Abstract
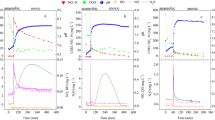
Nitrite denitrification has received increasing attention due to its high efficiency, low energy consumption, and sludge yield. However, the nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O) which are harmful to the environment, microorganisms, and humans are produced in this process. In order to mitigate NO and N2O production, the biological mechanisms of NO and N2O accumulation, as well as NO detoxification during nitrite denitrification in a sequencing batch reactor were studied. Results showed that the peak of NO accumulation increased from 0.29 \(\pm\) 0.01 to 3.12 \(\pm\) 0.34 mg L−1 with the increase of carbon to nitrogen ratio (COD/N), which is caused by the sufficient electron donor supply for NO2−-N reduction process at high COD/N. Furthermore, the result suggested that NO accumulation with no pH adjustment was 12 times higher than that with pH adjustment. It is related to the inhibition on NO reductase caused by the high free nitrous acid (FNA) and NO concentration with no pH adjustment. The pathways of NO detoxification included NO emission, reduction, and dismutation, and the more NO produced, the high proportion of NO dismutation pathway. Result showed that the maximum of oxygen production during NO dismutation reached to 1.39 mg L−1. N2O accumulation was mainly associated with FNA and NO inhibition, COD/N. The peak of N2O accumulation presented a completely opposite trend at pH adjustment and no pH adjustment, it is because that the higher FNA and NO concentration at high COD/N without pH adjustment will inhibit the N2O reductase activity, resulting in the N2O reduction was hindered during nitrite denitrification.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abeling U, Seyfried CF (1992) Anaerobic-aerobic treatment of high strength ammonium wastewater nitrogen removal via nitrite. Water Sci Technol 26:1007–1015. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1992.0542
Adouani N, Lendormi T, Limousy L, Sire O (2010) Effect of the carbon source on N2O emissions during biological denitrification. Resour Conserv Recy 54:299–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.07.011
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington DC
Bao Z, Ribera-Guardia A, Spinelli M, Sun D, Pijuan M (2018) The effect of temperature shifts on N2O and NO emissions from a partial nitritation reactor treating reject wastewater. Chemosphere 212:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.090
Baumann B, Meer JRvd, Snozzi M, Zehnder AJB (1997) Inhibition of denitrification activity but not ofmRNA induction in Paracoccus denitrificans by nitrite at a suboptimal pH. Anton Leeuw Int J G 72:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000342125891
Carr GJ, Ferguson SJ (1990) Nitric oxide formed by nitrite reductase of Paracoccus denitrificans is sufficiently stable to inhibit cytochrome oxidase activity and is reduced by its reductase under aerobic conditions. Bba-Biomembranes 1017:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2728(90)90178-7
Chislett M, Guo J, Bond PL, Wang Y, Donose BC, Yuan Z (2022) Reactive nitrogen species from free nitrous acid (FNA) cause cell lysis. Water Res 217:118401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118401
Dehghani S, Rezaee A, Hosseinkhani S (2018) Effect of alternating electrical current on denitrifying bacteria in a microbial electrochemical system: biofilm viability and ATP assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:33591–33598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3170-0
Dobbeleers T, Caluwé M, Daens D, Geuens L, Dries J (2018) Evaluation of two start-up strategies to obtain nitrogen removal via nitrite and examination of the nitrous oxide emissions for different nitritation levels during the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. J Chem Technol Biot 93:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5403
Ettwig KF et al (2010) Nitrite-driven anaerobic methane oxidation by oxygenic bacteria. Nature 464:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08883
Fu K, Zhang X, Liu F, Qiu F, Cao X (2021) Effect of C/N on denitrification and N2O release with glucose as the carbon source. Chin J Environ Eng 15:1279–1288 (in Chinese)
Glass CC, Silverstein J, Oh J (1997) Inhibition of denitrification in activated sludge by nitrite. Water Environ Res 69:1086–1093. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143097X125803
Goretski J, Zafiriou OC, Hollocher TC (1990) Steady-state nitric oxide concentrations during denitrification. J Biol Chem 265:11535–11538. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38430-3
Guo G, Wang Y, Hao T, Wu D, Chen G-H (2017) Enzymatic nitrous oxide emissions from wastewater treatment. Front Environ Sci Eng 12:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-018-1021-3
Hossini H, Rezaee A, Ayati B, Mahvic A (2015) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification using a polypyrrole/microbial cellulose electrode in a membraneless bio-electrochemical system. RSC Adv 5:72699–72708. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA09771A
Hu QQ, Zhou ZC, Liu YF, Zhou L, Mu BZ (2019) High microbial diversity of the nitric oxide dismutation reaction revealed by PCR amplification and analysis of the nod gene. Int Biodeter Biodegr 143:104708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.05.025
IPCC (2013) Fifth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2013 The Physical Science Basis. Stockholm, Sweden
Jia W, Liang S, Ngo HH, Guo W, Zhang J, Wang R, Zou Y (2013) Effect of phosphorus load on nutrients removal and N2O emission during low-oxygen simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process. Bioresour Technol 141:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.095
Jonoush ZA, Rezaee A, Ghaffarinejad A (2020) Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction using Fe0/Fe3O4 nanoparticles immobilized on nickel foam: selectivity and energy consumption studies. J Clean Prod 242:118569–118581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118569
Klaus S, Sadowski M, Jimenez J, Wett B, Chandran K, Murthy S, Bott CB (2017) Nitric oxide production interferes with aqueous dissolved oxygen sensors. Environ Eng Sci 3:687–691. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2016.0634
Lichtenberg M, Line L, Schrameyer V, Jakobsen TH, Rybtke ML, Toyofuku M, Nomura N, Kolpen M, Tolker-Nielsen T, Hl MK, Bjarnsholt T (2021) Nitric-oxide-driven oxygen release in anoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. iScience 24:103404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103404
Ma J, Yang Q, Wang S, Wang L, Takigawa A, Peng Y (2010) Effect of free nitrous acid as inhibitors on nitrate reduction by a biological nutrient removal sludge. J Hazard Mater 175:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.036
Ni BJ, Yuan Z (2013) A model-based assessment of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide production in membrane-aerated autotrophic nitrogen removal biofilm systems. J Membrane Sci 428:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.10.049
Pan Y, Ni BJ, Bond PL, Ye L, Yuan Z (2013) Electron competition among nitrogen oxides reduction during methanol-utilizing denitrification in wastewater treatment. Water Res 47:3273–3281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.054
Park JW (1993) S-nitrosylation of sulfhydryl groups in albumin by nitrosating agents. Arch Pharm Res 16:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974119
Richardson D, Felgate H, Watmough N, Thomson A, Baggs E (2009) Mitigating release of the potent greenhouse gas N2O from the nitrogen cycle - could enzymic regulation hold the key? Trends Biotechnol 27:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.03.009
Schulthess RV, Kühni M, Gujer W (1995) Release of nitric and nitrous oxides from denitrifying activated sludge. Water Res 29:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)E0108-I
Wang Y, Lin X, Zhou D, Ye L, Han H, Song C (2016) Nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emissions from a full-scale activated sludge anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process. Chem Eng J 289:330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.022
Wang S, Zhao J, Ding X, Zhao R, Huang T, Lan L, Naim Bin Nasry AA, Liu S (2019a) Effect of starvation time on NO and N2O production during heterotrophic denitrification with nitrite and glucose shock loading. Process Biochem 86:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.07.023
Wang S, Zhao J, Huang T (2019b) High NO and N2O accumulation during nitrite denitrification in lab-scale sequencing batch reactor: influencing factors and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:34377–34387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06391-5
Yu C, Qiao S, Yang Y, Jin R, Zhou J, Rittmann BE (2019) Energy recovery in the form of N2O by denitrifying bacteria. Chem Eng J 371:500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.015
Zhang D, Han X, Zhou S, Yuan S, Lu P, Peng S (2021) Nitric oxide-dependent biodegradation of phenanthrene and fluoranthene: the co-occurrence of anaerobic and intra-aerobic pathways. Sci Total Environ 760:144032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144032
Zhou Y, Pijuan M, Zeng RJ, Yuan Z (2008) Free nitrous acid inhibition on nitrous oxide reduction by a denitrifying-enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludge. Environ Sci Technol 42:8260–8265. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800650j
Zhou Y, Ganda L, Lim M, Yuan Z, Kjelleberg S, Ng WJ (2010) Free nitrous acid (FNA) inhibition on denitrifying poly-phosphate accumulating organisms (DPAOs). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2780-3
Zhou Y, Oehmen A, Lim M, Vadivelu V, Ng WJ (2011) The role of nitrite and free nitrous acid (FNA) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 45:4672–4682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.025
Zhou Y, Zhao S, Suenaga T, Kuroiwa M, Riya S, Terada A (2022) Nitrous oxide-sink capability of denitrifying bacteria impacted by nitrite and pH. Chem Eng J 428:132402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132402
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (No. 21JK0638) and Talent Project of Weinan Normal University (No. 2021RC27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by Bin Li. Data collection and analysis were performed by Fang Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sha Wang and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
NO and N2O accumulation was caused by imbalanced electron distribution.
NO detoxification was achieved by NO emission, reduction and dismutation.
The high DO concentration of 1.39 mg L−1 was produced during NO dismutation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Li, B. & Li, F. Nitric oxide and Nitrous oxide accumulation, oxygen production during nitrite denitrification in an anaerobic/anoxic sequencing batch reactor: exploring characteristics and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 35958–35971 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24874-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24874-w