Abstract
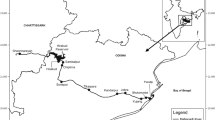
The present study aims to understand the spatio-temporal dynamics in habitat ecology and fish assemblage and determine the relationship of habitat transition and fish distribution in a large riverine-reservoir cascade system (Sardar Sarovar Reservoir part in Madhya Pradesh). This study was carried out along a 125-km riverine-reservoir interface (RRI) during 2018–2020. The study showed presence of a total of 110 fish species (104 spp. in upstream main Narmada River stretch excluding reservoirs, 56 in RRI, and 39 in Sardar Sarovar reservoir). We recorded 50 species common in upstream riverine stretch of Narmada and the RRI while RRI uniquely harbored 3 native species (Chitala chitala, Labeo boga, Salmostoma phulo) not previously reported from Narmada River stretch upstream. The similarity percentage (SIMPER) analysis showed presence of S. phulo causing 27.91%, Schistura dayi (3.71%), and Rita pavimentata (3.41%) of dissimilarity among Maheshwar (S1), Rajghat (S2), Koteshwar (S3) non-confluence zone, and Kakrana (S4)-confluence zone. The analysis of data indicated disappearance of some species like deccan peninsular carp Labeo fimbriatus, Mahseer Tor khudree which was earlier reported but was absent in recent years. The statistical correlation of environmental variables with observed abundances of fish feeding guilds showed significant positive correlation with specific conductivity and total dissolved solid content of the water. The canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) indicated association among omnivorous fishes of the reservoir with water temperature; total dissolved solids; specific conductivity; total alkalinity; chlorophyll; and NO3-N. The herbivore fishes were found to be more associated with magnesium, dissolved oxygen, and phosphorus content of the water while insectivorous fishes were more associated with the silicate and transparency of the water. The abundance of omnivores species indicated dominance of generalist fish species rather than specialists in the interface region of reservoir showing conservation and ecological importance of the ecosystem. The baseline information generated on fish assemblage and ecological perspectives of the river reservoir interface and science-based management recommendations formulated in the study are critical for sustaining fish diversity, promoting fisheries enhancement, and management planning of tropical large reservoirs.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
The data is available with the Principal Investigator of the project and the corresponding author.
References
Acre MR (2015) Can a river-reservoir interface serve as nursery habitat for riverine fishes?, Master’s Thesis. Texas Tech University, Lubbock
Agostinho AA, Gomes LC, Santos NCL, Ortega JCG, Pelicice FM (2016) Fish assemblages in Neotropical reservoirs: colonization pat- terns, impacts and management. Fish Res 173(1):26–36
Akopian M, Garnier J, Pourriot R (1999) A large reservoir as a source of zooplankton for the river: structure of the populations and influence of fish predation. J Plankton Res 21(2):285–297
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Bain MB, Stevenson NJ (1999) Aquatic habitat assessment: common methods. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, p 216
Bakawale S, Kanhere RR (2013) Study on the fish species diversity of the river Narmada in Western zone. Res J Anim Vet Fish Sci 1(6):18–20
Bascompte J, Melián CJ, Sala E (2005) Interaction strength combinations and the overfishing of a marine food web. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(15):5443–5447
Batcha ASM (1998) Studies on hydrography and domestic pollution problems in the north bank of river Cauvery. J Environ Pollut 5:69–71
Bhakta D, Meetei WA, Vaisakh G, Kamble S, Das SK, Das BK (2018) Finfish diversity of Narmada estuary in Gujarat of India. Proc Zool Soc 72(3):257–262
Bhakta D, Solanki S, Vadhel N, Meetei WA, Kamble SP, Chandra G, Samanta S, Das BK (2020) Finfish diversity of River narmada and its tributaries. Proc Zool Soc 73(4):325–337
Bhaumik U, Mukhopadhyay MK, Shrivastava NP, Sharma AP, Singh SN (2017) A case study of the Narmada River system in India with particular reference to the impact of dams on its ecology and fisheries. Aqua Eco Health Manag 20(1-2):151–159
Buckmeier DL, Smith NG, Daugherty DJ (2013) Alligator Gar movement and macrohabitat use in the lower Trinity River, Texas. Trans Am Fish Soc 142(4):1025–1035
Buckmeier DL, Smith NG, Fleming BP, Bodine KA (2014) Intra-annual variation in river–reservoir interface fish assemblages: implications for fish conservation and management in regulated rivers. River Res Appl 30(6):780–790
Carol J, Benejam L, Alcaraz C, Vila-Gispert A, Zamora L, Navarro E, Armengol J, García-Berthou E (2016) The effects of limnological features on fish assemblages of 14 Spanish reservoirs. Ecol Freshw Fish 15:66–77
Chhatawal GR (1998) Encyclopedia of environmental biology, vol 2. Anmol Pub. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Da Silva PS, Miranda LE, Makrakis S, Assumpção L, Dias JHP, Makrakis MC (2019) Tributaries as biodiversity preserves: an ichthyoplankton perspective from the severely impounded Upper Paraná River. Aquat Conserv 29(2):258–269
Das MK, Bandopadhyay MK, Sharma AP, Paul SK, Bhowmick S (2013) Fishes of River Narmada: a field identification manual. Bull Centr Inl Fish Res Inst Barrackpore 182:1–86
Dubey GP (1984) Narmada basin development plan: part 1: development of fisheries. Narmada Planning Agency. Narmada Planning Agency, India
Dubey AK, Shukla SK, Verma H (2012) Ichthyo-diversity of banisagar Dam at Chhatarpur Madhya Pradesh, India. Int J Fish Aquat 2:157–161
Duncan A, Kubečka J (1995) Land/water ecotone effects in reservoirs on the fish fauna. Hydrobiologia 303(1):11–30
Fricke R, Eschmeyer WN, van der Laan R (eds) (2022) Eschmeyer's catalog of fishes: genera, species, references. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp. Electronic version accessed 01 Jan 2022
Froese R, Pauly D (eds) (2021) FishBase, World Wide Web electronic publication. Available at: www.fishbase.org. Accessed 7 Aug 2021
Gilbert MD, Pease AA (2019) Use of fragmented reservoir habitats by larval fish assemblages across years with contrasting hydrological conditions. Environ Biol Fish 102(6):857–871
Gogola TM, Piana PA, Da Silva PRL, Topan DA, Sanches PV (2021) Fish reproductive activity reveals temporal variations predominating spatial heterogeneity in maintaining high functional diversity of a Neotropical reservoir. Ecol Freshw Fish 31(1):154–163
Graeb BDS, Willis DW, Spindler BD (2009) Shifts in Sauger spawning locations after 40 years of reservoir ageing: influence of a novel delta ecosystem in the Missouri River, USA. River Res Appl 25:153–159
Grenouillet G, Pont D, Seip KL (2002) Abundance and species richness as a function of food resources and vegetation structure: juvenile fish assemblages in rivers. Ecography 25(6):641–650
Guedes GHS, Mattos TM, Da Silva CG, Uehara W, De Paiva Ferreira DL, Araújo FG (2020) Artificial flow regime promotes abiotic and biotic gradients: testing the concept of longitudinal zonation in an off-river reservoir. Ecohydrol 20(2):256–264
Guenther CB, Spacie A (2006) Changes in fish assemblage structure upstream of impoundments within the upper Wabash River basin, Indiana. Trans Am Fish Soc 135:570–583
Gupta LP, Subramanian V (1994) Environmental geochemistry of the River Gomti, a tributary of the Ganges River. Environ Geol 24:235–243
Gupta D, Shukla R, Barya MP, Singh G, Mishra VK (2020) Appraisal of river water quality based on field observations: a case study on narmada river. Ind J Ecol 47(4):897–901
Hiware CJ, Jadhav BV (2001) Biological studies of Manjar River near Kallam, district Osmanabad, Maharashtra, India. J Aquac Biol 16:11–13
Hora SL, Nair KK (1941) Fishes of the Satpura range, Hoshangabad district, central Provinces. Rec Indian Mus 43(3):361–373
Huet M, Timmerman JA (1986) Text book of fish culture, breeding and cultivation, 2nd edn. Fishing News Book Ltd., England, p 438
ICAR-CIFRI (2019) Annual Report, April-December 2019. ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Kolkata
ICAR-CIFRI,, ICAR-CIFRI (2020) Annual Report, January-December 2020. ICAR-Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute, Kolkata
ICAR-CIFRI, (2022) Project report on investigation on ecological status conservation and enhancement of fisheries in Madhya Pradesh part of Sardar Sarovar reservoir. Barrackpore, Kolkata, p 94
Irz P, Laurent A, Messad S, Pronier O, Argillier C (2002) Influence of site characteristics on fish community patterns in French reservoirs. Ecol Freshw Fish 11(2):123–136
IUCN (2021) The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2021-2. https://www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed 8 Aug 2021
Jayaram KC (1981) The freshwater fishes of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh. In: Burma and Sri Lanka - a handbook. Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta, p 438
Jayaram KC (1999) The freshwater fishes of the Indian region. Narendra Publishing House, Delhi, p 570
Johnson C, Sarkar UK, Koushlesh SK, Das AK, Das BK, Naskar BK (2022) Fish assemblage, ecosystem status and potential impact of Nile Tilapia in Halali Reservoir of Central India. Environ Dev Sustain 24(6):7753–7775
Kaemingk MA, Graeb BDS, Hoagstrom CW, Willis DW (2007) Patterns of fish diversity in a mainstem Missouri River reservoir and associated delta in South Dakota and Nebraska, USA. River Res Appl 23:786–791
Karamchandani SJ, Desai VR, Pisolkar MD, Bhatnagar GK (1967) Biological Investigations on the Fish & Fisheries of Narbada River (1958-1966). Bull Centr Inl Fish Res Inst 10:1–40
Khan IA, Khan AA (1985) Physical and chemical condition in Seika Jheelat, Aligarh. Ecology 3:269–274
Khedkar GD, Jamdade R, Naik S, David L, Haymer D (2014) DNA barcodes for the fishes of the Narmada, one of India’s longest rivers. PLoS One 9(7):e101460. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101460
Kosygin L, Dhamendra H (2009) Physicochemical and biological characteristics of Awang Khujairok river, Manipur, India. Environ Ecol 27(1):82–85
Lambshead PJD, Platt HM, Shaw KM (1983) The detection of differences among assemblages of marine benthic species based on an assessment of dominance and diversity. J Nat Hist 17(6):859–874
Leonard LC (1971) Water and water pollution, 1st edn. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 256–263
Lianthuamluaia L, Mishal P, Panda D, Sarkar UK, Kumar V, Sandhya KM, Karnatak G, Kumari S, Bera AK, Das S, Ali Y (2019) Understanding spatial and temporal patterns of fish diversity and assemblage structure vis-a-vis environmental parameters in a tropical Indian reservoir. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(9):9089–9098
Malik DS, Negi KS (2007) Mahseer fish bionomics and population: barrage impact on fish biology. Daya Publishing House, New Delhi, p 231
Matthews WJ, Gido KB, Gelwick FP (2004) Fish assemblages of reservoirs, illustrated by Lake Texoma (Oklahoma-Texas, USA) as a representative system. Lake Reserv Manag 20:219–239
Meitei NS, Bhargava V, Patil PM (2004) Water quality of Purna River in Purna town, Maharastra state. J Aquat Biol 19:77–78
Mishra N, Pandey DN (2016) Fish-diversity of Atarital dam at Mauganj, Rewa Madhya Pradesh, India. Int J Appl Sci 3(5):21–24
Naskar M, Sahu SK, Sharma AP (2015) Assessment of fish species assemblage on mesohabitat scale: a case of middle stretch of Narmada River, India. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 18(2):232–239
Nath D, Shrivastava NP (1999) Decline in carp fishery in Narmada in the context of construction of dam on the river and its tributaries. J Inland Fish Soc India 31(2):25–27
Nath D, Srivastava NP (2001) Physico-chemical characteristics of Narmada for the stretch Sandia to Mola in M.P. state in the context of construction of reservoirs on the river or its tributaries. J Inland Fish Soc India 33:17–24
Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MV (2016) Fishes of the world, 5th edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, p 752
Nobile AB, Freitas-Souza D, Lima FP, Queiroz J, Bayona-Perez IL, Carvalho ED, Ramos IP (2019) Damming and seasonality as modulators of fish community structure in a small tributary. Ecol Freshw Fish. https://doi.org/10.1111/eff.12475
Pennock CA (2019) Movement, habitat use, and early life history of fishes in novel river-reservoir complexes. Dissertation. Kansas State University, Kansas
Pennock CA, Hines BA, Elverud DS, Francis TA, McKinstry MC, Schleicher BJ, Gido KB (2021a) Reservoir fish assemblage structure across an aquatic ecotone: can river-reservoir interfaces provide conservation and management opportunities? Fish Manag Ecol 28(1):1–13
Pennock CA, Ahrens ZT, McKinstry MC, Budy P, Gido KB (2021b) Trophic niches of native and non-native fishes along a river-reservoir continuum. Sci Rep 11(1):1–12
Perkin JS, Bonner TH (2011) Long-term changes in flow regime and fish assemblage composition in the Guadalupe and San Marcos rivers of Texas. River Res Appl 27:566–579
Pir FA, Sharma S, Sharma G (2019) Diversity and abundance of fishes inhabiting the western region of Narmada River, Madhya Pradesh, India. Int J Life Sci 9(1):11–17
Polis GA, Strong DR (1996) Food web complexity and community dynamics. Am Nat 147(5):813–46
Polis GA, Anderson WB, Holt RD (1997) Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: the dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 28:289–316
Prchalová M, Kubecka J, Cech M, Frouzová J, Drastík V, Hohausová E, Juza T, Kratochvíl M, Matena J, Peterka J, Ríha M, Tuser M, Vasek M (2009) The effect of depth, distance from dam and habitat on spatial distribution of fish in an artificial reservoir. Ecol Freshw Fish 18:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0633.2008.00342.x
Puthiyottil M, Sarkar UK, Karnatak G, Lianthuamluaia L, Das AK, Koushlesh SK, Kumari S, Das BK (2021) Effectiveness of carp seed stocking in large reservoir ecosystems of India. Int Rev Hydrobiol 106(5-6):259–276
Rafeeq MA, Khan AM (2002) Impact of sugar mill effluents on the water quality of the river Godavari near Kandakurthi village, Nizamabad district, Andhra Pradesh. J Aquat Biol 17:33–35
Ramya VL, Parakkandi J, Saha A, Salim SM, Panikkar P, Sarkar UK, Eregowda VM, Mani K, Das BK (2021) Habitat based fish assemblage and distribution pattern in a large reservoir of peninsular India. Arab J Geosci 14(8):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07059-6
Rao KS, Chatterjee SN, Singh AK (1991) Studies on preimpoundment fishery potential (Western Region) in the context of Indira Sagar, Maheshwar Omkareshwar and Sardar Sarovar. J Inland Fish Soc India 23(1):34–41
Ridhi JBC, Parashar A, Das AK, Bose AK (2013) Fishes of Gandhisagar reservoir in Madhya Pradesh. J Chem Biol Phys Sci, Section B 3(1):392–398
Rinke K, Keller PS, Kong X, Borchardt D, Weitere M (2019) Ecosystem services from inland waters and their aquatic ecosystems. In: Schröter M, Bonn A, Klotz S, Seppelt R, Baessler C (eds) Atlas of Ecosystem Services. Springer, Cham, pp 191–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96229-0_30
Saha A, Jesna PK, Ramya VL, Mol SS, Panikkar P, Vijaykumar ME, Sarkar UK, Das BK (2022) Phosphorus fractions in the sediment of a tropical reservoir, India: implications for pollution source identification and eutrophication. Environ Geochem Health 44(3):749–769
Sajina AM, Sarkar UK, Canciyal J, Das BK, Saha A, Mishal P, Jesna PK, Ramteke M, Das AK (2021) Influence of cage farming and environmental parameters on spatio-temporal variability of fish assemblage structure in a tropical reservoir of Peninsular India. Limnologica 1(91):25925
Saksena DN, Garg RK, Rao RJ (2008) Water quality and pollution status of Chambal River in National Chambal sanctuary, Madhya Pradesh. J Environ Biol 29(5):701–710
Sanches BO, Hughes RM, Macedo DR, Callisto M, Santos GB (2016) Spatial variations in fish assemblage structure in a southeastern Brazilian reservoir. Braz J Biol 76:185–193
Sanches PV, Gogola TM, Silva RO, Topan DA, dos Santos Picapedra PH, Piana PA (2020) Arms as areas for larval development of migratory fish species in a Neotropical reservoir and the influence of rainfall over abundances. J Fish Biol 97(5):1306–1316
Sandhya KM, Lianthuamluaia L, Karnatak G, Sarkar UK, Kumari S, Mishal P, Kumar V, Panda D, Ali Y, Naskar BK (2019) Fish assemblage structure and spatial gradients of diversity in a large tropical reservoir, Panchet in the Ganges basin, India. Env Sci Poll Res 26(18):18804–18813
Sarkar UK, Bain MB (2007) Priority habitats for the conservation of large river fish in the Ganges river basin. Aquat Conserv Mar Freshwat Ecosyst 17(4):349–359
Sarkar UK, Lakra WS, Dubey VK, Pandey A, Tripathi M, Sani R, Awasthi A (2014) Freshwater fish diversity in the River Ken of Ganga Basin: abundance, threats and their management. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 84(4):1043–1051
Sarkar UK, Mahapatra BK, Saxena SR, Singh AK (2015a) Mahseer in India: an overview on research status and future priorities. J Ecophysiol Occup Health 15(1-2):45–52
Sarkar UK, Sharma J, Mahapatra BK (2015b) A review on the fish communities in the Indian reservoirs and enhancement of fisheries and aquatic environment. J Aquac Res Dev 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000297
Sarkar UK, Sandhya KM, Mishal P, Karnatak G, Lianthuamluaia KS, Das BK (2018) Status, prospects, threats, and the way forward for sustainable management and enhancement of the tropical Indian reservoir fisheries: an overview. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 26(2):155–175
Shah MA, Vyas V, Yadav S (2018) Fish biodiversity and its periodic reduction: a case study of river Narmada in Central India. In: Singh VP, Yadav S, Yadav RN (eds) Environmental pollution. Springer, Singapore, pp 193–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5792-2_16
Shivhare R (2022) Sand mining a threat to the mahseer and other aquatic species in the Narmada. Mongabay series, 28 April 2022, https://india.mongabay.com/2022/04/sand-mining-a-threat-to-the-mahseer-and-other-aquatic-species-in-the-narmada/. Accessed 14 June 2022
Shrivastava VS, Patil PR (2002) Tapti River water pollution by industrial wastes: a statistical approach. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 1:279–283
Shukla R, Bhat A (2018) Beta-diversity partitioning and drivers of variations in tropical fish community structure in central India. Aquat Sci 80:18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-018-0568-1
Singh SN (2009) River Narmada, its environment and fisheries. Bull Centr Inl Fish Res Inst Barrackpore 157:1–64
Singh BN, Rai S (1999) Physico-chemical studies of Ganga river at Varanasi. J Environ Pollut 6:43–46
Singh SN, Nath D (2004) Strategies for development of fisheries in Sardar Sarovar during pre- and post-impoundment stage. A work plan. Bull Centr Inl Fish Res Inst Barrackpore 133:1–13
Singh HP, Mahaver LR, Mishra JP (1999) Limnochemical characteristics of river Ghaghara in U.P. J Inland Fish Soc India 31:28–32
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Smith NG, Buckmeler DL, Paul Fleming B (2022) Spatial variability in the fish assemblage of a large river-reservoir ecosystem. N Am J Fish Manag. https://doi.org/10.1002/nafm.10804
Sugunan VV (1995) Reservoir fisheries of India. In: FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, No. 345. FAO, Rome
Talwar PK, Jhingran AG (1991) Inland fishes of India and adjacent countries. Oxford-IBH Publishing Co.Pvt.Ltd, New Delhi, p 1158
Tan CS, Zhang TQ, Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Oloya T, Gaynor JD (2007) Water quality and crop production improvement using a wetland-reservoir and draining/subsurface irrigation system. Can Water Resour J 32(2):129–136
Terra BDF, Santos ABID, Araújo FG (2010) Fish assemblage in a dammed tropical river: an analysis along the longitudinal and temporal gradients from river to reservoir. Neotrop Ichthyol 8:599–606
Trivedi P, Bajpai A, Thareja S (2009) Evaluation of water quality: physico–chemical characteristics of Ganga River at Kanpur by using correlation study. Nat Sci 1(6):91–94
Unni KS (1996) Ecology of river Narmada. APH publishing, New Delhi, p 363
Virbickas T, Vezza P, Kriaučiūnienė J, Akstinas V, Šarauskienė D, Steponėnas A (2020) Impacts of low-head hydropower plants on cyprinid-dominated fish assemblages in Lithuanian rivers. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14
Vyas V, Parashar V, Bara S, Damde D (2007) Fish catch composition of River Narmada with reference to common fishing gears in Hoshangabad area. Nat Bull Life Sci 4(1&2):1–6
Vyas V, Damde D, Parashar V (2009) Fish diversity of Narmada in submergence area of IndiraSagar Reservoir. J Inland Fish Soc India 41(2):18–25
Vyas V, Bara S, Parashar V, Damde D, Tuli RP (2006) Temporal variation in fish biodiversity of River Narmada in Hoshangabad Region. Fish Chimes 27:49–53
WHO (1993) World Health Organization, guidelines for drinking water quality-I, recommendations, 2nd edn, Geneva, WHO. Accessed on 30 July 2021 http://www.lenntech.com/drinking-water-standards.htm
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Director ICAR-CIFRI for providing the necessary facilities. We would like to thank Mr. Lohit Kumar and Mr. Y. Ali for their assistance.
Funding
The authors also thank MP Fish Federation, Bhopal, for funding and other logistic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Satish Kumar Koushlesh: Explorations, field data collection, data analysis, draft manuscript preparation
Canciyal Johnson: Field data collection, manuscript preparation, data analysis
Uttam Kumar Sarkar: Conceptualization, implementation of work, guidance in manuscript preparation, manuscript corrections
Archan Kanti Das: Field data collection on water quality
Basanta Kumar Das: Overall guidance and support
Mishal P: Technical input, manuscript corrections
Lianthuamluaia: Data visualization and manuscript correction
Bablu Kumar Naskar: Field data collection
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in the process for publication of this paper.
Consent for publication
Consent of all authors was taken for publication of this MS.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas Hein
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Koushlesh, S.K., Johnson, C., Sarkar, U.K. et al. Exploring fish assemblage structure, feeding guild, and water quality in a typical river-reservoir interface of tropical large reservoir environment, Central India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 2179–2204 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22267-7
Keywords
Profiles
- Uttam Kumar Sarkar View author profile