Abstract
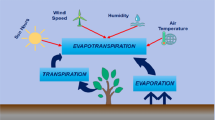
Evapotranspiration is an important quantity required in many applications, such as hydrology and agricultural and irrigation planning. Reference evapotranspiration is particularly important, and the prediction of its variations is beneficial for analyzing the needs and management of water resources. In this paper, we explore the predictive ability of hybrid ensemble learning to predict daily reference evapotranspiration (RET) under the semi-arid climate by using meteorological datasets at 12 locations in the Andalusia province in southern Spain. The datasets comprise mean, maximum, and minimum air temperatures and mean relative humidity and mean wind speed. A new modified variant of the grey wolf optimizer, named the PRSFGWO algorithm, is proposed to maximize the ensemble learning’s prediction accuracy through optimal weight tuning and evaluate the proposed model’s capacity when the climate data is limited. The performance of the proposed approach, based on weighted ensemble learning, is compared with various algorithms commonly adopted in relevant studies. A diverse set of statistical measurements alongside ANOVA tests was used to evaluate the predictive performance of the prediction models. The proposed model showed high-accuracy statistics, with relative root mean errors lower than 0.999% and a minimum R2 of 0.99. The model inputs were also reduced from six variables to only two for cost-effective predictions of daily RET. This shows that the PRSFGWO algorithm is a good RET prediction model for the semi-arid climate region in southern Spain. The results obtained from this research are very promising compared with existing models in the literature.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbas AT, Abubakr M, Hassan MA, Luqman M, Soliman MS, Hegab H (2020) An adaptive design for cost, quality and productivity-oriented sustainable machining of stainless steel 316. J Market Res 9(6):14568–14581
Abda Z, Chettih M, Zerouali B (2021) Assessment of neuro-fuzzy approach based different wavelet families for daily flow rates forecasting. Model Earth Syst Environ 7(3):1523–1538
Al-Mukhtar M (2021) Modeling of pan evaporation based on the development of machine learning methods. Theoret Appl Climatol 146(3–4):961–979
Allen-Dumas MR, Xu H, Kurte KR, Rastogi D (2021) Toward urban water security: broadening the use of machine learning methods for mitigating urban water hazards. Front Water 2:562304
Almorox J, Arnaldo JA, Bailek N, Martí P (2020) Adjustment of the Angstrom-Prescott equation from Campbell-Stokes and Kipp-Zonen sunshine measures at different timescales in Spain. Renew Energy 154:337–350
Bellido-Jiménez JA, Estévez J, García-Marín AP (2021) New machine learning approaches to improve reference evapotranspiration estimates using intra-daily temperature-based variables in a semi-arid region of Spain. Agric Water Manag 245:106558
Bouchouicha K, Bailek N, Bellaoui M, Oulimar B (2019a) Estimation of solar power output using ANN model: a case study of a 20-MW solar PV plan at Adrar, Algeria. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Springer International Publishing: 195–203
Bouchouicha K, Hassan MA, Bailek N, Aoun N (2019b) Estimating the global solar irradiation and optimizing the error estimates under Algerian desert climate. Renew Energy 139:844–858
Bouchouicha K, Bailek N, Razagui A, Mohamed E-S, Bellaoui M, Bachari NEIJIJOESM (2020) Comparison of artificial intelligence and empirical models for energy production estimation of 20 MWp solar photovoltaic plant at the Saharan Medium of Algeria
Chen S, He C, Huang Z, Xu X, Jiang T, He Z, Liu J, Su B, Feng H, Yu Q, He J (2022) Using support vector machine to deal with the missing of solar radiation data in daily reference evapotranspiration estimation in China. Agricu Forest Meteorol 316:108864
Chen Z, Zhu Z, Jiang H, Sun S (2020) Estimating daily reference evapotranspiration based on limited meteorological data using deep learning and classical machine learning methods. J Hydrol 591:125286
Cheng X, Feng Z-K, Niu W-J (2020) Forecasting monthly runoff time series by single-layer feedforward artificial neural network and grey wolf optimizer. IEEE Access 8:157346–157355
dos Santos Farias DB, Althoff D, Rodrigues LN, Filgueiras R (2020) Performance evaluation of numerical and machine learning methods in estimating reference evapotranspiration in a Brazilian agricultural frontier. Theoret Appl Climatol 142(3–4):1481–1492
El-Kenawy EM, Eid MM, Saber M, Ibrahim A (2020) MbGWO-SFS: modified binary grey wolf optimizer based on stochastic fractal search for feature selection. IEEE Access 8:107635–107649
El-kenawy E-SM, Ibrahim A, Bailek N, Bouchouicha K, Hassan MA, Jamei M, Al-Ansari N (2021) Sunshine duration measurements and predictions in Saharan Algeria region: an improved ensemble learning approach. Theoret Appl Climatol 147(3–4):1015–1031
El-Kenawy E-SM, Ibrahim A, Bailek N, Bouchouicha K, Hassan MA, Jamil B, Al-Ansari NJC (2022) Hybrid ensemble-learning approach for renewable energy resources evaluation in Algeria. Materials and Continua 71(3): 5837–5854
Elbeltagi A, Zerouali B, Bailek N, Bouchouicha K, Pande C, Santos CAG, Towfiqul Islam ARM, Al-Ansari N, El-kenawy E-SM (2022) Optimizing hyperparameters of deep hybrid learning for rainfall prediction: a case study of a Mediterranean basin. Arab J Geosci 15(10):933
Estévez J, Gavilán P, Giráldez JV (2011) Guidelines on validation procedures for meteorological data from automatic weather stations. J Hydrol 402:144–154
Fathian F, Dehghan Z (2019) Using hybrid weighting‐clustering approach for regional frequency analysis of maximum 24‐hr rainfall based on climatic, geographical, and statistical attributes. Int J Climatol 39(11):4413–4428
Fazel N, Berndtsson R, Uvo CB, Madani K, Kløve B (2018) Regionalization of precipitation characteristics in Iran’s Lake Urmia basin. Theor Appl Climatol 132:363–373
Feng K, Tian J (2021) Forecasting reference evapotranspiration using data mining and limited climatic data. Eur J Remote Sens 54(sup2):363–371
Ferreira LB, da Cunha FF (2020) New approach to estimate daily reference evapotranspiration based on hourly temperature and relative humidity using machine learning and deep learning. Agric Water Manag 234:106113
Freire PKMM, Santos SAG, da Silva GBL (2019) Analysis of the use of discrete wavelet transforms coupled with ANN for short-term streamflow forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 80:494–505
Freire PKMM, Santos CAG (2020) Optimal level of wavelet decomposition for daily inflow forecasting. Earth Sci Inform 13:1163–1173
Fu T, Li X, Jia R, Feng L (2021) A novel integrated method based on a machine learning model for estimating evapotranspiration in dryland. J Hydrol 603:126881
Ghoneim SS, Farrag TA, Rashed AA, El-Kenawy E-SM, Ibrahim AJIA (2021) Adaptive dynamic meta-heuristics for feature selection and classification in diagnostic accuracy of transformer faults, 9: 78324–78340
Graf R, Zhu S, Sivakumar B (2019) Forecasting river water temperature time series using a wavelet–neural network hybrid modelling approach. J Hydrol 578:124115
Granata F (2019) Evapotranspiration evaluation models based on machine learning algorithms—a comparative study. Agric Water Manag 217:303–315
Granata F, Di Nunno F (2021) Forecasting evapotranspiration in different climates using ensembles of recurrent neural networks. Agric Water Manag 255:107040
Granata F, Gargano R, de Marinis G (2020) Artificial intelligence based approaches to evaluate actual evapotranspiration in wetlands. Sci Total Environ 703:135653
Guermoui M, Bouchouicha K, Benkaciali S, Gairaa K, Bailek N (2022) New soft computing model for multi-hours forecasting of global solar radiation. Eur Phys J Plus 137:162
Hassan MA, Akoush BM, Abubakr M, Campana PE, Khalil A (2021a) High-resolution estimates of diffuse fraction based on dynamic definitions of sky conditions. Renew Energy 169:641–659
Hassan MA, Bailek N, Bouchouicha K, Nwokolo SC (2021b) Ultra-short-term exogenous forecasting of photovoltaic power production using genetically optimized non-linear auto-regressive recurrent neural networks. Renew Energy 171:191–209
Hassan MA, Khalil A, Kaseb S, Kassem MA (2017) Exploring the potential of tree-based ensemble methods in solar radiation modeling. Appl Energy 203:897–916
Hossein Kazemi M, Shiri J, Marti P, Majnooni-Heris A (2020) Assessing temporal data partitioning scenarios for estimating reference evapotranspiration with machine learning techniques in arid regions. J Hydrol 590:125252
Huang G, Wu L, Ma X, Zhang W, Fan J, Yu X, Zeng W, Zhou H (2019) Evaluation of CatBoost method for prediction of reference evapotranspiration in humid regions. J Hydrol 574:1029–1041
Kaood A, Abubakr M, Al-Oran O, Hassan MA (2021) Performance analysis and particle swarm optimization of molten salt-based nanofluids in parabolic trough concentrators. Renew Energy 177:1045–1062
Keshtegar B, Bouchouicha K, Bailek N, Hassan MA, Kolahchi R, Despotovic M (2022) Solar irradiance short-term prediction under meteorological uncertainties: survey hybrid artificial intelligent basis music-inspired optimization models. Eur Phys J Plus 137(3):362
Keshtegar B, Kisi O, Ghohani Arab H, Zounemat-Kermani MJWRM (2018) Subset modeling basis ANFIS for prediction of the reference evapotranspiration. 32(3): 1101–1116.
Kisi O (2016) Modeling reference evapotranspiration using three different heuristic regression approaches. Agric Water Manag 169:162–172
Kisi O, Keshtegar B, Zounemat-Kermani M, Heddam S, Trung N-T (2021) Modeling reference evapotranspiration using a novel regression-based method: radial basis M5 model tree. Theoret Appl Climatol 145(1–2):639–659
Kottek M, Grieser J, Beck C, Rudolf B, Rubel F (2006) World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol Z 15(3):259–263
Laaboudi A, Mouhouche B, Draoui B (2012) Neural network approach to reference evapotranspiration modeling from limited climatic data in arid regions. Int J Biometeorol 56(5):831–841
Lakra K, Chug A (2021) Improving software maintainability prediction using hyperparameter tuning of baseline machine learning algorithms. Springer, Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, pp 679–692
Liu Y, Wang L, Gu K (2021) A support vector regression (SVR)-based method for dynamic load identification using heterogeneous responses under interval uncertainties. Appl Soft Comput 110:107599
Mao W, Wang F-Y (2012) Chapter 8 - Cultural modeling for behavior analysis and prediction. In new advances in intelligence and security informatics, pages: 91–102, Academic Press: Boston. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-397200-2.00008-7
Maroufpoor S, Bozorg-Haddad O, Maroufpoor E (2020) Reference evapotranspiration estimating based on optimal input combination and hybrid artificial intelligent model: Hybridization of artificial neural network with grey wolf optimizer algorithm. J Hydrol 588:125060
Mohammadi B, Mehdizadeh S (2020) Modeling daily reference evapotranspiration via a novel approach based on support vector regression coupled with whale optimization algorithm. Agric Water Manag 237:106145
Mokari E, DuBois D, Samani Z, Mohebzadeh H, Djaman K (2021) Estimation of daily reference evapotranspiration with limited climatic data using machine learning approaches across different climate zones in New Mexico. Theoret Appl Climatol 147(1–2):575–587
Muhammad Adnan R, Chen Z, Yuan X, Kisi O, El-Shafie A, Kuriqi A, Ikram M (2020) Reference evapotranspiration modeling using new heuristic methods. Entropy (Basel) 22(5):547
Olago V, Muchengeti M, Singh E, Chen WC (2020) Identification of malignancies from free-text histopathology reports using a multi-model supervised machine learning approach. Information 11(9):455
Pereira LS, Paredes P, López-Urrea D, Jovanovic N (2021) Updates and advances to the FAO56 crop water requirements method. Agric Water Manag 248:106697
Qun’ou J, Lidan X, Siyang S, Meilin W, Huijie X (2021) Retrieval model for total nitrogen concentration based on UAV hyper spectral remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms – a case study in the Miyun Reservoir China. Ecol Indic 124:107356
Ramos-Giraldo P, Reberg-Horton C, Locke AM, Mirsky S, Lobaton E (2020) Drought stress detection using low-cost computer vision systems and machine learning techniques. IT Professional 22(3):27–29
Raza A, Shoaib M, Faiz MA, Baig F, Khan MM, Ullah MK, Zubair M (2020) Comparative assessment of reference evapotranspiration estimation using conventional method and machine learning algorithms in four climatic regions. Pure Appl Geophys 177(9):4479–4508
Roy DK (2021) Long short-term memory networks to predict one-step ahead reference evapotranspiration in a subtropical climatic zone. Environmental Processes 8(2):911–941
Salam R, Islam ARMT (2020) Potential of RT, bagging and RS ensemble learning algorithms for reference evapotranspiration prediction using climatic data-limited humid region in Bangladesh. J Hydrol 590:125241
Santos CAG, da Silva GBL (2014) Daily streamflow forecasting using a wavelet transform and artificial neural network hybrid models. Hydrol Sci J 59(2):312–324
Santos CA, Freire PK, da Silva RM, Akrami SA (2019) Hybrid wavelet neural network approach for daily inflow forecasting using tropical rainfall measuring mission data. J Hydrol Eng 24(2):04018062
Tabari H, Kisi O, Ezani A, Hosseinzadeh Talaee P (2012) SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J Hydrol 444–445:78–89
Tikhamarine Y, Malik A, Kumar A, Souag-Gamane D, Kisi O (2019) Estimation of monthly reference evapotranspiration using novel hybrid machine learning approaches. Hydrol Sci J 64(15):1824–1842
Tikhamarine Y, Malik A, Souag-Gamane D, Kisi O (2020a) Artificial intelligence models versus empirical equations for modeling monthly reference evapotranspiration. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(24):30001–30019
Tikhamarine Y, Souag-Gamane D, Najah Ahmed A, Kisi O, El-Shafie A (2020b) Improving artificial intelligence models accuracy for monthly streamflow forecasting using grey Wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm. J Hydrol 582:124435
VanDeventer W, Jamei E, Thirunavukkarasu GS, Seyedmahmoudian M, Soon TK, Horan B, Mekhilef S, Stojcevski A (2019a) Short-term PV power forecasting using hybrid GASVM technique. Renew Energy 140:367–379
VanDeventer W, Jamei E, Thirunavukkarasu GS, Seyedmahmoudian M, Soon TK, Horan B, Mekhilef S, Stojcevski A (2019b) Short-term PV power forecasting using hybrid GASVM technique. Renew Energy 140:367–379
Verheye W (2006) Dry lands and desertification. In: Verheye WH (ed) Land Use, Land Cover and Soil Sciences, vol 5. UNESCO-EOLSS Publishers, Paris
Wen X, Si J, He Z, Wu J, Shao H, Yu H (2015) Support-vector-machine-based models for modeling daily reference evapotranspiration with limited climatic data in extreme arid regions. Water Resour Manage 29(9):3195–3209
Wu P, Wood R, Ridley J, Lowe J (2010) Temporary acceleration of the hydrological cycle in response to a CO2 rampdown. Geophys Res Lett 37:12705
Yamaç SS, Todorovic M (2020) Estimation of daily potato crop evapotranspiration using three different machine learning algorithms and four scenarios of available meteorological data. Agric Water Manag 228:105875
Yang Y, Chui T, Fong M (2021) Modeling and interpreting hydrological responses of sustainable urban drainage systems with explainable machine learning methods. Sciences 25(11):5839–5858
Zerouali B, Al-Ansari N, Chettih M, Mohamed M, Abda Z, Santos CAG, Zerouali B, Elbeltagi A (2021) An enhanced innovative triangular trend analysis of rainfall based on a spectral approach. Water 13(5):727
Zerouali B, Chettih M, Abda Z, Mesbah M, Santos CAG, Brasil Neto RM (2022) A new regionalization of rainfall patterns based on wavelet transform information and hierarchical cluster analysis in northeastern Algeria. Theor Appl Climatol 147:1489–1510
Zhu B, Feng Y, Gong D, Jiang S, Zhao L, Cui N (2020) Hybrid particle swarm optimization with extreme learning machine for daily reference evapotranspiration prediction from limited climatic data. Comput Electron Agric, 173
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Agroclimatic-Information-Network of Andalusia (RIA) in providing the most used data.
Funding
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) through PTDC/CTA-OHR/30561/2017 (WinTherface).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EME: investigation, conceptualization, data curation, visualization, formal analysis, writing — original draft, writing—review and editing.
BZ: conceptualization, data curation, visualization, formal analysis, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, validation.
NB: conceptualization, data curation, visualization, formal analysis, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, validation.
KB: conceptualization, data curation, writing—original draft, writing — review and editing.
MAH: methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing — review and editing, validation.
JA: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing — review and editing.
AK: conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing — review and editing.
ME: resources, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing.
AI: resources, software, writing — original draft, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
We confirm that this manuscript is original, has not been published before, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Consent to participate
As the research team in this current contribution, we have voluntarily agreed to participate in this research study.
Consent for publication
We want to consent to publish identifiable details, including text, material and methods, figures, and tables published in the Journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-kenawy, ES.M., Zerouali, B., Bailek, N. et al. Improved weighted ensemble learning for predicting the daily reference evapotranspiration under the semi-arid climate conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 81279–81299 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21410-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21410-8