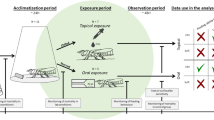
Abstract
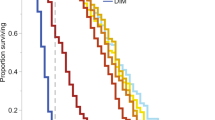
Toxicological studies in honeybees have long shown that a single pesticide dose or concentration does not necessarily induce a single response. Inter-individual differences in pesticide sensitivity and/or the level of exposure (e.g., ingestion of pesticide-contaminated matrices) may explain this variability in risk posed by a pesticide. Therefore, to better inform pesticide risk assessment for honeybees, we studied the risk posed by pesticides to two behavioral castes, nurse, and forager bees, which are largely represented within colonies and which exhibit large differences in their physiological backgrounds. For that purpose, we determined the sensitivity of nurses and foragers to azoxystrobin (fungicide) and sulfoxaflor (insecticide) upon acute or chronic exposure. Azoxystrobin was found to be weakly toxic to both types of bees. However, foragers were more sensitive to sulfoxaflor than nurses upon acute and chronic exposure. This phenomenon was not explained by better sulfoxaflor metabolization in nurses, but rather by differences in body weight (nurses being 1.6 times heavier than foragers). Foragers consistently consumed more sugar syrup than nurses, and this increased consumption was even more pronounced with pesticide-contaminated syrup (at specific concentrations). Altogether, the stronger susceptibility and exposure of foragers to sulfoxaflor contributed to increases of 2 and tenfold for the acute and chronic risk quotients, respectively, compared to nurses. In conclusion, to increase the safety margin and avoid an under-estimation of the risk posed by insecticides to honeybees, we recommend systematically including forager bees in regulatory tests.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adams E, Leeb C, Roodt AP, Brühl CA (2021) Interspecific sensitivity of European amphibians towards two pesticides and comparison to standard test species. Environ Sci Eur 33:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00491-1
Ardalani H (2021) Dietary quercetin impacts the concentration of pesticides in honey bees. Chemosphere 262:127848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127848
Ardalani H, Vidkjær NH, Kryger P et al (2021) Metabolomics unveils the influence of dietary phytochemicals on residual pesticide concentrations in honey bees. Environ Int 152:106503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106503
Azpiazu C, Bosch J, Bortolotti L et al (2021) Toxicity of the insecticide sulfoxaflor alone and in combination with the fungicide fluxapyroxad in three bee species. Sci Rep 11:6821. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86036-1
Barascou L, Sene D, Barraud A et al (2021) Pollen nutrition fosters honeybee tolerance to pesticides. R Soc Open Sci 8:210818. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.210818
Bendahou N, Bounias M, Fleche C (1997) Acute toxicity of cypermethrin and fenitrothion on honeybees (Apismelliferamellifera) according to age, formulations and (chronic paralysis virus) insecticide interaction. J Environ Biol 18:55–65
Berenbaum MR, Johnson RM (2015) Xenobiotic detoxification pathways in honey bees. Curr Opin Insect Sci 10:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2015.03.005
Brodschneider R, Crailsheim K (2010) Nutrition and health in honey bees. Apidologie 41:278–294. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2010012
Brodschneider R, Libor A, Kupelwieser V, Crailsheim K (2017) Food consumption and food exchange of caged honey bees using a radioactive labelled sugar solution. PLoS One 12:e0174684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174684
Calow P (1996) Variability: noise or information in ecotoxicology? Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2:121–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1382-6689(96)00041-5
Claudianos C, Ranson H, Johnson RM et al (2006) A deficit of detoxification enzymes: pesticide sensitivity and environmental response in the honeybee. Insect Mol Biol 15:615–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00672.x
Cox DR (1970) Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc 34:187–220
Crailsheim K (1992) The flow of jelly within a honeybee colony. J Comp Physiol B 162:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301617
Dahlgren L, Johnson RM, Siegfried BD, Ellis MD (2012) Comparative toxicity of acaricides to honey bee (Hymenoptera: apidae) workers and queens. J Econ Entomol 105:1895–1902. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC12175
EFSA (2010) Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance azoxystrobin. EFSA J 8:1–110
EFSA (2014) Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance sulfoxaflor. EFSA J 12:170
Free JB (1960) The distribution of bees in a honey-bee (Apis mellifera L.) colony. Proc R Entomol Soc Lond A 35:141
Gerig L (1991) Importance de l’Insegar pour l’apiculture et l’arboriculture. J Suisse Apic 88:235–238
Gerig L (1975) The effects of juvenile hormone analogues on summer bees (Apismellifera L.) in the field and laboratory. Schweiz Landwirtsch Forsch 14:355–370
Graves JB, Mackensen O (1965) Topical application and insecticide resistance studies on the honey bee. J Econ Entomol 58:990–993. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/58.5.990
Kessler SC, Tiedeken EJ, Simcock KL et al (2015) Bees prefer foods containing neonicotinoid pesticides. Nature 521:74–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14414
Knecht D, Kaatz HH (1990) Patterns of larval food production by hypopharyngeal glands in adult worker honeybees. Apidologie 21:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:19900507
Ladas A (1972) The influence of some internal and external factors upon the insecticide resistance of honeybee. Apidologie 3:55–78
Liao L-H, Wu W-Y, Berenbaum MR (2017) Behavioral responses of honey bees (Apismellifera) to natural and synthetic xenobiotics in food. Sci Rep 7:15924. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15066-5
Long EY, Krupke CH (2016) Non-cultivated plants present a season-long route of pesticide exposure for honey bees. Nat Commun 7:11629. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11629
Lu K, Song Y, Zeng R (2021) The role of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification in insect adaptation to xenobiotics. Curr Opin Insect Sci 43:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2020.11.004
Mayland PG, Burkhardt CC (1970) Honey bee mortality as related to insecticide-treated surfaces and bee age12. J Econ Entomol 63:1437–1439. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/63.5.1437
Mullin CA, Frazier M, Frazier JL et al (2010) High levels of miticides and agrochemicals in North American apiaries: implications for honey bee health. PLoS One 5:e9754. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009754
Niesen M, Sappington K, Ruhman M, Mroz R, Leader RAP, Housenger J, Chief B (2019) Ecological risk assessment for the registration of sulfoxaflor.
Nogueira-Couto RH, Abe CS, Pitelli RA (1996) Efeito do paraquat na mortalidade de operárias de Apismellifera (abelhas africanizadas). Naturalia 21:49–55
OECD (1998a) Test No. 213: honeybees, acute oral toxicity test, OECD publishing. Paris
OECD (1998b) Test No. 214: Honeybees, acute contact toxicity test, OECD Publishing. Paris
OECD (2017) Test No. 245: honey bee (Apis mellifera L.), chronic oral toxicity test (10-day feeding), OECD Publishing. Paris
Pain J (1966) Note technique nouveau modèle de cagettes expérimentales pour le maintien d’abeilles en captivité. Ann Abeille 9:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:19660106
Panini M, Manicardi GC, Moores GD, Mazzoni E (2016) An overview of the main pathways of metabolic resistance in insects. Invertebr Surviv J 326–335. https://doi.org/10.25431/1824-307X/ISJ.V13I1.326-335
Pernal SF, Currie RW (2000) Pollen quality of fresh and 1-year-old single pollen diets for worker honey bees (Apismellifera L.). Apidologie 31:387–409. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2000130
Poquet Y, Vidau C, Alaux C (2016) Modulation of pesticide response in honeybees. Apidologie 47:412–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-016-0429-7
Prado A, Requier F, Crauser D et al (2020) Honeybee lifespan: the critical role of pre-foraging stage. R Soc Open Sci 7:200998. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200998
R Core Team (2020) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for statistical computing.
Rinkevich FD, Margotta JW, Pittman JM et al (2015) Genetics, synergists, and age affect insecticide sensitivity of the honey bee ApisMellifera. Plos One 10:e0139841. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139841
Ritz C, Baty F, Streibig JC, Gerhard D (2015) Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS One 10:e0146021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146021
Robinson GE (2002) Genomics and integrative analyses of division of labor in honeybee colonies. Am Nat 160:S160–S172. https://doi.org/10.1086/342901
Robinson GE, Page RE, Strambi C, Strambi A (1992) Colony integration in honey bees: mechanisms of behavioral reversion. Ethology 90:336–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0310.1992.tb00844.x
Rodney S, Purdy J (2020) Dietary requirements of individual nectar foragers, and colony-level pollen and nectar consumption: a review to support pesticide exposure assessment for honey bees. Apidologie. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-019-00694-9
Rortais A, Arnold G, Halm M-P, Touffet-Briens F (2005) Modes of honeybees exposure to systemic insecticides: estimated amounts of contaminated pollen and nectar consumed by different categories of bees. Apidologie 36:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2004071
Sanchez-Bayo F, Goka K (2014) Pesticide residues and bees – a risk assessment. PLoS One 9:e94482. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094482
Schatz F, Wallner K (2009) Pflanzenschutzmittelapplikation in blühenden Raps (Brassica napus) und deren Auswirkungen auf die Rückstandssituation in Honig, Nektar und Pollen der Honigbiene (Apis mellifera L.). Universität Hohenheim
Sgolastra F, Medrzycki P, Bortolotti L et al (2017) Synergistic mortality between a neonicotinoid insecticide and an ergosterol-biosynthesis-inhibiting fungicide in three bee species: Synergistic interactions between pesticides in three bee species. Pest Manag Sci 73:1236–1243. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4449
Smirle MJ, Robinson GE (1989) Behavioral status and detoxifying enzyme activity are related in worker honey bees. J Insect Behav 2:285–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053300
Smith JN (1955) Detoxication mechanisms in insects. Biol Rev 30:455–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.1955.tb01548.x
Spurgeon D, Lahive E, Robinson A et al (2020) Species sensitivity to toxic substances: evolution, ecology and applications. Front Environ Sci 8:588380. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2020.588380
Szabó B, Lang Z, Kövér S, Bakonyi G (2021) The inter-individual variance can provide additional information for the ecotoxicologists beside the mean. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 217:112260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112260
Tahori AS, Sobel Z, Soller M (1969) Variability in insecticide tolerance of eighteen honey-bee colonies. Entomol Exp Appl 12:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1570-7458.1969.tb02501.x
Thompson HM (2021) The use of the hazard quotient approach to assess the potential risk to honeybees (Apismellifera) posed by pesticide residues detected in bee-relevant matrices is not appropriate. Pest Manag Sci 77:3934–3941. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6426
Thompson HM, Hunt LV (1999) Extrapolating from honeybees to bumblebees in pesticide risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 8:147–166
Tosi, Nieh (2019) Lethal and sublethal synergistic effects of a new systemic pesticide, flupyradifurone (Sivanto®), on honeybees. Proc Roayl Soc B 286:20190433. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.0433
Tsvetkov N, Zayed A (2021) Searching beyond the streetlight: Neonicotinoid exposure alters the neurogenomic state of worker honey bees. Ecol Evol 11:18733–18742. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8480
Uhl P, Franke LA, Rehberg C et al (2016) Interspecific sensitivity of bees towards dimethoate and implications for environmental risk assessment. Sci Rep 6:34439. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34439
van der Steen JJM, Cornelissen B, Donders J et al (2012) How honey bees of successive age classes are distributed over a one storey, ten frames hive. J Apic Res 51:174–178. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.1.51.2.05
Vance JT, Williams JB, Elekonich MM, Roberts SP (2009) The effects of age and behavioral development on honey bee (Apismellifera) flight performance. J Exp Biol 212:2604–2611. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.028100
Vannette RL, Mohamed A, Johnson BR (2015) Forager bees (Apismellifera) highly express immune and detoxification genes in tissues associated with nectar processing. Sci Rep 5:16224. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16224
Whitfield CW, Cziko A-M, Robinson GE (2003) Gene expression profiles in the brain predict behavior in individual honey bees. Science 302:296–299. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086807
Williams GR, Alaux C, Costa C et al (2013) Standard methods for maintaining adult Apismellifera in cages under in vitro laboratory conditions. J Apic Res 52:1–36. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.1.52.1.04
Zhu YC, Caren J, Reddy GVP et al (2020) Effect of age on insecticide susceptibility and enzymatic activities of three detoxification enzymes and one invertase in honey bee workers (Apismellifera). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 238:108844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108844
Funding
This project received funding from the European Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement no. 773921 (LB, YLC, and CA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LB, YLC, and CA conceived the study. LB, DS, and CA conducted the experiments. LB and CA analyzed the data. YLC and CA contributed to reagents. LB, YLC, and CA wrote the manuscript. All authors read and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barascou, L., Sene, D., Le Conte, Y. et al. Pesticide risk assessment: honeybee workers are not all equal regarding the risk posed by exposure to pesticides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 90328–90337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21969-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21969-2