Abstract
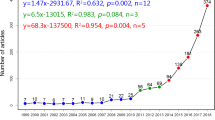
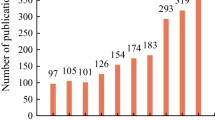
Prussian blue analogs (PBAs), a type of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), have attracted much attention because of their large specific surface area, high porosity, easy synthesis, and low cost. This paper presents the first review of PBAs by applying the bibliometric visualization software CiteSpace. The co-occurrence, co-citation, and clustering analysis of 2214 articles in the Web of Science database on the topic of “Prussian blue analogs” over the past 20 years were performed. The results provide a comprehensive overview of the evolution of the research hotspots for this material, and most importantly, it is identified that the research hotspots and trends for PBAs materials are concentrated in the environmental and energy fields. For example, the material is used as an adsorbent or catalyst to reduce pollutants, produce clean energy, or for energy storage applications such as batteries or supercapacitors. Finally, some outlooks are provided on the future research trends of this material in the environmental and energy fields, presenting the challenges faced by this material. For instance, the conductivity and corrosion resistance of the material needs to be improved and secondary contamination should be decreased or even avoided. It is believed that this paper would provide a comprehensive, systematic, and dynamic overview of the research of PBAs, and promote the future research of PBAs in the fields of environment and energy.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used for analysis are available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Akram N, Ma W, Guo J, Guo Y, Yansong Z, Hassan A, Wang J (2021) Synergistic catalysis of Fe3O4/CuO bimetallic catalyst derived from Prussian blue analogues for the efficient decomposition of various organic pollutants. Chem Phys 540:110974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2020.110974
Alsaç EP, Ulker E, Nune SVK, Karadas F (2017) A Cyanide-Based Coordination Polymer for Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis. Catal Lett 148:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-017-2271-6
Asakura D, Li CH, Mizuno Y, Okubo M, Zhou H, Talham DR (2013) Bimetallic cyanide-bridged coordination polymers as lithium ion cathode materials: core@shell nanoparticles with enhanced cyclability. J Am Chem Soc 135:2793–2799. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja312160v
Azhar A, Young C, Kaneti YV, Yamauchi Y, Badjah AY, Naushad M, Habila M, Wabaidur S, Alothman ZA, Kim J (2018) Cyano-Bridged Cu-Ni Coordination Polymer Nanoflakes and Their Thermal Conversion to Mixed Cu-Ni Oxides. Nanomaterials (basel) 8:968. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8120968
Azhar A, Li Y, Cai Z, Zakaria MB, Masud MK, Hossain MSA, Kim J, Zhang W, Na J, Yamauchi Y, Hu M (2019) Nanoarchitectonics: A New Materials Horizon for Prussian Blue and Its Analogues. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 92:875–904. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20180368
Bai R, Chen P, Zeng S, Zhou Y, Nie W, Xu Y (2021) Lattice water removal from nickel-cobalt Prussian blue analogues by polyaniline coating for flexible sodium ion supercapacitor devices. IJER 45:14870–14878. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6760
Bian XZ, Luo HQ, Li NB (2010) A New Material Based on Nanostructured Prussian Blue Analogue Film Doped with Ce(III) for Development of Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor. Electroanalysis 22:1364–1368. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200900574
Boudjema L, Long J, Petitjean H, Larionova J, Guari Y, Trens P, Salles F (2019) Adsorption of Volatile Organic Compounds by ZIF-8, Cu-BTC and a Prussian blue analogue: A comparative study Inorg. Chim. Acta 501:119316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2019.119316
Cao L-M, Lu D, Zhong D-C, Lu T-B (2020) Prussian blue analogues and their derived nanomaterials for electrocatalytic water splitting. Coord Chem Rev 407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.213156
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. JASIS 57:359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen C, Song M (2019) Visualizing a field of research: A methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS ONE 14:e0223994. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223994
Chen M, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Zou J, Tang H (2017) Cobalt particles encapsulated and nitrogen-doped bamboo-like carbon nanotubes as a catalytic and adsorptive bifunctional material for efficient removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5322–5330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.10.011
Du G, Pang H (2021) Recent advancements in Prussian blue analogues: Preparation and application in batteries. Energy Storage Mater 36:387–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.01.006
Eftekhari A (2004) Fabrication of all-solid-state thin-film secondary cells using hexacyanometallate-based electrode materials. J Power Sources 132:291–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.01.002
Feng S, Zhang H, Lv J, Dyck M, Wu Q, He H (2021) A Scientometric Review of Research Status on Unfrozen Soil Water. Water 13:708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050708
Fetiveau L, Paul G, Nicolas-Boluda A, Volatron J, George R, Laurent S, Muller R, Sancey L, Mejanelle P, Gloter A, Gazeau F, Catala L (2019) Tailored ultra-small Prussian blue-based nanoparticles for MRI imaging and combined photothermal/photoacoustic theranostics. Chem Commun (camb) 55:14844–14847. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc07116d
Ge J, Fan L, Rao AM, Zhou J, Lu B (2021) Surface-substituted Prussian blue analogue cathode for sustainable potassium-ion batteries. Nat Sustain 5:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-021-00810-7
Han L, Yu XY, Lou XW (2016) Formation of Prussian-Blue-Analog Nanocages via a Direct Etching Method and their Conversion into Ni-Co-Mixed Oxide for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution. Adv Mater 28:4601–4605. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201506315
Hoffman RS (2003) Thallium toxicity and the role of prussian blue in therapy. Toxicol Rev 22:29–40. https://doi.org/10.2165/00139709-200322010-00004
Hu L, Mei JY, Chen QW, Zhang P, Yan N (2011) Magnetically separable Prussian blue analogue Mn3[Co(CN)6]2·nH2O porous nanocubes as excellent absorbents for heavy metal ions. Nanoscale 3:4270–4274. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10506j
Hu L, Huang Y, Chen Q (2013) FexCo3−xO4 nanoporous particles stemmed from metal–organic frameworks Fe3[Co(CN)6]2: A highly efficient material for removal of organic dyes from water. J Alloys Compd 559:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.095
Hu E, Yao Y, Cui Y, Qian G (2021) Strategies for the enhanced water splitting activity over metal-organic frameworks-based electrocatalysts and photocatalysts. Materials Today Nano 15:100124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtnano.2021.100124
Hurlbutt K, Wheeler S, Capone I, Pasta M (2018) Prussian blue analogs as battery materials. Joule 2:1950–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.07.017
Johari-Ahar M, Barar J, Karami P, Asgari D, Davaran S, Rashidi MR (2018) Nafion-coated cadmium pentacyanonitrosylferrate-modified glassy carbon electrode for detection of dopamine in biological samples. Bioimpacts 8:263–270. https://doi.org/10.15171/bi.2018.29
Ju H, Liu XD, Tao CY, Yang F, Liu XL, Luo X, Zhang L (2021) Prussian blue analogue derived low-crystalline Mn2O3/Co3O4 as high-performance supercapacitor electrode. J Alloys Compd 856:157134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157134
Kamioka H, Moritomo Y, Kosaka W, Ohkoshi S (2008) Charge-Transfer Dynamics in Cyano-Bridged MA-Fe System (MA=Mn, Fe, and Co). J Phys Soc Jpn 77:093710–093710. https://doi.org/10.1143/jpsj.77.093710
Kokol P, Blažun Vošner H, Železnik D (2017) Clinical Simulation in Nursing : A Bibliometric Analysis after Its Tenth Anniversary. CLIN SIMUL NURS 13:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2016.11.007
Li X, Yuan L, Wang J, Jiang L, Rykov AI, Nagy DL, Bogdan C, Ahmed MA, Zhu K, Sun G, Yang W (2016) “copolymer-co-morphology” conception for shape-controlled synthesis of Prussian blue analogues and as-derived spinel oxides. Nanoscale 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr07193c
Liang YD, Li Y, Zhao J, Wang XY, Zhu HZ, Chen XH (2017) Study of acupuncture for low back pain in recent 20 years: a bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace. J Pain Res 10:951–964. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S132808
Liang S, Liu JQ, Xu XN, Lei NF (2022) Current status of research on concave rods - visual analysis based on CiteSpace. NCM 50:51–57. https://doi.org/10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2022.02.011
Liu Z, Yin Y, Liu W, Dunford M (2015) Visualizing the intellectual structure and evolution of innovation systems research: a bibliometric analysis. Scim 103:135–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1517-y
Liu PS, Cui G, Guo YJ (2016) A lightweight porous ceramic foam loading Prussian blue analogue for removal of toxic ions in water. Mater Lett 182:273–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.07.019
Liu J (2019) Study on the Modulation of Prussian Blue Analogues Nanostructure for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Doctor Thesis, Jilin university
López YC, Ortega GA, Martínez MA, Reguera E (2021) Magnetic Prussian Blue derivative like absorbent cages for an efficient thallium removal. J Clean Prod 283:124587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124587
Lu Y, Zhang X, Mao X, Huang Y (2019) Engineering FeCo alloy@N-doped carbon layers by directly pyrolyzing Prussian blue analogue: new peroxidase mimetic for chemiluminescence glucose biosensing. J Mater Chem B 7:4661–4668. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb00797k
Ma F, Li Q, Wang T, Zhang H, Wu G (2017) Energy storage materials derived from Prussian blue analogues. Science Bulletin 62:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.01.030
Ma D (2020) Study of Adsorption Treatment and Mechanism of Prussian Blue compound on lead-containing wastewater. Master Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology
Moazezi N, Moosavian MA (2016) Removal of rubidium ions by polyaniline nanocomposites modified with cobalt-Prussian blue analogues. J Environ Chem Eng 4:2440–2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.04.018
Mule AR, Ramulu B, Yu JS (2022) Prussian-Blue Analogue-Derived Hollow Structured Co3 S4 /CuS2 /NiS2 Nanocubes as an Advanced Battery-Type Electrode Material for High-Performance Hybrid Supercapacitors. Small 18:e2105185. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202105185
Ohara E, Soejima T, Ito S (2021) Removal of low concentration Cs(I) from water using Prussian blue. Inorg Chim Acta 514:120029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.120029
Ohkoshi S, Tokoro H, Matsuda T, Takahashi H, Irie H, Hashimoto K (2007) Coexistence of ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism in a rubidium manganese hexacyanoferrate. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:3238–3241. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200604452
Ojwang DO, Grins J, Svensson G (2018) The adsorption kinetics of CO2 on copper hexacyanoferrate studied by thermogravimetric analysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 272:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.06.019
Okubo M, Li CH, Talham DR (2014) High rate sodium ion insertion into core-shell nanoparticles of Prussian blue analogues. Chem Commun (camb) 50:1353–1355. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc47607c
Pi Y, Ma L, Zhao P, Cao Y, Gao H, Wang C, Li Q, Dong S, Sun J (2018) Facile green synthetic graphene-based Co-Fe Prussian blue analogues as an activator of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of levofloxacin hydrochloride. J Colloid Interface Sci 526:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.04.070
Pritchard A (1969) Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics? JD 25:348–349
Roque-Malherbe R, Lugo F, Polanco R (2016) Synthesis, structural elucidation and carbon dioxide adsorption on Zn (II) hexacyanoferrate (II) Prussian blue analogue. Appl Surf Sci 385:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.139
Shan Y, Zhang G, Yin W, Pang H, Xu Q (2022) Recent Progress in Prussian Blue/Prussian Blue Analogue-Derived Metallic Compounds. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 95:230–260. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20210324
Shi C, Ye S, Wang X, Meng F, Liu J, Yang T, Zhang W, Wei J, Ta N, Lu GQM, Hu M, Liu J (2021) Modular Construction of Prussian Blue Analog and TiO2 Dual-Compartment Janus Nanoreactor for Efficient Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Adv Sci (weinh) 8:2001987. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202001987
Singh B, Indra A (2020) Prussian blue- and Prussian blue analogue-derived materials: progress and prospects for electrochemical energy conversion. Mater Today Energy 16:100404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100404
Song J, Wang L, Lu Y, Liu J, Guo B, Xiao P, Lee JJ, Yang XQ, Henkelman G, Goodenough JB (2015) Removal of interstitial H2O in hexacyanometallates for a superior cathode of a sodium-ion battery. J Am Chem Soc 137:2658–2664. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja512383b
Su JW (2017) Prussian blue analogues-Derived Composite Nanomaterials as Active Electrocatalysts for Water Splitting in Alkaline Media. Doctor Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China
Sun Y (2019) Preparation of KxMnFe(CN)6 material and their electrochemical mechanism. Master Thesis, XinJiang University
Takahashi A, Minami K, Noda K, Sakurai K, Kawamoto T (2020) Trace Ammonia Removal from Air by Selective Adsorbents Reusable with Water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:15115–15119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22384
Tanaka S, Salunkhe RR, Kaneti YV, Malgras V, Alshehri SM, Ahamad T, Zakaria MB, Dou SX, Yamauchi Y, Hossain MSA (2017) Prussian blue derived iron oxide nanoparticles wrapped in graphene oxide sheets for electrochemical supercapacitors. RSC Adv 7:33994–33999. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra03179c
Tanaka S, Zakaria MB, Kaneti YV, Jikihara Y, Nakayama T (2018) Gold-Loaded Nanoporous Iron Oxide Cubes Derived from Prussian Blue as Carbon Monoxide Oxidation Catalyst at Room Temperature. ChemistrySelect 3:13464–13469. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201803594
Tian JW (2019) The Synthesis and Application of Prussian Blue Analogue Derived Composite Materials in Sodium-ion Battery Anodes. Doctor Thesis, Zhejiang university
Varret F, Goujon A, Boukheddaden K, NoguÈS M, Bleuzen A, Verdaguer M (2010) Thermally Induced Dilution of the Photo-Induced Magnetic State of Prussian Blue Analogues. MCLC 379:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/713738677
Wan M, Tang Y, Wang L, Xiang X, Li X, Chen K, Xue L, Zhang W, Huang Y (2016) Core-shell hexacyanoferrate for superior Na-ion batteries. J Power Sources 329:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.059
Wang C (2020) Research Hotspots And Development Trends Of Rural Grassroots Governance In China —— Visual Analysis Based On Citespace Software. Journal of Nanyang Institute of Technology 12:8
Wang W, Li C, Yao J, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Liu J (2013) Rapid adsorption of neutral red from aqueous solutions by Zn3[Co(CN)6]2·nH2O nanospheres. J Mol Liq 184:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2013.04.018
Wang B, Han Y, Wang X, Bahlawane N, Pan H, Yan M, Jiang Y (2018) Prussian Blue Analogs for Rechargeable Batteries. iScience 3:110–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2018a.04.008
Wang N, Ma W, Ren Z, Du Y, Xu P, Han X (2018b) Prussian blue analogues derived porous nitrogen-doped carbon microspheres as high-performance metal-free peroxymonosulfate activators for non-radical-dominated degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 6:884–895. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta08472b
Wang D-W, Zhu Y-D, Lei S, Chen S-M, Gu Z-G, Zhang J (2021) Epitaxial growth of prussian blue analogue derived NiFeP thin film for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. J Solid State Chem 293:121779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121779
Wang X, Zhang G, Yin W, Zheng S, Kong Q, Tian J, Pang H (2022) Metal–organic framework-derived phosphide nanomaterials for electrochemical applications. Carbon Energy 4:246–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/cey2.182
Wang JJ (2019) Application of Fe based PBAs materials in electrochemistry. Master Thesis, Xinjiang University
Wu S, Shen X, Zhou H, Zhu G, Wang R, Ji Z, Chen K, Chen C (2016) Morphological synthesis of Prussian blue analogue Zn3[Fe(CN)6]2·xH2O micro-/nanocrystals and their excellent adsorption performance toward methylene blue. J Colloid Interface Sci 464:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.036
Wu X, Ru Y, Bai Y, Zhang G, Shi Y, Pang H (2022) PBA composites and their derivatives in energy and environmental applications. Coord Chem Rev 451:214260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214260
Xia T, Lin Y, Li W, Ju M (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by MOFs based materials: A review. Chin Chem Lett 32:2975–2984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.02.058
Xiang R, Duan Y, Tong C, Peng L, Wang J, Shah SSA, Najam T, Huang X, Wei Z (2019) Self-standing FeCo Prussian blue analogue derived FeCo/C and FeCoP/C nanosheet arrays for cost-effective electrocatalytic water splitting. Electrochim Acta 302:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.01.170
Xiao F, Li C, Sun J, Zhang L (2017) Knowledge Domain and Emerging Trends in Organic Photovoltaic Technology: A Scientometric Review Based on CiteSpace Analysis. Front Chem 5:67. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00067
Xie Y, Chen C, Lu X, Luo F, Wang C, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2019) Porous NiFe-oxide nanocubes derived from prussian blue analogue as efficient adsorbents for the removal of toxic metal ions and organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 379:120786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120786
Xie J, Ma L, Li J, Yin X, Wen Z, Zhong Y, Li C, Liu Y, Shen Z, Mai W, Hong G, Zhang W (2022) Self-Healing of Prussian Blue Analogues with Electrochemically Driven Morphological Rejuvenation. Adv Mater e2205625. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202205625
Xu J, Bu FX, Guo YF, Zhang W, Hu M, Jiang JS (2018) Rational Synthesis of Hollow Prussian Blue Analogue Through Coordination Replication and Controlled-Etching for Cs-Ion Removal. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:3230–3238. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14546
Xu Y, Zhu Y, Chen P, Nie W, Zhou Y (2019) Trace interstitial water removal from copper-cobalt Prussian analogues by rGO coating for high performance sodium ion supercapacitor devices. Appl Surf Sci 481:919–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.189
Yang Y, Lun Z, Xia G, Zheng F, He M, Chen Q (2015) Non-precious alloy encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene layers derived from MOFs as an active and durable hydrogen evolution reaction catalyst. Energy Environ Sci 8:3563–3571. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ee02460a
Yang S, Liao S, Ren X, Li Y, Ma Y, Zhang Z (2020) Highly selective enrichment of radioactive cesium from solution by using zinc hexacyanoferrate(III)-functionalized magnetic bentonite. J Colloid Interface Sci 580:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.06.115
Ye J, Zhuang G, Wen Y, Wei J, Chen J, Zhuang Z, Yu Y (2019) Three-dimensional zigzag Prussian blue analogue and its derivates for bisphenol A scavenging: Inhomogeneous spatial distribution of FeIII in anisotropic etching of PBA. Chem Eng J 372:260–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.076
Yin J, Shen Y, Li C, Fan C, Sun S, Liu Y, Peng J, Qing L, Han J (2019) In Situ Self-Assembly of Core-Shell Multimetal Prussian Blue Analogues for High-Performance Sodium-Ion Batteries. Chemsuschem 12:4786–4790. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201902013
Yin W, Zhang G, Wang X, Pang H (2021) One-dimensional metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 298:102562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102562
You Y, Wu X-L, Yin Y-X, Guo Y-G (2014) High-quality Prussian blue crystals as superior cathode materials for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 7:1643–1647. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee44004d
Yue Y, Binder AJ, Guo B, Zhang Z, Qiao ZA, Tian C, Dai S (2014) Mesoporous Prussian blue analogues: template-free synthesis and sodium-ion battery applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:3134–3137. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201310679
Zakaria MB, Chikyow T (2017) Recent advances in Prussian blue and Prussian blue analogues: synthesis and thermal treatments. Coord Chem Rev 352:328–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.014
Zeng L, Xiao L, Shi X, Wei M, Cao J, Long Y (2019) Core-shell Prussian blue analogues@poly (m-phenylenediamine) as efficient peroxymonosulfate activators for degradation of Rhodamine B with reduced metal leaching. J Colloid Interface Sci 534:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.074
Zhang W, Zhang H, Luo R, Zhang M, Yan X, Sun X, Shen J, Han W, Wang L, Li J (2019) Prussian blue analogues-derived bimetallic iron-cobalt selenides for efficient overall water splitting. J Colloid Interface Sci 548:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.029
Zhang G, Li Y, Xiao X, Shan Y, Bai Y, Xue HG, Pang H, Tian Z, Xu Q (2021a) In Situ Anchoring Polymetallic Phosphide Nanoparticles within Porous Prussian Blue Analogue Nanocages for Boosting Oxygen Evolution Catalysis. Nano Lett 21:3016–3025. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00179
Zhang S, Zhao S, Huang S, Hu B, Wang M, Zhang Z, He L, Du M (2021b) Photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline under visible light by nanohybrids of CoFe alloy nanoparticles and nitrogen-/sulfur-codoped mesoporous carbon. Chem Eng J 420:130516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130516
Zhao Z, Xiong Y, Cheng X, Hou X, Yang Y, Tian Y, You J, Xu L (2020) Adsorptive removal of trace thallium(I) from wastewater: A review and new perspectives. J Hazard Mater 393:122378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122378
Zheng K, Wang X (2019) Publications on the Association Between Cognitive Function and Pain from 2000 to 2018: A Bibliometric Analysis Using CiteSpace. Med Sci Monit 25:8940–8951. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.917742
Zhu PY (2020) Controllable synthesis and electrochemical applications of Prussian blue analogs and their derivative materials. Master Thesis, YangZhou University
Zuo Z, Cheng J, Guo H, Li Y (2021) Knowledge mapping of research on strategic mineral resource security: A visual analysis using CiteSpace. Resources Pol 74:102372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102372
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Fundation of Hebei Province, P.R. China [No. B2018208188].
Funding
This work was supported by the [Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province] (Grant numbers [No.B2018208188]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Literature search, data collection, and analysis were performed by Xiaohan Du. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xiaohan Du and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The final version of the manuscript was reviewed and approved by all authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Hou, Y. Hotspots analysis and perspectives of Prussian blue analogues (PBAs) in environment and energy in recent 20 years by CiteSpace. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 11141–11174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24600-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24600-6