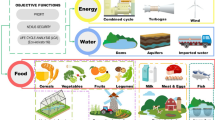
Abstract
In this study, a back-propagation-neural-network-based ecologically extended input–output model (abbreviated as BPNN-EIOM) is developed for virtual water metabolism network (VWMN) management. BPNN-EIOM can identify key consumption sectors, simulate performance of VWMN, and predict water consumption. BPNN-EIOM is then applied to analyzing VWMN of Kazakhstan, where multiple scenarios under different gross domestic production (GDP) growth rates, sectoral added values, and final demands are designed for determining the optimal management strategies. The major findings are (i) Kazakhstan typically relies on net virtual water import (reaching 1497.9 × 106 m3 in 2015); (ii) agriculture is the major exporter and advanced manufacture is the major importer; (iii) by 2025, Kazakhstan’s water consumption would increase to [19322, 22016] × 106 m3 under multiple scenarios; (iv) when Kazakhstan’s GDP growth rate, manufacturing’s added value, and final demand are scheduled to 5.5%, 8.5%, and 5.8%, its VWMN can reach the optimum. The findings are useful for decision makers to optimize Kazakhstan’s industrial structure, mitigate the national water scarcity, and promote its socio-economic sustainable development.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors do not have permission to share data.
References
Aguiar A, Chepeliev M, Corong EL, McDougall R, Van Der Mensbrugghe D (2019) The GTAP data base: version 10. J Global Econ Anal 4(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.21642/JGEA.040101AF
Almazán-Gómez MA, Duarte R, Langarita R, Sánchez-Chóliz J (2019) Effects of water reallocation in the Ebro river basin: a multiregional input-output and geographical analysis. J Environ Manage 241:645–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.042
Bozhko L (2018) Development scenarios for the interregional economic interaction in the context of economy clustering in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Energy Procedia 147:397–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.07.109
Chen YF, Shen LG, Li RJ, Xu XC, Hong HC, Lin HJ, Chen JR (2020) Quantification of interfacial energies associated with membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor by using BP and GRNN artificial neural networks. J Colloid Interface Sci 565:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.01.003
Cui YQ, Liu HF, Wang QL, Zheng ZQ, Wang H, Yue ZY, Ming ZY, Wen MS, Feng L, Yao MF (2022) Investigation on the ignition delay prediction model of multi-component surrogates based on back propagation (BP) neural network. Combustion and Flame 237:111852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2021.111852
Deng Y, Zhou X, Shen J, Xiao G, Hong HC, Lin HJ, Wu FY, Liao BQ (2021) New methods based on back propagation (BP) and radial basis function (RBF) artificial neural networks (ANNs) for predicting the occurrence of haloketones in tap water. Sci Total Environ 772(6):145534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145534
Ding XW, Lin L (2019) Long-term effects of anthropogenic factors on nonpoint source pollution in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Sustainability 11(8):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082246
Ding YK, Li YP, Liu YR (2020) Spatial-temporal assessment of agricultural virtual water and uncertainty analysis: the case of Kazakhstan (2000–2016). Sci Total Environ 724:138155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138155
Du YB, Tu Y, Li ZM, Nie L (2022) Regional water resources security grading evaluation considering both visible and virtual water: a case study on Hubei province. China Environmental Science and Pollution Research 29(17):25824–25847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17506-2
Eamen L, Brouwer R, Razavi S (2020) The economic impacts of water supply restrictions due to climate and policy change: a transboundary river basin supply-side input-output analysis. Ecol Econ 172:106532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106532
ElFetyany M, Farag H, Abd El Ghany SH (2021) Assessment of national water footprint versus water availability-case study for Egypt. Alex Eng J 60(4):3577–3585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.12.038
Florke M, Schneider C, McDonald R (2018) Water competition between cities and agriculture driven by climate change and urban growth. Nature Sustainability 1(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-017-0006-8
Fu YP, Huang GH, Liu LR, Li JY, Zhang XY, Zhai MY, Pan XJ (2021) Multi-hierarchy virtual-water management-a case study of Hubei province, China. J Clean Prod 293(4):126244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126244
Han DC, Huang GH, Liu LR, Zhai MY, Gao SC (2021) Multi-regional industrial wastewater metabolism analysis for the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ Pollut 284:117118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021a.117118
Han X, Wei Z, Zhang BZ, Li YN, Du TS, Chen H (2021b) Crop evapotranspiration prediction by considering dynamic change of crop coefficient and the precipitation effect in back-propagation neural network model. J Hydrol 596:12614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126104
He CY, Huang GH, Liu LR, Xu XL, Li YP (2020) Evolution of virtual water metabolic network in developing regions: a case study of Guangdong province. Ecological Indictors 108:105750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105750
Hiramatsu T, Inoue H, Kato Y (2016) Estimation of interregional input-output table using hybrid algorithm of the RAS method and real-coded genetic algorithm. Transportation Research Part e: Logistics and Transportation Review 95:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2016.07.007
Ilgin MA (2022) Integrating linear physical programming and fuzzy programming for the management of third party reverse logistics providers. J Environ Inf 39(1):11–21. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.202100466
Islam KN, Kenway SJ, Renouf MA, Wiedmann T, Lam KL (2021) A multi-regional input-output analysis of direct and virtual urban water flows to reduce city water footprints in Australia. Sustainable Cities and Society 75:103236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103236
Issanova G, Jilili R, Abuduwaili J, Kaldybayev A, Saparov G, Ge YX (2018) Water availability and state of water resources within water-economic basins in Kazakhstan. Paddy Water Environ 16(1):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-018-0630-6
Kang L, Liu Y (2020) Characteristics of industrial structure evolution and isomorphism in Central Asia. J Geog Sci 30(11):1781–1801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-020-1812-x
Lan WQ, Yang X, Gong TS, Xie J (2022) Predicting the shelf life of Trachinotus ovatus during frozen storage using a back propagation (BP) neural network model. Aquaculture and Fisheries. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaf.2021.12.016
Li F, Zhou MJ, Shao JQ, Qin ZX (2020) Evolution forms of land systems based on ascendency and overhead: a case study of Shaanxi Province, China. Ecological Modelling 419:108960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.108960
Liang W, Wang GW, Ning XJ, Zhang JL, Li YJ, Jiang CH, Zhang N (2020) Application of BP neural network to the prediction of coal ash melting characteristic temperature. Fuel 260:116324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116324
Liu YF, Wang Q, Zhang XD, Song SY, Niu CC, Shangguan YL (2018) Using ANFIS and BPNN methods to predict the unfrozen water content of saline soil in Western Jilin. China Symmetry 11(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010016
Liu XF, Zhou XX, Zhu BZ, He KJ, Wang P (2019) Measuring the maturity of carbon market in China: an entropy-based TOPSIS approach. J Clean Prod 229:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.380
Lyu X, Fan Y (2021) Characterizing impact factors on the performance of data assimilation for hydroclimatic predictions through multilevel factorial analysis. J Environ Inf 38(1):68–82. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.202100463
Ministry of National. Economy of the republic of Kazakhstan committee on statistics. Available at. https://stat.gov.kz/.
Mohan G, Chapagain SK, Fukushi K, Papong S, Sudarma IM, Rimba AB, Osawa T (2021) An extended input-output framework for evaluating industrial sectors and provincial-level water consumption in Indonesia. Water Resources and Industry 25:100141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2021.100141
Mohd Azlan NNI, Abdul Malek M, Zolkepli M, Mohd Salim J, Ahmed AN (2021) Sustainable management of water demand using fuzzy inference system: a case study of Kenyir Lake, Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(16):20261–20272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11908-4
Nie S, Huang CZ, Huang WW, Liu J (2021) A non-deterministic integrated optimization model with risk measure for identifying water resources management strategy. J Environ Inf 38(1):41–55. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.202100459
Rivotti P, Karatayev M, Mourão ZS, Shah N, Clarke ML, Konadu DD (2019) Impact of future energy policy on water resources in Kazakhstan. Energ Strat Rev 24:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.04.009
Roshan A, Kumar M (2020) Water end-use estimation can support the urban water crisis management: a critical review. J Environ Manag 268:110663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110663
Tabatabaie SMH, Murthy GS (2021) Development of an input-output model for food-energy-water nexus in the pacific northwest, USA. Resources Conservation and Recycling 168:105267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105267
Wang PP, Li YP, Huang GH, Wang SG, Suo C, Ma Y (2021) A multi-scenario factorial analysis and multi-regional input-output model for analyzing CO2 emission reduction path in Jing-Jin-Ji region. Journal of Cleaner Production 300:126782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126782
Wang T, Mao DH, Jiang ZL (2022) Quantitative assessment of agricultural horizontal ecological compensation in China, from the perspective of virtual land and virtual water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23220-4
Wu XJ, Li YP, Liu J, Huang GH, Ding YK, Sun J, Zhang H (2021) Identifying optimal virtual water management strategy for Kazakhstan: a factorial ecologically-extended input-output model. J Environ Manag 297:113303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113303
Xiao Y, Fang L, Hipel KW (2021) Conservation-targeted hydrologic-economic models for water demand management. J Environ Inf 37(1):49–61. https://doi.org/10.3808/jei.201900418
Yang ZF, Zhang Y, Li SS, Liu H, Zheng HM, Zhang JY, Su MR, Liu GY (2014) Characterizing urban metabolic systems with an ecological hierarchy method, Beijing. China Landsc Urban Planning 121:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2013.09.004
Yang XW, Wang NL, Chen AA, He J, Hua T, Qian YF (2020) Changes in area and water volume of the Aral Sea in the arid Central Asia over the period of 1960–2018 and their causes. Catena 191:104566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104566
Yao X, Zheng G, Cao Y, Yu B (2021) Life cycle and economic assessment of enhanced ecological floating beds applied water purification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(36):49574–49587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14008-z
Yao JQ, Wu ZY, Liu Y, Zheng XY, Zhang HB, Dong RJ, Qiao W (2022) Predicting membrane fouling in a high solid AnMBR treating OFMSW leachate through a genetic algorithm and the optimization of a BP neural network model. J Environ Manag 307:114585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114585
Yu DY, Ding TC (2021) Assessment on the flow and vulnerability of water footprint network of Beijing city, China. J Clean Prod 293:126126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126126
Zhang G, Huang GH, Liu LR, Niu G, Li JZ, McBean E (2019) Ecological network analysis of an urban water metabolic system based on input-output model: a case study of Guangdong, China. Sci Total Environ 670:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.132
Zhang H, Li YP, Sun J, Liu J, Huang GH, Ding YK, Wu XJ (2021) A two-stage factorial-analysis-based input-output model for virtual-water quantification and metabolic-network identification in Kyrgyzstan. J Clean Prod 301:126960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126960
Zheng BY, Huang GH, Liu LR, Zhai MY, Guan YR (2019) Metabolism of urban wastewater: ecological network analysis for Guangdong Province, China. J Clean Prod 217:510–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.222
Zheng XG, Huang GH, Liu LR, Zheng BY, Zhang XY (2020) A multi-source virtual water metabolism model for urban systems. J Clean Prod 275:124107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124107
Zheng XG, Huang GH, Li JY, Liu LR, Zhang XY, Pan XJ (2021) Development of a factorial water policy simulation approach from production and consumption perspectives. Water Res 193:116892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116892
Zhu MM, Wang JG, Zhang J, Xing ZC (2022) The impact of virtual water trade on urban water scarcity: a nested MRIO analysis of Yangtze River Delta cities in China. J Clean Prod 381:135165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135165
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA20060302), the Fund for Innovative Research Group of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52221003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52279003), and the Youth Program of Fujian Provincial Social Sciences Foundation of China (FJ2020C010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhenhao Ma: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing; Jing Liu: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing—review & editing; Yongping Li: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing—review & editing; Hao Zhang: Writing—review & editing; Licheng Fang: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Liu, J., Li, Y. et al. A BPNN-based ecologically extended input–output model for virtual water metabolism network management of Kazakhstan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43752–43767 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25280-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25280-6