Abstract
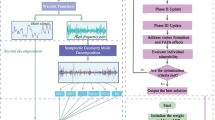
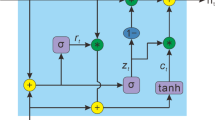
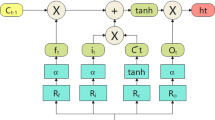
As one of the renewable energy power generation methods, wind power generation shows a high growth trend. However, while wind power is connected to the grid, the volatility and instability of wind power make the power system produce a lot of uncertain fluctuations, which greatly affects the power quality and jeopardizes the stable operation of the power system. Therefore, high wind speed forecasting accuracy can provide a solid basis for grid management, improve the power system’s ability to consume wind power, and ensure the safety and stabilization of the power system. In order to solve the problem of inaccurate prediction caused by the non-linearity and unsteadiness of wind speed series, this paper proposes a Fractal Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (FEEMD)-Permutation Entropy (PE)-Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA)-Error Back Propagation (BP) neural network method for short-term wind speed prediction. This method first uses FEEMD to decompose the original wind speed in order from high to low frequency; then calculates the entropy value of each component, and merges the components with similar entropy values to effectively reduce the computation; and finally, the new sub-series are predicted by SSA-BP model, and the predicted value of the merged new sub-sequences are accumulated to obtain the final wind speed prediction results. The simulation study shows that the proposed prediction model is not only fast and accurate, but also suitable for short-term wind speed prediction.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets that has been used in the study are available from co-author on reasonable request.
References
Aasim SSN, Mohapatra A (2019) Repeated wavelet transform based ARIMA model for very short-term wind speed forecasting. Renew Energ 136:758–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.031
Chaurasiya PK, Warudkar V, Ahmed S (2019) Wind energy development and policy in India: a review. Energy Strategy Rev 24:342–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.04.010
Ding Y, Chen Z, Zhang H, Wang X, Guo Y (2022) A short-term wind power prediction model based on CEEMD and WOA-KELM. Renew Energ 189:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.02.108
Feng B-f, Xu Y-s, Zhang T, Zhang X (2022) Hydrological time series prediction by extreme machine learning and sparrow search algorithm. Water Supply 22:3143–3157. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.419
Fu W, Wang K, Li C, Tan J (2019) Multi-step short-term wind speed forecasting approach based on multi-scale dominant ingredient chaotic analysis, improved hybrid GWO-SCA optimization and ELM. Energ Convers Manage 187:356–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.02.086
Gu B, Zhang T, Meng H, Zhang J (2021) Short-term forecasting and uncertainty analysis of wind power based on long short-term memory, cloud model and non-parametric kernel density estimation. Renew Energ 164:687–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.09.087
Harty TM, Holmgren WF, Lorenzo AT, Morzfeld M (2019) Intra-hour cloud index forecasting with data assimilation. Sol Energy 185:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.03.065
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MLC, Shih HH, Zheng QN, Yen NC, Tung CC, Liu HH (1998) The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. P Roy Soc A-Math Phy 454:903–995. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Ilhan A, Sahin B, Bilgili M (2022) A review: diffuser augmented wind turbine technologies. Int J Green Energy 19:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2021.1914628
Li J, Wang G, Li Z, Yang S, Chong WT, Xiang X (2020) A review on development of offshore wind energy conversion system. Int J Energ Res 44:9283–9297. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5751
Li Z, Luo X, Liu M, Cao X, Du S, Sun H (2022) Wind power prediction based on EEMD-Tent-SSA-LS-SVM. Energy Rep 8:3234–3243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.150
Liu J, Wang Z (2021) A hybrid sparrow search algorithm based on constructing similarity. Ieee Access 9:117581–117595. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3106269
Liu H, Tian H-q, Li Y-f, Zhang L (2015) Comparison of four Adaboost algorithm based artificial neural networks in wind speed predictions. Energ Convers Manage 92:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.12.053
Liu H, Mi X, Li Y (2018a) Smart multi-step deep learning model for wind speed forecasting based on variational mode decomposition, singular spectrum analysis, LSTM network and ELM. Energ Convers Manage 159:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.01.010
Liu H, Mi X, Li Y (2018b) Comparison of two new intelligent wind speed forecasting approaches based on Wavelet Packet Decomposition, Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise and Artificial Neural Networks. Energ Convers Manage 155:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.10.085
Liu F, Gao J, Liu H (2020) A fault diagnosis solution of rolling bearing based on MEEMD and QPSO-LSSVM. Ieee Access 8:101476–101488. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2998722
Nazir MS, Bilal M, Sohail HM, Liu B, Chen W, Iqbal HMN (2020) Impacts of renewable energy atlas: reaping the benefits of renewables and biodiversity threats. Int J Hydrogen Energ 45:22113–22124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.195
Nguyen H-P, Baraldi P, Zio E (2021) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network for multi-step predictions of time series signals in nuclear power plants. Appl Energ 283:116346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116346
Qian J, Zhu M, Zhao Y, He X (2021) Short-term wind speed prediction with a two-layer attention-based LSTM. Comput Syst Sci Eng 39:197–209. https://doi.org/10.32604/csse.2021.016911
Ren C, An N, Wang J, Li L, Hu B, Shang D (2014) Optimal parameters selection for BP neural network based on particle swarm optimization: a case study of wind speed forecasting. Knowl-Based Syst 56:226–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.11.015
Wabukala BM, Otim J, Mubiinzi G, Adaramola MS (2021) Assessing wind energy development in Uganda: opportunities and challenges. J Wind Eng Ind Aerod 45:1714–1732. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309524x20985768
Wang J, Song Y, Liu F, Hou R (2016a) Analysis and application of forecasting models in wind power integration: a review of multi-step-ahead wind speed forecasting models. Renew Sust Energ Rev 60:960–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.114
Wang S, Zhang N, Wu L, Wang Y (2016b) Wind speed forecasting based on the hybrid ensemble empirical mode decomposition and GA-BP neural network method. Renew Energ 94:629–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.03.103
Wu Y, Sun L, Sun X, Wang B (2022) A hybrid XGBoost-ISSA-LSTM model for accurate short-term and long-term dissolved oxygen prediction in ponds. Environ Sci Pollut R 29:18142–18159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17020-5
Yang L, Li Z, Wang D, Miao H, Wang Z (2021) Software defects prediction based on hybrid particle swarm optimization and sparrow search algorithm. Ieee Access 9:60865–60879. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3072993
Yu C, Li Y, Zhang M (2017) An improved wavelet transform using singular spectrum analysis for wind speed forecasting based on Elman Neural Network. Energ Convers Manage 148:895–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.05.063
Zhang Y, Pan G (2020) A hybrid prediction model for forecasting wind energy resources. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:19428–19446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08452-6
Zhang Y, Chen B, Pan G, Zhao Y (2019) A novel hybrid model based on VMD-WT and PCA-BP-RBF neural network for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energ Convers Manage 195:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.05.005
Zhang Y, Pan G, Chen B, Han J, Zhao Y, Zhang C (2020) Short-term wind speed prediction model based on GA-ANN improved by VMD. Renew Energ 156:1373–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.047
Zhang S, Chen Y, Xiao J, Zhang W, Feng R (2021a) Hybrid wind speed forecasting model based on multivariate data secondary decomposition approach and deep learning algorithm with attention mechanism. Renew Energ 174:688–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.04.091
Zhang Y, Han J, Pan G, Xu Y, Wang F (2021b) A multi-stage predicting methodology based on data decomposition and error correction for ultra-short-term wind energy prediction. J Clean Prod 292:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125981
Zheng J, Cheng J, Yang Y (2014) Partly ensemble empirical mode decomposition: an improved noise-assisted method for eliminating mode mixing. Signal Process 96:362–374
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous referees for the thoughtful and constructive suggestions that led to a considerable improvement of the paper.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61671338 and Grant 51877161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhu Ting: conceptualization, methodology, software, model building, writing original draft.
Wenbo Wang: writing review and editing.
Min Yu: writing review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Wang, W. & Yu, M. Short-term wind speed prediction based on FEEMD-PE-SSA-BP. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 79288–79305 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21414-4