Abstract
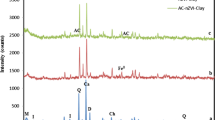
Removal of emerging contaminants, such as antibiotics, from wastewater by adsorption is a simple, low-cost, and high-performance process; however, regeneration and reuse of the exhausted adsorbent are necessary to make the process economically viable. This study aimed to investigate the possibility of electrochemical-based regeneration of clay-type materials. For this, the calcined Verde-lodo (CVL) clay was saturated with the antibiotics ofloxacin (OFL) and ciprofloxacin (CIP) in one-component systems by an adsorption process and then subjected to photo-assisted electrochemical oxidation (0.45 A, 0.05 mol/L NaCl, UV-254 nm, and 60 min), which promotes both pollutant degradation and adsorbent regeneration. The external surface of the CVL clay was investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy before and after the adsorption process. The influence of regeneration time was evaluated for the CVL clay/OFL and CVL clay/CIP systems, and the results demonstrate high regeneration efficiencies after 1 h of photo-assisted electrochemical oxidation. Clay stability during regeneration was investigated by four successive cycles in different aqueous matrices (ultrapure water, synthetic urine, and river water). The results indicated that the CVL clay is relatively stable under the photo-assisted electrochemical regeneration process. Furthermore, CVL clay was able to remove antibiotics even in the presence of natural interfering agents. The hybrid adsorption/oxidation process applied here demonstrated the electrochemical-based regeneration potential of CVL clay for the treatment of emerging contaminants, since it can be operated quickly (1h of treatment) and with lower consumption of energy (3.93 kWh kg−1) than the traditional method of thermal regeneration (10 kWh kg−1).




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Almeida Neto AF, Vieira MGA, da Silva MGC (2012) Cu (II) adsorption on modified bentonitic clays: different isotherm behaviors in static and dynamic systems. Mater Res 15:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-14392011005000089
Alvarez-Pugliese CE, Acuña-Bedoya J, Vivas-Galarza S et al (2019) Electrolytic regeneration of granular activated carbon saturated with diclofenac using BDD anodes. Diam Relat Mater 93:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2019.02.018
Alves PA, Malpass GRP, Johansen HD et al (2010) Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of real textile wastewater. Water Sci Technol 61:491–498. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.870
Antonelli R, Malpass GRP, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020a) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin onto thermally modified bentonite clay: experimental design, characterization, and adsorbent regeneration. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104553
Antonelli R, Martins FR, Malpass GRP et al (2020b) Ofloxacin adsorption by calcined Verde-lodo bentonite clay: batch and fixed bed system evaluation. J Mol Liq 315:113718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113718
Antonelli R, Malpass GRP, da Silva MGC, Vieiral MGA (2021) Fixed-bed adsorption of ciprofloxacin onto bentonite clay: characterization, mathematical modeling, and DFT-based calculations. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05700
Antonelli R, Malpass GRP, Carlos da Silva MG, Vieira MGA (2022a) Ofloxacin degradation in chloride-containing medium by photo-assisted sonoelectrochemical process using a mixed metal oxide anode. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107174
Antonelli R, Malpass GRP, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2022b) Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of ciprofloxacin using DSA® anode with NaCl electrolyte and simultaneous chlorine photolysis. J Water Process Eng 47:102698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102698
Berenguer R, Marco-Lozar JP, Quijada C et al (2010) Electrochemical regeneration and porosity recovery of phenol-saturated granular activated carbon in an alkaline medium. Carbon N Y 48:2734–2745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.03.071
Bila DM, Dezotti M (2003) Fármacos no meio ambiente. Quim Nova 26:523–530. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422003000400015
Brown NW, Roberts EPL, Chasiotis A et al (2004) Atrazine removal using adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. Water Res 38:3067–3074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.043
Chen M, Ding W, Wang J, Diao G (2013) Removal of azo dyes from water by combined techniques of adsorption, desorption, and electrolysis based on a supramolecular sorbent. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:2403–2411. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300916d
Clem AG, Doehler RW (1961) Industrially attractive properties of bentonite. Am Colloid Co, pp 272–283
Cruz G, da LP RA, da Silva DF, Gomes WC (2021) Physical–chemical characterization and thermal behavior of cassava harvest waste for application in thermochemical processes. J Therm Anal Calorim 143:3611–3622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09330-6
da Silva PMM, Camparotto NG, Neves TF et al (2021) Instantaneous adsorption and synergic effect in simultaneous removal of complex dyes through nanocellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposites: batch, fixed-bed experiments and mechanism. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 16:100584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100584
das Gracas Santos NT, Moraes LF, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Recovery of gold through adsorption onto sericin and alginate particles chemically crosslinked by proanthocyanidins. J Clean Prod 253:119925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119925
de Andrade JR, Oliveira MF, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from water and wastewater using nonconventional low-cost materials: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:3103–3127. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b05137
de Freitas ED, de Almeida HJ, de Almeida Neto AF, Vieira MGA (2018) Continuous adsorption of silver and copper by Verde-lodo bentonite in a fixed bed flow-through column. J Clean Prod 171:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.036
Prefeitura de Uberaba (2006) Centro Operacional de Desenvolvimento e Saneamento de Uberaba - CODAU. I.
dos Santos AJ, Kronka MS, Fortunato GV, Lanza MRV (2021) Recent advances in electrochemical water technologies for the treatment of antibiotics: a short review. Curr Opin Electrochem 26:100674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100674
Freitas ED, Carmo ACR, Almeida Neto AF, Vieira MGA (2017) Binary adsorption of silver and copper on Verde-lodo bentonite: kinetic and equilibrium study. Appl Clay Sci 137:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.12.016
García-Espinoza JD, Robles I, Durán-Moreno A, Godínez LA (2021) Photo-assisted electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for the disinfection of aqueous solutions: a review. Chemosphere 274:129957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129957
Ghani AA, Shahzad A, Moztahida M et al (2021) Adsorption and electrochemical regeneration of intercalated Ti3C2Tx MXene for the removal of ciprofloxacin from wastewater. Chem Eng J 421:127780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127780
Hussain SN, Roberts EPL, Asghar HMA et al (2013) Oxidation of phenol and the adsorption of breakdown products using a graphite adsorbent with electrochemical regeneration. Electrochim Acta 92:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.01.020
Hussain SN, Asghar HMA, Sattar H, Roberts EPL (2015) Electrochemical regeneration of GIC adsorbent in a continuous electrochemical reactor. Int J Chem Eng Appl 6:258–261. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijcea.2015.v6.492
Karime IB, Hamza M, Sellami A et al (2017) New hybrid process combining adsorption on sawdust and electroxidation using a BDD anode for the treatment of dilute wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 175:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.11.020
Kloprogge JT, Ponce CP, Ortillo DO (2021) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of some organic and inorganic modified clay minerals. Materials (Basel) 14:7115
Laube N, Mohr B, Hesse A (2001) Laser-probe-based investigation of the evolution of particle size distributions of calcium oxalate particles formed in artificial urines. J Cryst Growth 233:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(01)01547-0
Lei X, Li M, Zhang Z et al (2009) Electrochemical regeneration of zeolites and the removal of ammonia. J Hazard Mater 169:746–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.012
Lofrano G (2012) Emerging compounds removal from wastewater: natural and solar based treatments. Springer, Netherlands, Dordrecht
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Santos RL et al (2012) Unexpected toxicity decrease during photoelectrochemical degradation of atrazine with NaCl. Environ Chem Lett 10:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-011-0340-4
Munonde TS, September NP, Mpupa A, Nosizo P (2022) Applied clay science two agitation routes for the adsorption of Reactive Red 120 dye on NiFe LDH/AC nanosheets from wastewater and river water. Appl Clay Sci 219:106438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106438
Narayanan DP, Gopalakrishnan A, Yaakob Z et al (2020) A facile synthesis of clay – graphene oxide nanocomposite catalysts for solvent free multicomponent Biginelli reaction. Arab J Chem 13:318–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.04.011
Narbaitz RM, Karimi-Jashni A (2009) Electrochemical regeneration of granular activated carbons loaded with phenol and natural organic matter. Environ Technol 30:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330802422803
Oliveira MF, De SVM, Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Fixed-bed adsorption of caffeine onto thermally modified Verde-lodo bentonite. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:17480–17487. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b03734
Oliveira MF, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2019) Equilibrium and kinetic studies of caffeine adsorption from aqueous solutions on thermally modified Verde-lodo bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 168:366–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.12.011
Park Y, Ayoko GA, Horváth E et al (2013) Structural characterisation and environmental application of organoclays for the removal of phenolic compounds. J Colloid Interface Sci 393:319–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.10.067
Parra KN, Gul S, Aquino JM et al (2016) Electrochemical degradation of tetracycline in artificial urine medium. J Solid State Electrochem 20:1001–1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-2833-8
Pelegrini RT, Freire RS, Duran N, Bertazzoli R (2001) Photoassisted electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants on a DSA type oxide electrode: Process test for a phenol synthetic solution and its application for the E1 bleach Kraft mill effluent. Environ Sci Technol 35:2849–2853. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001784j
Sausen MG, Scheufele FB, Alves HJ et al (2018) Efficiency maximization of fixed-bed adsorption by applying hybrid statistical-phenomenological modeling. Sep Purif Technol 207:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.002
Schampera B, Solc R, Woche SK et al (2015) Surface structure of organoclays as examined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. Clay Miner 50:353–367. https://doi.org/10.1180/claymin.2015.050.3.08
Seid L, Lakhdari D, Berkani M et al (2022) High-efficiency electrochemical degradation of phenol in aqueous solutions using Ni-PPy and Cu-PPy composite materials. J Hazard Mater 423:126986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126986
Sharif F, Roberts EPL (2020) Anodic electrochemical regeneration of a graphene/titanium dioxide composite adsorbent loaded with an organic dye. Chemosphere 241:125020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125020
Sharif F, Gagnon LR, Mulmi S, Roberts EPL (2017) Electrochemical regeneration of a reduced graphene oxide/magnetite composite adsorbent loaded with methylene blue. Water Res 114:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.042
Siedlecka EM, Ofiarska A, Borzyszkowska AF et al (2018) Cytostatic drug removal using electrochemical oxidation with BDD electrode: degradation pathway and toxicity. Water Res 144:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.035
Tonhela MA, Almeida MEV, Granato Malpass AC et al (2021) Electrodegradation of cyclophosphamide in artificial urine by combined methods. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 0:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.2012270
Tran NH, Reinhard M, Gin KYH (2018) Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res 133:182–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.029
Wang L, Balasubramanian N (2009) Electrochemical regeneration of granular activated carbon saturated with organic compounds. Chem Eng J 155:763–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.020
Weng CH, Hsu MC (2008) Regeneration of granular activated carbon by an electrochemical process. Sep Purif Technol 64:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2008.10.006
Xu P, Zheng D, He Q, Yu J (2020) The feasibility of ofloxacin degradation and electricity generation in photo-assisted microbial fuel cells with LiNbO3/CF photocatalytic cathode. Sep Purif Technol 250:117106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117106
Xu X, He Z, Tang H et al (2022) Chemosphere removal of diclofenac and oxytetracycline from synthetic urine by furfuryl alcohol-derived mesoporous carbon. Chemosphere 288:132317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132317
Zhang H (2002) Regeneration of exhausted activated carbon by electrochemical method. Chem Eng J 85:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(01)00176-0
Zhou MH, Lei LC (2006) Electrochemical regeneration of activated carbon loaded with p-nitrophenol in a fluidized electrochemical reactor. Electrochim Acta 51:4489–4496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.12.028
Zhou X, Cuasquer GJP, Li Z et al (2021) Occurrence of typical antibiotics, representative antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and genes in fresh and stored source-separated human urine. Environ Int 146:106280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106280
Alves PA, Johansen HD, Neto SA et al (2014) Photo-assisted electrochemical degradation of textile effluent to reduce organic halide (AOX) production. Water Air Soil Pollut 225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2144-1
Carneiro JF, Aquino JM, Silva BF et al (2020) Comparing the electrochemical degradation of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin using distinct electrolytes and a BDD anode: evolution of main oxidation byproducts and toxicity. J Environ Chem Eng 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104433
de Vargas Brião G, da Silva MG, Vieira MGA (2022) Adsorption potential for the concentration and recovery of rare earth metals from NdFeB magnet scrap in the hydrometallurgical route: a review in a circular economy approach. J Clean Prod 380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135112
Do Nascimento DC, Da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2021) Adsorption of propranolol hydrochloride from aqueous solutions onto thermally treated bentonite clay: a complete batch system evaluation. J Mol Liq 337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116442
Ferrández-Gómez B, Ruiz-Rosas R, Beaumont S et al (2021) Electrochemical regeneration of spent activated carbon from drinking water treatment plant at different scale reactors. Chemosphere 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128399
Mansouri F, Chouchene K, Roche N, Ksibi M (2021) Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption and advanced oxidation processes: state of the art and trends. Appl Sci 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146659
Mokudai T, Nakamura K, Kanno T, Niwano Y (2012) Presence of hydrogen peroxide, a source of hydroxyl radicals, in acid electrolyzed water. PLoS One 7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046392
Park JE, Lee GB, Hong BU, Hwang SY (2019) Regeneration of activated carbons spent by waste water treatment using KOH chemical activation. Appl Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9235132
Pryor W a (1986) Oxy-radicals and related species: their formation, lifetimes, and reactions. Annu Rev Physiol 48:657–667
Valle Junior RF, Abdala VL, Guidolini JF et al (2013) Diagnóstico temporal e espacial da qualidade das águas superficiais do Rio Uberaba MG. Caminhos Geogr:1–11
WHO - World Health Organization (2020) Antibiotic resistance. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance. Accessed 3 Jan 2022
Yañez-Rios AE, Carrera-Crespo JE, Luna-Sanchez RM et al (2020) The influence of pH and current density on an UV254 photo-assisted electrochemical process generating active chlorine and radicals for efficient and rapid ciprofloxacin mineralization compared to individual techniques. J Environ Chem Eng 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104357
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dolomil for donating the Verde-lodo clay, EMS Pharmaceutical for kindly providing us with the antibiotics ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, Laboratório de Caracterização de Biomassa, Recursos Analíticos e de Calibração (LRAC) for the characterization analyses, and MS. Lucas Queiroz Pinto for collecting water from the river.
Funding
This work was supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brazil (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo – Brazil (FAPESP) (Proc. 2016/05007-1; 2019/11353-8), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais – Brazil (FAPEMIG) (Proc. PPM 00147-17), and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – Brazil (CNPq) (Proc. 406193/2018-5; 307836/2018-5; 313447/2021-7, 308046/2019-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the development and design of the study. Raissa Antonelli developed the experimental methodology, data collection, and analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Geoffroy R. P. Malpass was responsible for the supervision and revision of the manuscript versions. Melissa G. A. Vieira and Meuris G. C. da Silva were responsible for coordinating the execution of research activities, acquiring financial support, and revising previous versions of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Weiming Zhang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Figures S1–S2 and Tables S1–S2 (DOCX 158 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Antonelli, R., Malpass, G.R.P., da Silva, M.G.C. et al. Hybrid process of adsorption and electrochemically based green regeneration of bentonite clay for ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 53648–53661 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26175-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26175-2