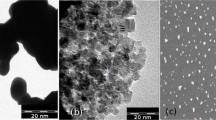
Abstract
Removal of pharmaceuticals in wastewater has been the focus of many research due to the recalcitrant nature and hazardous effects of these compounds. The photoelectrochemical degradation process has proven to be suitable to harness solar energy for the mineralization of organic compounds in wastewater. Herein, we report the application of BiOI/MnO2 heterostructured anode for the photoelectrochemical degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in aqueous solution. The photoanode was prepared through electrodeposition technique and fully characterized through microscopic, spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques. The results showed that formation of p-n heterojunction between BiOI and MnO2 in the photoanode led to improved charge separation which was evident in improved optical and photoelectrochemical properties. The FTO-BiOI/MnO2 electrode attained a photocurrent density of 0.104 mA cm−2 with applied potential of 1.0 V (vs Ag/AgCl) which was almost double that of pristine BiOI suggesting efficient charge separation. The heterostructured photoanode achieved 94% removal of tetracycline hydrochloride after 120 min through the PEC degradation process with 61% mineralization efficiency. The electrode showed good reusability and stability with 92% PEC removal after eight cycles. Hence, the FTO-BiOI/MnO2 has a great potential as anode for PEC wastewater treatments.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Adhikari S, Selvaraj S, Kim DH (2019) Construction of heterojunction photoelectrode via atomic layer deposition of Fe2O3 on Bi2WO6 for highly efficient photoelectrochemical sensing and degradation of tetracycline. Appl Catal B Environ 244:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.043
Arotiba OA, Orimolade BO, Koiki BA (2020) Visible light driven photoelectrocatalytic semiconductor heterojunction anodes for water treatment applications. Curr Opin Electrochem 1–10.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.03.018
Atashgahi S, Sánchez-Andrea I, Heipieper HJ et al (2018) Prospects for harnessing biocide resistance for bioremediation and detoxification. Science (80-) 80(360):743–746. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar3778
Cao D, Wang Y, Qiao M, Zhao X (2018) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of norfloxacin by an Ag3PO4/BiVO4 electrode with low bias. J Catal 360:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2018.01.017
Chang X, Huang J, Cheng C et al (2010) BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) photocatalysts prepared using NaBiO3 as the Bi source: Characterization and catalytic performance. Catal Commun 11:460–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2009.11.023
Cheng H, Huang B, Dai Y et al (2010) One-step synthesis of the nanostructured AgI/BiOI composites with highly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performances. Langmuir 26:6618–6624. https://doi.org/10.1021/la903943s
Dada AO, Adekola FA, Odebunmi EO (2017) Liquid phase scavenging of Cd (II) and Cu (II) ions onto novel nanoscale zerovalent manganese (nZVMn): Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 8:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2017.05.001
Daskalaki VM, Fulgione I, Frontistis Z et al (2013) Solar light-induced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A on TiO2/ITO film anode and BDD cathode. Catal Today 209:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.07.026
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA (2008) TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf Sci Rep 63:515–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2008.10.001
Ganiyu SO, Oturan N, Raffy S et al (2019) Efficiency of plasma elaborated sub-stoichiometric titanium oxide (Ti4O7) ceramic electrode for advanced electrochemical degradation of paracetamol in different electrolyte media. Sep Purif Technol 208:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.076
Garcia-Segura S, Brillas E (2017) Applied photoelectrocatalysis on the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters. J Photochem Photobiol C Photochem Rev 31:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2017.01.005
Gu X, Li C, Yuan S et al (2016) ZnO based heterojunctions and their application in environmental photocatalysis. Nanotechnology 27:402001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/40/402001
Hou J, Jiang K, Shen M et al (2017) Micro and nano hierachical structures of BiOI/activated carbon for efficient visible-light-photocatalytic reactions. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12266-x
Intaphong P, Phuruangrat A, Thongtem S, Thongtem T (2018) Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of BiOI nanoplates for using as visible-light-driven photocatalyst. Mater Lett 213:88–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.11.014
Kahng S, Kim JH (2022) Heterojunction photoanode of SnO2 and Mo-doped BiVO4 for boosting photoelectrochemical performance and tetracycline hydrochloride degradation. Chemosphere 291:132800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132800
Koiki BA, Orimolade BO, Zwane BN et al (2020) Cu2O on anodised TiO2 nanotube arrays: a heterojunction photoanode for visible light assisted electrochemical degradation of pharmaceuticals in water. Electrochim Acta 340:135944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.135944
Li Y, Zhang X, Hu X et al (2022) Facile fabrication of SnO2/TiO2 nanotube arrays for efficient degradation of pollutants. Opt Mater (amst) 127:112252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112252
Liu D, Li H, Gao R et al (2021) Enhanced visible light photoelectrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by I and P co-doped TiO2 photoelectrode. J Hazard Mater 406:124309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124309
Liu S, Liu H, Jin G, Yuan H (2015) Preparation of a novel flower-like MnO2/BiOI composite with highly enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 5:45646–45653. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra02402a
Liu S, Zhao M, He Z et al (2019) Preparation of a p-n heterojunction 2D BiOI nanosheet/1DBiPO4 nanorod composite electrode for enhanced visible light photoelectrocatalysis. Chinese J Catal 40:446–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63186-9
Lu J, Wu J, Xu W et al (2018) Room temperature synthesis of tetragonal BiOI photocatalyst with surface heterojunction between (0 0 1) facets and (1 1 0) facets. Mater Lett 219:260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.175
Lu X, Li Q, Liu S et al (2020) Fabrication of a novel BiOI/KTaO3 p-n heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. RSC Adv 10:10921–10931. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra10231k
Ma C, Zou X, Li H et al (2020) Flame synthesized MoO3 nanobelts and nanoparticles coated with BiVO4 for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production. Energy Convers Manag 205:112332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112332
Ma M, Lei E, Zhao D et al (2022) The p-n heterojunction of BiVO4/Cu2O was decorated by plasma Ag NPs for efficient photoelectrochemical degradation of Rhodamine B. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 633:127834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127834
Ma Q, Song R, Ren F et al (2022b) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of refractory pollutants over WO3/W network photoelectrode with heterophase junction for enhancing mass transportation and charge separation. Appl Catal B Environ 309:121292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121292
Ma Q, Wang H, Zhang H et al (2017) Fabrication of MnO2/TiO2 nano-tube arrays photoelectrode and its enhanced visible light photoelectrocatalytic performance and mechanism. Sep Purif Technol 189:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.08.007
Medel A, Ramírez JA, Cárdenas J et al (2019) Evaluating the electrochemical and photoelectrochemical production of hydroxyl radical during electrocoagulation process. Sep Purif Technol 208:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.05.021
Mishra RK, Prajapati CS, Shahi RR et al (2018) Influence of electrodeposition modes on the electrochemical performance of MnO2 films prepared using anionic MnO4− (Mn7+) precursor. Ceram Int 44:5710–5718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.224
Mondal D, Paul BK, Das S et al (2018) Synthesis and property of copper-impregnated α-MnO2 semiconductor quantum dots. Langmuir 34:12702–12712. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01745
Montoya-Zamora JM, Martínez-de la Cruz A, López Cuéllar E (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of BiOI synthesized in presence of EDTA. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 75:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.03.031
Murgolo S, De Ceglie C, Di Iaconi C, Mascolo G (2021) Novel TiO2-based catalysts employed in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis for effective degradation of pharmaceuticals (PhACs) in water: a short review. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 30:100473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2021.100473
Narubayashi M, Chen Z, Hasegawa K, Noda S (2016) 50–100 μm-thick pseudocapacitive electrodes of MnO2 nanoparticles uniformly electrodeposited in carbon nanotube papers. RSC Adv 6:41496–41505. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra06433g
Orimolade BO, Arotiba OA (2019) An exfoliated graphite-bismuth vanadate composite photoanode for the photoelectrochemical degradation of acid orange 7 dye. Electrocatalysis 10:429–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-00534-5
Orimolade BO, Koiki BA, Peleyeju GM, Arotiba OA (2019a) Visible light driven photoelectrocatalysis on a FTO/BiVO4/BiOI anode for water treatment involving emerging pharmaceutical pollutants. Electrochim Acta 307:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.03.217
Orimolade BO, Koiki BA, Zwane BN et al (2019b) Interrogating solar photoelectrocatalysis on an exfoliated graphite–BiVO4/ZnO composite electrode towards water treatment. RSC Adv 9:16586–16595. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02366F
Orimolade BO, Zwane BN, Koiki BA, et al (2020) Solar photoelectrocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin at a FTO/BiVO4/MnO2 anode: Kinetics, intermediate products and degradation pathway studies. J Environ Chem Eng 8.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103607
Palmas S, Mais L, Mascia M, Vacca A (2021) Trend in using TiO2 nanotubes as photoelectrodes in PEC processes for wastewater treatment. Curr Opin Electrochem 28:100699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100699
Pedanekar RS, Madake SB, Narewadikar NA et al (2022) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B by spray deposited Bi2WO6 photoelectrode under solar radiation. Mater Res Bull 147:111639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111639
Peleyeju MG, Arotiba OA (2018) Recent trend in visible-light photoelectrocatalytic systems for degradation of organic contaminants in water/wastewater. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:1389–1411. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00276b
Relekar BP, Mahadik SA, Jadhav ST et al (2018) Effect of electrodeposition potential on surface free energy and supercapacitance of MnO2 thin films. J Electron Mater 47:2731–2738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6109-9
Santhosh K, SK S, Chouti S, et al (2021) Tailoring hierarchical porous TiO2 based ternary rGO/NiO/TiO2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen production and degradation of Rhodamine B. J Mol Struct 1235:130222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130222
Umukoro EH, Kumar N, Ngila JC, Arotiba OA (2018) Expanded graphite supported p-n MoS2-SnO2 heterojunction nanocomposite electrode for enhanced photo-electrocatalytic degradation of a pharmaceutical pollutant. J Electroanal Chem 827:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.09.027
Wang D, Shen H, Guo L et al (2016) Design and construction of the sandwich-like Z-scheme multicomponent CdS/Ag/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic performance in RhB photodegradation. New J Chem 40:8614–8624. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NJ01893A
Wang J, Jiang L, Liu F et al (2021) Enhanced photoelectrochemical degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride with FeOOH and Au nanoparticles decorated WO3. Chem Eng J 407:127195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127195
Wang Q, Gao Q, Wu H et al (2019) In situ construction of semimetal Bi modified BiOI-Bi2O3 film with highly enhanced photoelectrocatalytic performance. Sep Purif Technol 226:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.06.002
Wannapop S, Somdee A (2022) Highly orientated one-dimensional Cu2O/TiO2 heterostructure thin film for photoelectrochemical photoanode and photocatalytic degradation applications. Thin Solid Films 747:139144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2022.139144
Wei Y-L, Rong B, Chen X et al (2021) Porous and visible-light-driven p–n heterojunction constructed by Bi2O3 nanosheets and WO3 microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Sep Purif Technol 256:117815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117815
Wu S, Hu YH (2021) A comprehensive review on catalysts for electrocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. Chem Eng J 409:127739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127739
Wu Y, Liu S, Zhao K et al (2016) Synthesis of δ-MnO2 film on FTO glass with high electrochemical performance. Ionics (kiel) 22:637–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1579-8
Xiao X, Lin Y, Pan B et al (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by BiOI/Bi4O5I2 microspheres under visible light irradiation. Inorg Chem Commun 93:65–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2018.05.009
Yan W, Xiao Y, Yan W et al (2019) The effect of bioelectrochemical systems on antibiotics removal and antibiotic resistance genes: a review. Chem Eng J 358:1421–1437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.128
Yang Y, Zeng Z, Zhang C et al (2018) Construction of iodine vacancy-rich BiOI/Ag@AgI Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts for visible-light-driven tetracycline degradation: Transformation pathways and mechanism insight. Chem Eng J 349:808–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.093
Ye KH, Chai Z, Gu J et al (2015) BiOI-BiVO4 photoanodes with significantly improved solar water splitting capability: P-n junction to expand solar adsorption range and facilitate charge carrier dynamics. Nano Energy 18:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.10.018
Yong X, Schoonen MAA (2000) The absolute energy positions of conduction and valence bands of selected semiconducting minerals. Am Mineral 85:543–556
Zeng Q, Chang S, Beyhaqi A et al (2020a) Efficient electricity production coupled with water treatment via a highly adaptable, successive water-energy synergistic system. Nano Energy 67:104237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104237
Zeng Q, Chang S, Beyhaqi A et al (2020b) Efficient solar hydrogen production coupled with organics degradation by a hybrid tandem photocatalytic fuel cell using a silicon-doped TiO2 nanorod array with enhanced electronic properties. J Hazard Mater 394:121425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121425
Zeng Q, Chang S, Wang M et al (2021) Highly-active, metal-free, carbon-based ORR cathode for efficient organics removal and electricity generation in a PFC system. Chinese Chem Lett 32:2212–2216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.12.062
Zeng Q, Lyu L, Gao Y et al (2018) A self-sustaining monolithic photoelectrocatalytic/photovoltaic system based on a WO3/BiVO4 photoanode and Si PVC for efficiently producing clean energy from refractory organics degradation. Appl Catal B Environ 238:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.07.005
Zhang M, Pu W, Pan S et al (2015) Photoelectrocatalytic activity of liquid phase deposited α-Fe2O3 films under visible light illumination. J Alloys Compd 648:719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.026
Zhou Q, Zhang L, Zuo P et al (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of spherical BiOI/MnO2 composite and mechanism investigation. RSC Adv 8:36161–36166. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra06930a
Funding
This study is financially supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), South Africa (Grant Number: 145431).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Benjamin Orimolade and Azeez Idris. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Benjamin Orimolade, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Orimolade, B.O., Idris, A.O., Feleni, U. et al. Enhanced visible light driven photoelectrochemical degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using a BiOI photoanode modified with MnO2 films. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 23678–23690 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23866-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23866-0