5G green network with a planned multi-tier architecture. J Netw Comput Appl 118:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.06.002
Song ML, Guo X, Wu KY, Wang GX (2015) Driving effect analysis of energy-consumption carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Delta region. J Clean Prod 103:620–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.05.095
Song YW, Zhang JR, Song YK, Fan XR, Zhu YQ, Zhang C (2020) Can industry-university-research collaborative innovation efficiency reduce carbon emissions? Technol Forecast Soc Chang 157:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120094
Su CW, Naqvi B, Shao XF, Li JP, Jiao ZL (2020) Trade and technological innovation: the catalysts for climate change and way forward for COP21. J Environ Manag 269:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110774
Tan FF, Yang LX, Lu ZH, Niu ZY (n.d.) Impact of urban innovation on urban green development in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: perspectives of scale and network. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21042-y
Tobelmann D, Wendler T (2020) The impact of environmental innovation on carbon dioxide emissions. J Clean Prod 244(14). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118787
van Burg E, Giannopapa C, Reymen I (2017) Open innovation in the European space sector: existing practices, constraints and opportunities. Acta Astronaut 141:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.09.019
Vecchio G, Tricarico L (2019) “May the Force move you”: roles and actors of information sharing devices in urban mobility. Cities 88:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.11.007
Wang B, Yu MX, Zhu YC, Bao PJ (2021) Unveiling the driving factors of carbon emissions from industrial resource allocation in China: a spatial econometric perspective. Energy Policy 158(11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112557
Wang JE, Mo HH, Wang FH, Jin FJ (2011) Exploring the network structure and nodal centrality of China’s air transport network: a complex network approach. J Transp Geogr 19(4):712–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2010.08.012
Xie XM, Wang HW (2020) How can open innovation ecosystem modes push product innovation forward? An fsQCA analysis. J Bus Res 108:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.10.011
Xu L, Fan MT, Yang LL, Shao S (2021) Heterogeneous green innovations and carbon emission performance: evidence at China’s city level. Energy Econ 99(16). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105269
Yang CJ, Liu SN (2020) Spatial correlation analysis of low-carbon innovation: a case study of manufacturing patents in China. J Clean Prod 273(14). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122893
Ye Q, Xu XL (2021) Determining factors of cities’ centrality in the interregional innovation networks of China’s biomedical industry. Scientometrics 126(4):2801–2819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03853-3
Yin CH, Gu HY, Zhang SJ (2020) Measuring technological collaborations on carbon capture and storage based on patents: a social network analysis approach. J Clean Prod 274(10). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122867
Yue XG, Liao YY, Zheng SY, Shao XF, Gao J (2021) The role of green innovation and tourism towards carbon neutrality in Thailand: evidence from bootstrap ADRL approach. J Environ Manag 292(9). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112778
Zhang F, Tang T, Su J, Huang KM (2020a) Inter-sector network and clean energy innovation: evidence from the wind power sector. J Clean Prod 263(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121287
Zhang ML, Liu Y (2022) Influence of digital finance and green technology innovation on China's carbon emission efficiency: empirical analysis based on spatial metrology. Sci Total Environ 838(15). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156463
Zhang W, Li GX, Uddin MK, Guo SC (2020b) Environmental regulation, foreign investment behavior, and carbon emissions for 30 provinces in China. J Clean Prod 248(11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119208
Zhang YJ, Peng YL, Ma CQ, Shen B (2017) Can environmental innovation facilitate carbon emissions reduction? Evidence from China. Energy Policy 100:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.10.005
Zhong HL, Hu ZW, Yip TL (2019) Carbon emissions reduction in China’s container terminals: optimal strategy formulation and the influence of carbon emissions trading. J Clean Prod 219:518–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.074
Funding
National Social Science Foundation of China, Research on Innovation Efficiency Losses of Competitive SOEs and Their Optimization Measures, Project No. 20BGL047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Huimei Liu; methodology, Huifang Liu; software, Xiaoyi Shi; validation, Huifang Liu and Xiaoyi Shi; formal analysis, Jinjiao Sun and Xiaoqing Dong; investigation, Xiaoyi Shi; resources, Huifang Liu; data curation, Huifang Liu and Huimei Liu; writing original draft preparation, Huifang Liu and Xiaoyi Shi; writing review and editing, Pengwei Yuan and Jinjiao Sun; visualization, Xiaoqing Dong; supervision, Pengwei Yuan; project administration, Pengwei Yuan. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors agree to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(XLSX 47 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Yuan, P., Shi, X. et al. Study on the evolution of green innovation city network and its carbon emission effect in Yellow River Basin cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 80884–80900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27869-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27869-3