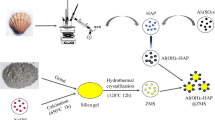
Abstract
The environmental pollution with fluoride compounds was currently being paid more and more attention as it threatens the safety of animal and human life in an ecosystem. In this study, an eco-friendly adsorbing material for removing fluoride ion (F−) was prepared by hydroxyapatite nanowires (HAnWs), a typical biocompatible inorganic conjugates. UiO66, a typical zirconium-based metal–organic framework (MOF), was conjugated onto HAnW by a simple in situ hydrothermal reaction, which afforded a novel HAnW-based nanotwigs of conjugates like millet (UiO66@HAnWs). Being characterized by SEM, EDS, FT-IR, XRD, XPS, and TGA, the obtained UiO66@HAnWs were applied to removing F− in wastewater, and its adsorption capacity was optimized. It was found that UiO66@HAnWs had a bigger specific surface area (115.310 m2/g), and its efficiency for removing F− got to 99.3%, which was greatly improved than that of related materials. It was considered that the adsorption of F− on UiO66@HAnWs was mainly multi-molecular layer adsorption, which fluoride ions aggregate on the Zr(IV) active sites to attain ligand switching, and the nanoconjugated structure like nanotwigs of millet greatly improved its adsorption capacity. In summary, a novel eco-friendly UiO66@HAnWs with nanoconjugated structure could be constructed by simple hydrothermal method, which the agglomeration defects of MOFs were not only ameliorated, but also its adsorption capacity was greatly improved.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Change history
17 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24795-8
References
Agnihotri N, Gupta G, Mondal M, (2022) Thermo-kinetic analysis, thermodynamic parameters and comprehensive pyrolysis index of Melia azedarach sawdust as a genesis of bioenergy. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02524-y
Bakhta S, Sadaoui Z, Bouazizi N, Samir B, Allalou O, Devouge-Boyer C, Mignot M, Vieillard J (2022) Functional activated carbon: from synthesis to groundwater fluoride removal. RSC Adv 12:2332–2348. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra08209d
Cao P, Zhang Y, Gao D, Chen H, Zhou M, He Y, Song P, Wang R (2022) Constructing nano-heterojunction of MOFs with crystal regrowth for efficient degradation of tetracycline under visible light. J Alloys Compd 904:164061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164061
Carrieri V, Fernández JÁ, Aboal JR, Picariello E, Nicola FD (2021) Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the devitalized aquatic moss Fontinalis antipyretica: from laboratory to field conditions. J Environ Qual 50(5):1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1002/jeq2.20267
Dou X, Zhang Y, Wang H, Wang T, Wang Y (2011) Performance of granular zirconium -iron oxide in the removal of fluoride from drinking water. Water Res 45:3571–3578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.04.002
Foroughi HO, Kargar M, Erjaee Z, Zarenezhad E (2020) One-pot three-component reaction for facile and efficient green synthesis of chromene pyrimidine-2,4-dione derivatives and evaluation of their anti-bacterial activity. Monatsh Chem 151:1603–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-020-02692-5
Fernando M, Wimalasiri A, Dziemidowicz K, Williams G, Koswattage K, Dissanayake D, Nalin de Silva K, de Silva R (2021) Biopolymer-based nanohydroxyapatite composites for the removal of fluoride, lead, cadmium, and arsenic from water. ACS Omega 6:8517–8530. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c0031
Feng J, Wang Z, Zhang W, Zhao X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Yan W (2021) Insight into the ion exchange in the adsorptive removal of fluoride by doped polypyrrole from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:67267–67279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15027-6
Gao D, Zhang Y, Yan HY, Li B, He Y, Song P, Wang R (2021) Construction of UiO-66@MoS2 flower-like hybrids through electrostatically induced self-assembly with enhanced photodegradation activity towards lomefloxacin. Sep Purif Techn 265:118486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118486
Ghosh A, Das G (2020) Green synthesis of a novel water-stable Sn (II)-TMA metal-organic framework (MOF): an efficient adsorbent for fluoride in aqueous medium in a wide pH range† Check for updates. New J Chem 44:1354–1361. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ05861C
Ghosh A, Chakrabarti S, Biswas K, Ghosh UC (2015) Column performances on fluoride removal by agglomerated Ce (IV)–Zr (IV) mixed oxide nanoparticles packed fixed-beds. J Environ Chem Eng 3:653–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.001
He J, Xu Y, Xiong Z, Lai B, Sun Y, Yang Y, Yang L (2020) The enhanced removal of phosphate by structural defects and competitive fluoride adsorption on cerium-based adsorbent. Chemosphere 256:127056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127056
He J, Zhang K, Wu S, Cai X, Chen K, Li Y, Sun B, Jia Y, Meng F, Jin Z, Kong L, Liu J (2016) Performance of novel hydroxyapatite nanowires in treatment of fluoride contaminated water. J Hazard Mater 303:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.028
Huang S, Hu M, Li D, Wang L, Zhang C, Li K, He Q (2020) Fluoride sorption from aqueous solution using Al(OH)3-modified hydroxyapatite nanosheet. Fuel 297:118486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118486
Huang L, Yang ZH, Hou LXH, LJ, Alhassan SI, Wang HY, (2021) Synthesis of hierarchical hollow MIL-53 (Al)-NH2 as an adsorbent for removing fluoride: experimental and theoretical perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:6886–6897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10975-x
Laonapakul T, Suthi T, Otsuka Y, Mutoh Y, Chaikool P, Chindaprasirt P (2022) Fluoride adsorption enhancement of calcined-kaolin/hydroxyapatite composite. Arab J Chem 15:104220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104220
Joly F, Devaux P, Loiseau T, Arab M, Morel B, Volkringer C (2019) Optimization of the synthesis of UiO-66 (Zr) in ionic liquids. Micro Meso Mater 288:109564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109564
Jeyaseelan A, Naushad M, Ahamad T, Viswanathan N (2021) Fabrication of amino functionalized benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid facilitated cerium based metal organic frameworks for efficient removal of fluoride from water environment. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 7:384–395. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00843E
Jeyaseelan A, Viswanathan N (2022) Investigation of hydroxyapatite-entrenched cerium organic frameworks incorporating biopolymeric beads for efficient fluoride removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 61:7911–7925. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c00487
Kannaujiya M, Gupta G, Mondal M, Mandal T, (2022) Adsorption of acid yellow 2gl dye from simulated water using brinjal waste. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-02131-3
Kannaujiya M, Kumar R, Mandal T, Mondal M (2021a) Experimental investigations of hazardous leather industry dye (Acid Yellow 2GL) removal from simulated wastewater using a promising integrated approach. Process Saf Environ Prot 155:444–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.09.040
Kannaujiya M, Prajapati A, Mandal T, Das A, Mondal M, (2021b) Extensive analyses of mass transfer, kinetics, and toxicity for hazardous acid yellow 17 dye removal using activated carbon prepared from waste biomass of Solanum melongena. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01160-8
Khan TA, Khan EA (2015) Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto binary iron-manganese oxide coated kaolinite: non-linear isotherm and kinetics modeling. Appl Clay Sci J 107:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.01.005
Li BZ, Li YM, Ren JR, Dai F, Zhang YP, He YF, Song PF, Wang RM (2021) Construction of CoMOF@HAnW moniliform-like heterojunction for effective catalytic degradation of organics. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:9370–9381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c01839
Lin K-YM, Liu Y-T, Che S-Y (2016) Adsorption of fluoride to UiO-66-NH2 in water: stability, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 461:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.08.061
Meng S, Wen S, Han G, Wang X, Feng Q (2022) Wastewater treatment in mineral processing of non-ferrous metal resources: a review. Water 14(5):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050726
Nayak B, Samant A, Patel R, Misra P (2017) Comprehensive understanding of the kinetics and mechanism of fluoride removal over a potent nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite surface. ACS Omega 2:8118–8128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00370
Nadimpalli N, Bandyopadhyaya R, Runkana V (2018) Thermodynamic analysis of hydrothermal synthesis of nanoparticles. Fluid Phase Equilib 456:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2017.10.002
Pitrolino K, Felfel R, McLaren J, Alexander A, Sottile P, Colin Scotchford A, Scammell BE, Roberts GAF, David MG (2022) Development and in vitro assessment of a bi-layered chitosan-nano-hydroxyapatite osteochondral scaffold. Carbohydr Polym 282:119126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119126
Prajapati A, Mondal M (2019) Hazardous As (III) removal using nanoporous activated carbon of waste garlic stem as adsorbent: kinetic and mass transfer mechanisms. Korean J Chem Eng 36:1900–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-019-0376-x
Qiu Y, Ren L, Xia L, Shao J, Zhao Y, Bruggen B (2022) Investigation of fluoride and silica removal from semiconductor wastewaters with a clean coagulation-ultra filtration process. J Chem Eng 438:135562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135562
Qin Y, Chai B, Wang C, Yan J, Fan G, Song G (2022a) New insight into remarkable tetracycline removal by enhanced graphitization of hierarchical porous carbon aerogel: performance and mechanism. Colloids Surf a: Physicochem Eng Asp 655:130197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130197
Qin Y, Chai B, Wang C, Yan J, Fan G, Song G (2022b) Removal of tetracycline onto KOH-activated biochar derived from rape straw: affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability inspection. Colloids Surf a: Physicochem Eng Asp 640:128466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128466
Raghav S, Kumar D (2019) Comparative kinetics and thermodynamic studies of fluoride adsorption by two novel synthesized biopolymer composites. Carbohydr Polym 203:430–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.054
Reinsch H, Frohlich D, Waitschat S, Chavan S, Lillerud K, Henninger S, Stock N (2018) Optimisation of synthesis conditions for UiO-66-CO2H towards scale-up and its vapour sorption properties. Reac Chem Eng 3:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7re00214a
Ruan Z, Tian Y, Ruan J, Cui G, Iqbal K, Iqbal A, Ye H, Yang Z, Yan S (2017) Synthesis of hydroxyapatite/multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the removal of fluoride ions from solution. Appl Surf Sci 12:578–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.215
Scheverin V, Horst M, Lassalle V (2022) Novel hydroxyapatite-biomass nanocomposites for fluoride adsorption. NENG 16:100648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100648
Sternitzke V, Kaegi R, Audinot J, Lewin E, Hering J, Johnson C (2012) Uptake of fluoride from aqueous solution on nano-sized hydroxyapatite: examination of a fluoridated surface layer. Environ Sci Technol 46:802–809. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202750t
Sha Z, Chana H, Wu JS (2015) Ag2CO3/UiO-66(Zr) composite with enhanced visible-light promotedphotocatalytic activity for dye degradation. J Hazard Mater 299(15):132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.016
Solanki YS, Agarwal M, Maheshwari K, Gupta S, Shukla P, Gupta AB (2020) Removal of fluoride from water by using a coagulant (inorganic polymeric coagulant). Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 3(28):3897–3905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09579-2
Wang Q, Chen X, Hu H, Wei X, Wang X, Peng Z, Ma R, Zhao Q, Zhao J, Liu J, Deng F (2021) Structural changes in the oral microbiome of the adolescent patients with moderate or severe dental fluorosis. Sci Rep 11:2897. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMicm2103503
Wang Z, Li B, Ren J, He Y, Song P, Wang R (2022) Construction of coral rod-like MoS2@HA nanowires hybrids for highly effective green antisepsis. J Inorg Biochem 229:111724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2022.111724
Yan Y, Lu L, Li Y, Han W, Gao A, Zhao S (2022) Robust and multifunctional 3D graphene-based aerogels reinforced by hydroxyapatite nanowires for highly efficient organic solvent adsorption and fluoride removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:25385–25396. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c03622
Zhang D, Gao K, Zhang X, Wang M (2022) Removal of fluorine from RECl3 in solution by adsorption, ion exchange and precipitation. Minerals 12(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010031
Zhou C, Song X, Wang Y, Wang H, Ge S (2022) The sorption and short-term immobilization of lead and cadmium by nano-hydroxyapatite/biochar in aqueous solution and soil. Chemosphere 286:131810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131810
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21865030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Meiling Zhou: validation; writing—review and editing. Hua Yang: validation; writing—review and editing. Zejun Wang: writing—original draft; data curation; formal analysis; writing. Jiarui Ren: investigation, conceptualization. Rongmin Wang: supervision; project administration; funding acquisition; conceptualization; writing—review and editing. Yufeng He: project administration, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The correct affiliation of Rongmin Wang is modified in the original published proof.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Yang, H., Wang, Z. et al. Construction of HAnW-based nanotwigs for removing inorganic fluorion in wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 32641–32654 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24436-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24436-0