Abstract
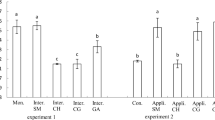
Intercropping can affect the growth and elemental absorption of vegetables. This study investigated the physiology and cadmium (Cd) content of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.), lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. ramosa Hort.), and radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings under monoculture, mutual intercropping of two or three varieties. Intercropping is not conducive to the accumulation of chlorophyll and biomass content of pakchoi, lettuce, and radish. When three seedlings were intercropped together, the antioxidant enzyme activity of pakchoi, lettuce, and radish increased and the content of malondialdehyde decreased, except that the superoxide dismutase activity of radish is inferior to the value of radish and pakchoi intercropping. Intercropping increased the soluble sugar and proline content in the lettuce seedlings, while those in the radish and lettuce seedlings reduced or had no significant effect. When intercropped with pakchoi and lettuce, the Cd content in the roots and shoots of pakchoi is higher and lower, respectively. At the same time, root or shoot bio-concentration factors also performed the same trend, and TF was the smallest and less than 1; however, the TF of lettuce is greater than 1. When intercropping with pakchoi or lettuce separately or together, it promoted the accumulation of Cd in radish root; when intercropping with pakchoi, the value of TF was the smallest. From the antioxidant system, the performance of the three seedlings intercropped together is better than the two; however, the accumulation of Cd shows the opposite trend, and the participation of cabbage in the intercropping is relatively conducive to reducing the Cd content in the edible parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ai S, Guo R, Liu B, Ren L, Naeem S, Zhang WY, Zhang YM (2016) A field study on the dynamic uptake and transfer of heavy metals in Chinese cabbage and radish in weak alkaline soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20719–20727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7277-x
An L, Pan Y, Wang Z, Zhu C (2011) Heavy metal absorption status of five plant species in monoculture and intercropping. Plant Soil 345:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0775-1
Bao SD (2000) Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing (in Chinese)
Cao X, Luo J, Wang X, Chen ZQ, Liu GQ, Khan MB, Kang KJ, Feng Y, He ZL, Yang XE (2020) Responses of soil bacterial community and Cd phytoextraction to a Sedum alfredii-oilseed rape (Brassica napus L. and Brassica juncea L.) intercropping system. Sci Total Environ 723:138152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138152
Chen H, Lin L, Liao MA, Wang J, Tang Y, Sun GC, Liang D, Xia H, Deng QX, Wang X, Lv XL, Ren W (2019) Effects of intercropping with floricultural accumulator plants on cadmium accumulation in grapevine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24474–24481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05697-8
Chen Y, Wang S, Nan Z, Ma JM, Zang F, Li YP, Zhang Q (2017) Effect of fluoride and cadmium stress on the uptake and translocation of fluoride and cadmium and other mineral nutrition elements in radish in single element or co-taminated sierozem. Environ Exp Bot 134:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.11.002
Cui T, Fang L, Wang M, Jiang M, Shen GT (2018) Intercropping of Gramineous Pasture Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and Leguminous Forage Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Increases the Resistance of Plants to Heavy Metals. J Chem 2018:. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7803408
Da Cunha-Chiamolera TPL, Cecílio Filho AB, Dos Santos DMM, Cruz FJR (2017) Gas exchange, photosynthetic pigments, and growth in tomato: lettuce intercropping. Chil J Agric Res 77:295–302. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392017000400295
Ekvall L, Greger M (2003) Effects of environmental biomass-producing factors on Cd uptake in two Swedish ecotypes of Pinus sylvestris. Environ Pollut 121(3):401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00232-4
Ghosh M, Singh SP (2005) A comparative study of cadmium phytoextraction by accumulator and weed species. Environ Pollut 133:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.015
He ZB, Cang J, Xu Z, et al. (2004) Plant Physiology Experiment. Beijing (in Chinese)
Hu J, Wu F, Wu S, Cao ZH, Lin XG, Wong MH (2013) Bioaccessibility, dietary exposure and human risk assessment of heavy metals from market vegetables in Hong Kong revealed with an in vitro gastrointestinal model. Chemosphere 91:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.066
Huang Y, He C, Shen C, Guo JJ, Mubeen S, Yuan JG, Yan ZYg (2017) Toxicity of cadmium and its health risks from leafy vegetable consumption. Food Funct 8:1373–1401. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo01580h
Jensen ES, Bedoussac L, Carlsson G, Journet EP, Justes E, Hauggaard-Nielsen H (2015) Enhancing yields in organic crop production by eco-functional intensification. Sustain Agric Res 4:42. https://doi.org/10.5539/sar.v4n3p42
Lavres J, Silveira Rabêlo FH, Capaldi FR, Capaldi FR, dos Reis AR, Rosssi ML, Franco MR, Azevedo RA, Abreu-Junior CH, Nogueira NL (2019) Investigation into the relationship among Cd bioaccumulation, nutrient composition, ultrastructural changes and antioxidative metabolism in lettuce genotypes under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:578–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.033
Li L, Sun J, Zhang F, Li XL, Rengel Z, Yan SC (2001) Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping II. Recovery or compensation of maize and soybean after wheat harvesting. F Crop Res 71:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00157-5
Li ZR, Wang JX, An LZ, Tan JB, Zhan FD, Wu J, Zu YQ (2019) Effect of root exudates of intercropping Vicia faba and Arabis alpina on accumulation and sub-cellular distribution of lead and cadmium. Int J Phytoremediation 21:4–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1523867
Lin L, Chen F, Wang J, Liao MA, Lv XL, Wang ZH, Li HX, Deng QX, Xia H, Liang D, Tang Y, Wang X, Lai YS, Ren W (2018) Effects of living hyperaccumulator plants and their straws on the growth and cadmium accumulation of Cyphomandra betacea seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 155:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.072
Lin L, Liu Q, Shi J, Sun JL, Liao MA, Mei LY (2014) Intercropping different varieties of radish can increase cadmium accumulation in radish. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:1950–1955. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2626
Liu H, Gao Y, Gao C, Liu SW, Zhang J, Chen GQ, Zhang SJ, Wu FZ (2019) Study of the physiological mechanism of delaying cucumber senescence by wheat intercropping pattern. J Plant Physiol 234–235:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2019.02.003
Liu J, Qian M, Cai G, Yang JC, Zhu QS (2007) Uptake and translocation of Cd in different rice cultivars and the relation with Cd accumulation in rice grain. J Hazard Mater 143:443–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.057
Maucieri C, Nicoletto C, Schmautz Z, Sambo P, Komives T, Borin M, Junge R (2017) Vegetable intercropping in a small-scale aquaponic system. Agronomy 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7040063
Messner B, Knoflach M, Seubert A, Ritsch A, Pfaller K, Henderson B, Shen YH, Zeller I, Willeit J, Laufer G, Wick G, Kiechl S, Bernhard D (2009) Cadmium is a novel and independent risk factor for early atherosclerosis mechanisms and in vivo relevance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1392–1398. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.190082
Mi B, Liu F, Xie L, Zhou HQ, Wu FF, Dai XZ (2019) Evaluation of the uptake capacities of heavy metals in Chinese cabbage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.022
Murakami M, Nakagawa F, Ae N, Ito M, Arao T (2009) Phytoextraction by rice capable of accumulating Cd at high levels: reduction of Cd content of rice grain. Environ Sci Technol 43:5878–5883. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8036687
Pan S, Lu R, Li H, Lin LJ, Li LP, Xiang J, Chen L, Tang YW (2021) Effects of mutual intercropping on cadmium accumulation in seedlings of three varieties of eggplant. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1691180
Sarwar N, Saifullah MSS, Zia MH, Naeem A, Bibi S, Farid G (2010) Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J Sci Food Agric 90:925–937. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3916
Satarug S, Haswell-Elkins MR, Moore MR (2000) Safe levels of cadmium intake to prevent renal toxicity in human subjects. Br J Nutr 84:791–802. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114500002403
Shirani Bidabadi S, Abolghasemi R, Zheng SJ (2018) Grafting of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus cv. Mahbubi) onto different squash rootstocks as a means to minimize cadmium toxicity. Int J Phytoremediation 20:730–738. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1413338
Tang X, Pang Y, Ji P, Gao PC, Nguyen TH, Tong YA (2016) Cadmium uptake in above-ground parts of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:102–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.033
Tang Y, Liao J, Yu X, Li HX, Lin L, Liao MA, Wang ZH, Xiong B, Sun GC, Wang X, Liang D, Xia H, Tu LH (2020a) Effects of intercropping hyperaccumulators on growth and cadmium accumulation of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk). Int J Environ Anal Chem 100:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1637430
Tang Y, Wang L, Xie Y, Yu XN, Lin LJ, Li HX, Liao MA, Wang ZH, Sun GC, Liang D, Xia H, Wang X, Tu LH (2020b) Effects of intercropping accumulator plants and applying their straw on the growth and cadmium accumulation of Brassica chinensis L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:39094–39104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09148-7
Wang J, Yu N, Mu G, Shinwari KI, Shen ZG, Zheng LQ (2017) Screening for Cd-safe cultivars of Chinese cabbage and a preliminary study on the mechanisms of Cd accumulation. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:6–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14040395
Wu C, Huan Y, Yang L, Lin LJ, Liao MA, Wang J, Wang ZH, Liang D, Hi X, Tang Y, Lv XL, Wang X (2020) Effects of intercropping with two Solanum species on the growth and cadmium accumulation of Cyphomandra betacea seedlings. Int J Phytoremediation 22:1242–1248. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1759505
Xie Y, Tan H, Sun G, Li HX, Liang D, Xia H, Wang X, Liao MA, Deng HH, Wang J, TangY (2020) Grafting alleviates cadmium toxicity and reduces its absorption by tomato. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:2222–2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00289-9
Xie Y, Wang L, Yang L, Yan WY, He ZQ, Tang Y, Liao MA, Zhou XT (2021) Intercropping with Eclipta prostrata and Crassocephalum crepidioides decrease cadmium uptake of tomato seedlings. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:1231–1239. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1678606
Yazdi M, Kolahi M, Mohajel Kazemi E, Goldson Barnaby A (2019) Study of the contamination rate and change in growth features of lettuce (Lactuca sativa Linn.)in response to cadmium and a survey of its phytochelatin synthase gene. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:295–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.071
Yin W, Chai Q, Zhao C, Yu AZ, Fan ZL, Hu FL, Fan H, Guo Y, Coulter JA (2020) Water utilization in intercropping: a review. Agric Water Manag 241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106335
Zhao Y, Liu LJ, Dang JH, Zhang L, Xiang Y, Shi XK (2014) Effects of intercropping different crops with maize in its uptake of the PAHs and heavy metal. Environ Eng 7:138-114. 10.13205/j.hjgc.201407030 (in Chinese)
Zhang L, van der Werf W, Bastiaans L, Zhang S, Li B, Spiertz JHJ (2008) Light interception and utilization in relay intercrops of wheat and cotton. F Crop Res 107:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.12.014
Zhang N, Wang D, Liu Y, Li SQ, Shen QR, Zhang RF (2014) Effects of different plant root exudates and their organic acid components on chemotaxis, biofilm formation and colonization by beneficial rhizosphere-associated bacterial strains. Plant Soil 374:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1915-6
Zhou FL (2020) Effect of night temperature on photosynthetic pigment of pepper seedling leaves. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology 9:22–27. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-1463.2020.09.007 (in Chinese)
Zhuang P, Li Y, Zou B, Su F, Zhang CS, Mo H, Li ZA (2016) Oral bioaccessibility and human exposure assessment of cadmium and lead in market vegetables in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:24402–24410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7801-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. The experiment was designed by Tang Yi. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Xuemei Peng, Ran Zhang, Wanjia Tang, Yiping Dong, and Xiaomei Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Le Liang and revised by Huanxiu Li, and all authors commented on the previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, L., Li, X., Li, H. et al. Intercropping affects the physiology and cadmium absorption of pakchoi, lettuce, and radish seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 4744–4753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22381-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22381-6