Abstract
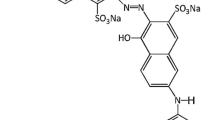
In recent years, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have indicated the greatest potential in the removal of stable organic compounds, including dyes. In this study, the ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) combined with chlorine was evaluated to remove Reactive Blue 19 (RB19) dye from aqueous solution. The effect of key experimental parameters including pH, initial chlorine concentration, initial dye concentration, and reaction time on the performance of UV-LED irradiation, UV-LED/chlorine, and the chlorination method for the removal of RB19 was studied in this research. Results showed that, more than 99% of RB19 was removed after 30 min of reaction time under optimized conditions (pH = 5, [chlorine] = 300 μM, and [RB19] = 20 mg L−1) with apparent kinetic rate constant (kapp) of 17.1 × 10−2 min−1 in UV-LED/chlorine process. However, for the chlorination method, removal efficiency was 64.7% (kapp = 3.41 × 10−2 min−1) with an apparent kinetic rate constant of 0.0341 min−1. Results also showed that UV-LED irradiation is not effective at all in removing RB19. The scavenging assay showed that OH• radicals (67.23%) had the highest contribution in RB19 removal in UV-LED/chlorine process while Cl• (17.82%) and \({\mathrm{Cl}}_2^{-\bullet }\) (8.56%) had a minor role in the degradation of the dye. The RB19 degradation kinetics analysis revealed that the processes of UV-LED/chlorine and chlorination degradation followed the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. In this study, the impact of chloride, nitrate, bicarbonate, carbonate, sulfate, and sulfite anions on the performance of the process was investigated. It indicated that sulfite anion has the most negative impact on the RB19 removal process. By evaluating the synergistic effect between UV-LED lamp and chlorine, a synergy index of 5.0 was obtained for the UV-LED/chlorine process. The results presented that the UV-LED/chlorine process has a better performance than each of them alone and has the necessary efficiency for RB19 removal. Measuring COD reported its removal efficiency of 98% during the UV-LED/chlorine process under optimized conditions. Experiments continued with textile factory wastewater and indicated 30.9% of its COD removed after treatment when 1.0 μM chlorine was used.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are included in the manuscript.
Change history
13 August 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22545-4
References
Aghajari N, Yonesi H, Bahramifar N, Ghasemi Z (2017) Photocatalytic removal of Reactive Red 198 from aqueous solution using titanium dioxide photocatalyst supported on Fe-ZSM-5 zeolite. J Mazandaran Uni Med Sci 27:137–157 http://jmums.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-9153-en.html
Belghit A, Merouani S, Hamdaoui O, Alghyamah A, Bouhelassa M (2020) Influence of processing conditions on the synergism between UV irradiation and chlorine toward the degradation of refractory organic pollutants in UV/chlorine advanced oxidation system. Sci Total Environ 736:139623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139623
Besharatian S (2017) Photocatalytic removal of metformin drug residuals from wastewater using LED lamp and TiO2 photo catalyst. Dissertation. Kharazmi University, Kharazmi
Cai WW, Peng T, Zhang JN, Hu LX, Yang B, Yang YY, Chen J, Ying GG (2019) Degradation of climbazole by UV/chlorine process: kinetics, transformation pathway and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere 219:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.023
Cai A, Deng J, Xu M, Zhou S, Li J, Wang G, Li X (2020) Degradation of tetracycline by UV activated monochloramine process: kinetics, degradation pathway, DBPs formation and toxicity assessment. Chem Eng J 395:125090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125090
Cai A, Deng J, Ling X, Ye C, Sun H, Deng Y, Zhou S, Li X (2022) Degradation of bisphenol A by UV/persulfate process in the presence of bromide: role of reactive bromine. Water Res 215:118288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118288
Canle M, Isabel Fernandez Perez M, Arturo Santaballa J (2017) Photo catalyzed degradation/abatement of endocrine disruptors. Green Sustain Chem 6:101–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2017.06.008
Chemical Book, CAS Database List (n.d.) Reactive Blue 19. https://chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB5413212.htm. Accessed 21 Nov 2018
Chen X, Memon HA, Wang Y, Marriam I, Tebyetekerwa M (2021) Circular economy and sustainability of the clothing and textile industry. Mater Circ Econ 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-021-00026-2
Davididou K, Nelson R, Monteagudo JM, Duran A, Exposito AJ, Chatzisymeon E (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A under UV-LED, black light and solar irradiation. J Clean Prod 203:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.247
Deng J, Wu G, Yuan S, Zhan X, Wang W, Hu ZH (2018) Ciprofloxacin degradation in UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process: influencing factors, mechanisms and degradation pathways. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 371:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.043
Dong H, Qiang Z, Hu J, Qu J (2017) Degradation of chloramphenicol by UV/chlorine treatment: kinetics, mechanism and enhanced formation of halo nitromethanes. Water Res 121:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.030
Elmolla ES, Chaudhuri M (2011) The feasibility of using combined TiO2 photo catalysis-SBR process for antibiotic wastewater treatment. Desalination 272:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.020
Eskandarian MR, Choi H, Fazli M, Rasoulifard MH (2016) Effect of UV-LED wavelengths on direct photolytic and TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of emerging contaminants in water. Chem Eng J 300:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.049
Fanchiang JM, Tseng DH (2009) Degradation of anthraquinone dye CI Reactive Blue 19 in aqueous solution by ozonation. Chemosphere 77:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.038
Gao YQ, Gao NY, Chu WH, Yang QL, Yin DQ (2017) Kinetics and mechanistic investigation into the degradation of naproxen by a UV/chlorine process. RSC Adv 7:33627–33634. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA0454
Gao ZC, Lin YL, Xia BY, Hu CY, Cao TC, Zou XY, Gao NY (2018) Evaluating iopamidol degradation performance and potential dual-wavelength synergy by UV-LED irradiation and UV-LED/chlorine treatment. Chem Eng J 360:806–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.022
Gao YQ, Gao NY, Chen JX, Zhang J, Yin DQ (2020a) Oxidation of β-blocker atenolol by a combination of UV light and chlorine: kinetics, degradation pathways and toxicity assessment. Sep Purif Technol 231:115927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115927
Gao YQ, Zhang J, Li C, Tian FX, Gao NY (2020b) Comparative evaluation of metoprolol degradation by UV/chlorine and UV/H2O2 processes. Chemosphere 243:125325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125325
Hu CY, Houa YZ, Lin YL, Lia AP, Denga YG (2018) Degradation kinetics of diatrizoate during UV photolysis and UV/chlorination. Chem Eng J 360:1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.189
Jallouli N, Pastrana-Martínez LM, Ribeiro AR, Moreira NFF, Faria JL, Hentati O, Silva AMT, Ksibi M (2018) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen in ultrapure water, municipal and pharmaceutical industry wastewaters using a TiO2/UV-LED system. Chem Eng J 334:976–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.045
Kalikeri S, Kamath N, Gadgil DJ, Kodialbail VS (2017) Visible light-induced photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Blue-19 over highly efficient polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposite: a comparative study with solar and UV photo catalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3731–3744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0663-1
Katheresan V, Kansedo J, Lau SY (2018) Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4676–4697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Khan MAN, Siddique M, Wahid F, Khan R (2015) Removal of reactive blue 19 dye by sono, photo and sonophotocatalytic oxidation using visible light. Ultrason Sonochem 26:370–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.04.012
Khataee A, Saadi Sh, Vahid B, Joo SW (2016) Sonochemical synthesis of holmium doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: characterization, sonocatalysis of reactive orange 29 and kinetic study. J Ind Eng Chem 35:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.12.028
Kim TK, Kim Y, Jo A, Park S, Choi KH, Zoh KD (2018) Degradation mechanism of cyanide in water using a UV-LED/H2O2/Cu2+ system. Chemosphere 208:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.198
Kong X, Jiang J, Ma J, Yang Y, Liu W, Liu Y (2016) Degradation of atrazine by UV/chlorine: efficiency, influencing factors, and products. Water Res 90:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.068
Kwon HJ, Jeong JS (2019) Clearing up the oxygen dip in HPAEC–PAD sugar analysis: sodium sulfite as an oxygen scavenger. J Chromatogr 1128:121759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121759
Kwon M, Yoon Y, Kima S, Jung Y, Hwang TM, Kang JW (2018) Removal of sulfamethoxazole, ibuprofen and nitrobenzene by UV and UV/chlorine processes: a comparative evaluation of 275 nm LED-UV and 254 nm LP-UV. Sci Total Environ 638:1351–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.080
LeClech P, Lee EK, Chen V (2006) Hybrid photo catalysis/membrane treatment for surface waters containing low concentrations of natural organic matters. Water Res 40:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.011
Lee JE, Kim MK, Lee JY, Lee YM, Zoha KD (2018) Degradation kinetics and pathway of 1H-benzotriazole during UV/chlorination process. Chem Eng J 359:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.026
Li GQ, Huo ZY, Wu QY, Lu Y, Hu HY (2018) Synergistic effect of combined UV-LED and chlorine treatment on Bacillus subtilis spore inactivation. Sci Total Environ 639:1233–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.240
Li J, Zhou S, Li M, Du E, Liu X (2019) Mechanism insight of acetaminophen degradation by the UV/chlorine process: kinetics, intermediates, and toxicity assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25012–25025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05747-1
Luo C, Ma J, Jiang J, Liu Y, Song Y, Yang Y, Guan Y, Wu D (2015) Simulation and comparative study on the oxidation kinetics of atrazine by UV/H2O2, UV/HSO5− and UV/S2O82−. Water Res 80:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.019
Moreira AJ, Borges AC, Gouvea LFC, MacLeod TCO, Freschi GPG (2017) The process of atrazine degradation, its mechanism, and the formation of metabolites using UV and UV/MW photolysis. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 347:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.07.022
Nikravesh B, Shomalnasab A, Nayyer A, Aghababaei N, Zarebi R, Ghanbari F (2020) UV/chlorine process for dye degradation in aqueous solution: mechanism, affecting factors and toxicity evaluation for textile wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104244
Pan M, Wua Z, Tanga C, Guoa K, Cao Y, Fanga J (2018) Comparative study of naproxen degradation by the UV/chlorine and the UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 4:1219–1230. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00105G
Peng Y, Zhang Y, Huang H, Zhong C (2018) Flexibility induced high-performance MOF-based adsorbent for nitro imidazole antibiotics capture. Chem Eng J 333:678–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.138
Qin L, Lin YL, Xu B, Hu CY, Tian FX, Zhang TY, Zhu WQ, Huang H, Gao NY (2014) Kinetic models and pathways of ronidazole degradation by chlorination, UV irradiation and UV/chlorine processes. Water Res 65:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.041
Rashid KH, Khodam AA (2020) Sodium sulfite as an oxygen scavenger for the corrosion control of mild steel in petroleum refinery wastewater: optimization, mathematical modeling, surface morphology and reaction kinetics studies. React Kinet Mech Catal 129:1027–1046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01738-3
Remucal CK, Manley D (2016) Emerging investigators series: the efficacy of chlorine photolysis as an advanced oxidation process for drinking water treatment. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 2:565–579. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00029K
Rezaei Mofrad MR, Miranzadeh MB, Pourgholi M, Akbari H, Dehghani R (2013) Evaluating the efficiency of advanced oxidation methods on dye removal from textile wastewater. J Kashan Univ Med Sci 17:32–39 http://feyz.kaums.ac.ir/article-1-1843-en.html
Sarathy SR (2009) Effects of UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation on physical and chemical characteristics of natural organic matter in raw drinking water sources. Dissertation. the University of British Columbia, British Columbia
Sarro M, Gule NP, Laurenti E, Gamberini R, Cristina PM, Mallon PE, Calza P (2018) ZnO-based materials and enzymes hybrid systems as highly efficient catalysts for recalcitrant pollutants abatement. Chem Eng J 334:2530–2538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.146
Song K, Mohseni M, Taghipour F (2016) Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) for water disinfection: a review. Water Res 94:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.003
Wang J, Qin L, Lin J, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Liu J, VanderBruggen B (2017) Enzymatic construction of antibacterial ultrathin membranes for dyes removal. Chem Eng J 323:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.089
Xiong P, Hu J (2012) Degradation of acetaminophen by UVA/LED/TiO2 process. Sep Purif Technol 91:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.11.012
Yaseen DA, Scholz M (2019) Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1193–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2130-z
Yin K, Deng Y, Liu C, He Q, Wei Y, Chen S, Liu T, Luo S (2018a) Kinetics, pathways and toxicity evaluation of neonicotinoid insecticides degradation via UV/chlorine process. Chem Eng J 346:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.168
Yin K, He Q, Liu C, Deng Y, Wei Y, Chen S, Liu T, Luo S (2018b) Prednisolone degradation by UV/chlorine process: influence factors, transformation products and mechanism. Chemosphere 212:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.032
Yin R, Ling L, Shang C (2018c) Wavelength-dependent chlorine photolysis and subsequent radical production using UV-LEDs as light sources. Water Res 142:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.018
Zhang X, Jun H, Xiao S, Yang X (2019) Elimination kinetics and detoxification mechanisms of microcystin-LR during UV/chlorine process. Chemosphere 214:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.162
Zhu T, Deng J, Zhu S, Cai A, Ye C, Ling X, Guo H, Wang Q, Li X (2022) Kinetic and mechanism insights into the degradation of venlafaxine by UV/chlorine process: a modelling study. Chem Eng J 431:133473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133473
Zupanovich JD (2002) Oxidation and degradation products of common oxygen scavengers. The Analyst, ChemTreat Inc. https://www.awt.org/pub/?id=0149322F-0C20-5CEC-AE62-1E826AF61A4C
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Alireza Gholizade: investigation, data curation, validation. Gholamreza Asadollahfardi: investigation, writing — review and editing. Reza Rezaei: investigation, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This is not applicable for my study.
Consent to participate
All authors give informed consent to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content, and all gave explicit consent to publish their data on the paper submitted in the Journal of Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• UV-LED/chlorine process is effective in Reactive Blue 19 removal.
• RB19 removal efficiency is affected by pH, chlorine, and dye concentration in UV-LED/chlorine.
• The presence of anions in RB19 solution inhibits the degradation in UV-LED/chlorine.
• Hydroxyl radicals had the highest contribution in RB19 removal.
• UV-LED/chlorine process reduces COD.
The original online version of this article was revised: The 2nd affiliation of the 1st Author is deleted.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gholizade, A., Asadollahfardi, G. & Rezaei, R. Reactive Blue 19 dye removal by UV-LED/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 1704–1718 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22273-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22273-9