Abstract
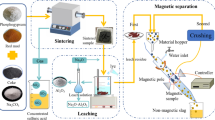
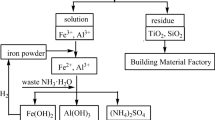
In this work, a collaborative strategy for the aluminum and iron industry based on red mud recycling through the hydrometallurgy method was proposed. In this method, Fe3+ and Al3+ were firstly separated from the red mud by using H2SO4 as a leaching agent, which was by-produced from the sintering process of an iron and steel industry. Multiple influence factors on the leaching process were investigated, with the H2SO4 addition amount showing the strongest influence on the leaching rates of Al and Fe. The main components of the filter residue were CaSO4, TiO2, and SiO2, which could be reused as additives in the building materials. Subsequently, the final Fe recovery product was obtained through the co-precipitation, Fe/Al separation, and Fe(OH)3 calcination. In the final product, the content of Fe2O3 reached 82.87%, and the iron grade was 58.01%, meeting the requirement being raw materials for sinter production.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials in this study were included in this paper.
References
Borra CR, Blanpain B, Pontikes Y, Binnemans K, Van Gerven T (2016) Recovery of rare earths and other valuable metals from Bauxite residue (red mud): a review. J Sustain Metall 2:365–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0068-2
Brunori C, Cremisini C, Massanisso P, Pinto V, Torricelli L (2005) Reuse of a treated red mud bauxite waste: studies on environmental compatibility. J Hazard Mater 117:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.09.010
Burke IT, Mayes WM, Peacock CL, Brown AP, Jarvis AP, Gruiz K (2012) Speciation of arsenic, chromium, and vanadium in red mud samples from the Ajka spill site, Hungary. Environ Sci Technol 46:3085–3092. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3003475
DeğerUzun MG (2007) Dissolution kinetics of iron and aluminium from red mud in sulphuric acid solution. Indian J Chem Technol 14:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.01.001
Evans K (2016) The history, challenges, and new developments in the management and use of bauxite residue. J Sustain Metall 2:316–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0060-x
Geng C, Liu J, Wu S, Jia Y, Du B, Yu S (2020) Novel method for comprehensive utilization of MSWI fly ash through co-reduction with red mud to prepare crude alloy and cleaned slag. J Hazard Mater 384:121315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121315
Guo T, Yang H, Liu Q, Gu H, Wang N, Yu W, Dai Y (2018) Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using different types of red mud. Water Sci Technol 2017:570–577. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.182
He Z, Zhou J, Tang J, Li C, Jiang J, Chen W, Zhu F, Xue S (2022) Accelerated alkalinity regulation and long-term dry-wet aging durability for bauxite residue remediated with biomass pyrolysis. J Environ Sci 111:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.03.021
Hou D, Wu D, Wang X, Gao S, Yu R, Li M, Wang P, Wang Y (2021) Sustainable use of red mud in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): design and performance evaluation. Cement Concrete Comp. 115:103862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103862
Hu A, Ren G, Che J, Guo Y, Ye J, Zhou S (2020a) Phosphate recovery with granular acid-activated neutralized red mud: Fixed-bed column performance and breakthrough curve modelling. J Environ Sci 90:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.10.018
Hu G, Lyu F, Khoso SA, Zeng H, Sun W, Tang H, Wang L (2020) Staged leaching behavior of red mud during dealkalization with mild acid. Hydrometallurgy 196:105422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105422
Huang L, Li C, Wang H, Qi Y, Zhu X (2021) Research Progress on Comprehensive Utilization of Red Mud. J Phys: Conf Ser 2009:012021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2009/1/012021
Iizuka A, Sakai Y, Yamasaki A, Honma M, Hayakawa Y, Yanagisawa Y (2012) Bench-scale operation of a concrete sludge recycling plant. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6099–6104. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300620u
Ju S-H, Lu S-D, Peng J-H, Zhang L-B, Srinivasakannan C, Guo S-H, Li W (2012) Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using red mud granulated with cement. T Nonferr Metal Soc 22:3140–3146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(12)61766-x
Krivenko P, Kovalchuk O, Pasko A, Croymans T, Hult M, Lutter G, Vandevenne N, Schreurs S, Schroeyers W (2017) Development of alkali activated cements and concrete mixture design with high volumes of red mud. Constr Build Mater 151:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.031
Kumar A, Kumar S (2013) Development of paving blocks from synergistic use of red mud and fly ash using geopolymerization. Constr Build Mater 38:865–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.013
Li B, Liu Y, Zhao X, Ning P, Liu X, Zhu T (2021) O3 oxidation excited by yellow phosphorus emulsion coupling with red mud absorption for denitration. J Hazard Mater 403:123971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123971
Li B, Wu H, Liu X, Zhu T, Liu F, Zhao X (2020) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO using a novel method with red mud as absorbent combined with O3 oxidation. J Hazard Mater 392:122270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122270
Li C, Sheng Y, Sun X (2019) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx by a combination of red mud and coal mine drainage. Environ Eng Sci 36:444–452. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2018.0360
Li C, Tang L, Jiang J, Zhu F, Zhou J, Xue S (2020b) Alkalinity neutralization and structure upgrade of bauxite residue waste via synergistic pyrolysis with biomass. J Environ Sci 93:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.012
Li M (2022) Status quo of comprehensive utilization of red mud. Int Core J Eng 8:797–801. https://doi.org/10.6919/ICJE.202205_8(5).0102
Li S, Pan J, Zhu D, Guo Z, Shi Y, Dong T, Lu S, Tian H (2021) A new route for separation and recovery of Fe, Al and Ti from red mud. Resour Conserv Recy 168:105314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105314
Li YC, Min XB, Ke Y, Chai LY, Shi MQ, Tang CJ, Wang QW, Liang YJ, Lei J, Liu DG (2018) Utilization of red mud and Pb/Zn smelter waste for the synthesis of a red mud-based cementitious material. J Hazard Mater 344:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.046
Liu C-J, Li Y-Z, Luan Z-K, Chen Z-Y, Zhang Z-G, Jia Z-P (2007) Adsorption removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by active red mud. J Environ Sci 19:1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(07)60190-9
Liu Q, Xin R, Li C, Xu C, Yang J (2013) Application of red mud as a basic catalyst for biodiesel production. J Environ Sci 25:823–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(12)60067-9
Liu Y, Li B, Lei X, Liu S, Zhu H, Ding E, Ning P (2022) Novel method for high-performance simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 by coupling yellow phosphorus emulsion with red mud. Chem Eng J 428:131991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131991
Mayes WM, Jarvis AP, Burke IT, Walton M, Feigl V, Klebercz O, Gruiz K (2011) Dispersal and attenuation of trace contaminants downstream of the Ajka bauxite residue (red mud) depository failure, Hungary. Environ Sci Technol 45:5147–5155. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200850y
Nikbin IM, Aliaghazadeh M, Sh C, Fathollahpour A (2018) Environmental impacts and mechanical properties of lightweight concrete containing bauxite residue (red mud). J Clean Prod 172:2683–2694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.143
Panda S, Costa RB, Shah SS, Mishra S, Bevilaqua D, Akcil A (2021) Biotechnological trends and market impact on the recovery of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud) – a review. Resour Conserv Recy 171:105645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105645
Samal S (2021) Utilization of red mud as a source for metal ions-a review. Materials 14:2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14092211
Tuncuk A, Ciftlik S, Akcil A (2013) Factorial experiments for iron removal from kaolin by using single and two-step leaching with sulfuric acid. Hydrometallurgy 134–135:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.02.006
Ujaczki E, Feigl V, Molnar M, Vaszita E, Uzinger N, Erdelyi A, Gruiz K (2016) The potential application of red mud and soil mixture as additive to the surface layer of a landfill cover system. J Environ Sci 44:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.12.014
Wang C, Zhang X, Sun R, Cao Y (2020) Neutralization of red mud using bio-acid generated by hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass for potential soil application J Clean. Prod 271:122525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122525
Wang S, Jin H, Deng Y, Xiao Y (2021) Comprehensive utilization status of red mud in China: a critical review. J Clean Prod 289:125136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125136
Wang S, Luo X, Jin H (2019) Preparation of imitation basalt compound based on thermodynamic calculation. Materials 12:3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203458
Wang Y, Yu Y, Li H, Shen C (2016) Comparison study of phosphorus adsorption on different waste solids: fly ash, red mud and ferric-alum water treatment residues. J Environ Sci 50:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.04.025
Wang Y, Zhang T-A, Lyu G, Guo F, Zhang W, Zhang Y (2018) Recovery of alkali and alumina from bauxite residue (red mud) and complete reuse of the treated residue. J Clean Prod 188:456–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.009
Wang Z, Wang Y, Wu L, Wu A, Ruan Z, Zhang M, Zhao R (2022) Effective reuse of red mud as supplementary material in cemented paste backfill: durability and environmental impact. Constr Build Mater 328:127002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127002
Wei D, Jun-Hui X, Yang P, Si-Yue S, Tao C (2019) Iron extraction from red mud using roasting with sodium salt. Min Proc Ext Met Rev 42:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2019.1706049
Wu Y, Li M, Zhu F, Hartley W, Liao J, An W, Xue S, Jiang J (2020) Variation on leaching behavior of caustic compounds in bauxite residue during dealkalization process. J Environ Sci 92:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.02.004
Xuan D, Zhan B, Poon CS, Zheng W (2016) Innovative reuse of concrete slurry waste from ready-mixed concrete plants in construction products. J Hazard Mater 312:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.036
Xue S, Li M, Jiang J, Millar GJ, Li C, Kong X (2019) Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: conversion of its alkaline characteristics. J Environ Sci 77:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.016
Yang Z, Mocadlo R, Zhao M, Sisson RD, Tao M, Liang J (2019) Preparation of a geopolymer from red mud slurry and class F fly ash and its behavior at elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater 221:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.034
Zhang M, El-Korchi T, Zhang G, Liang J, Tao M (2014) Synthesis factors affecting mechanical properties, microstructure, and chemical composition of red mud–fly ash based geopolymers. Fuel 134:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.05.058
Zhu C, Luan Z, Wang Y, Shan X (2007) Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on granular red mud (GRM). Sep Purif Technol 57:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.03.013
Zinoveev D, Pasechnik L, Fedotov M, Dyubanov V, Grudinsky P, Alpatov A (2021) Extraction of valuable elements from red mud with a focus on using liquid media—a review. Recycling 6:1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling6020038
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Mr. Tang for his valuable suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51978644) and Innovative and Enterprising Team “Linghang Project” of Zhanjiang (2020LHJH004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaolong Liu: investigation and original draft writing; Yang Zou: investigation and original draft writing; Ran Geng: investigation; Bin Li: review and editing; Tingyu Zhu: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zou, Y., Geng, R. et al. Red mud recycling by Fe and Al recovery through the hydrometallurgy method: a collaborative strategy for aluminum and iron industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43377–43386 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25389-8