Abstract
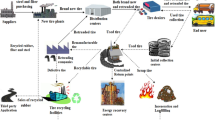
The conditions of global competition and environmental sensitivities have made organizations and factories to collect returned products, in such a way that these organizations have tried to rehabilitate, recycle, or destroy these products in order to protect the environment. This paper propose a mathematical model for the green closed-loop supply chain network of heavy tire by considering the economic pricing of its products under conditions of uncertainty, which economically determines the price and leads to more profitability. In addition, the relevant model is a two-objective fuzzy model, the first objective of which is to minimize costs and maximize profits, and the second objective is to minimize environmental issues. The proposed model can also determine the optimal location of each center based on potential locations, the optimal amount of production, distribution, collection, recycling, as well as the reproduction of products. The ε-constraint method is used to solve the model with two objective functions; this method ensures strong Pareto optimal answers and prevents weak Pareto answers. Independent two-sample t-test is used to verify the results of certain and uncertain models in the studied model. In order to evaluate the effectiveness and profitability of the proposed method, a case study in the field of heavy tires is finally used, through which very useful results are obtained.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Atasu A, Guide R Jr, Van Wassenhove N (2010) So what if remanufacturing cannibalizes my new product sales? California Management Review. 52(2):56–76
Chen M, Chang I (2012) The co-opetitive strategy of a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review. 48(2):387–400
Choi M, Li Y, Xu L (2013) Channel leadership, performance and coordination in closed loop supply chains. International Journal of Production Economics. 146(1):371–380
Dekker R, Fleischmann M, Inderfurth K, van Wassenhove L (2013) Reverse logistics: quantitative models for closed-loop supply chains. Springer Science & Business Media
Ferguson M, Toktay B (2004) The effect of external competition on recovery strategies. Georgia Institute of Technology College of Business working paper.
Gutowski T, Sahni G, Boustani S, Graves S (2011) Remanufacturing and energy savings. Environmental science & technology 45(10):4540–4547
Jeguirim M, Limousy L (2017) Process engineering for pollution control and waste minimization, Springer.
Karakayali I, Emir-Farinas H, Akcali E (2007) An analysis of decentralized collection and processing of end-of-life products. Journal of Operations Management. 25(6):1161–1183
Klibi W, Martel A, Guitouni A (2010) The design of robust value-creating supply chain networks: a critical review. European Journal of Operational Research. 203(2):283–293
Kumar L, Jain P, Sharma A (2020) A fuzzy goal programme–based sustainable Greenfield supply network design for tyre retreading industry. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 108(9):2855–2880
Labaki M, Jeguirim M (2017) Thermochemical conversion of waste tyres—a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 24(11):9962–9992
Leung C, Tsang O, Ng W, Wu Y (2007) A robust optimization model for multi-site production planning problem in an uncertain environment. European journal of operational research 181(1):224–238
Listeş O (2007) A generic stochastic model for supply-and-return network design. Computers & Operations Research. 34(2):417–442
Qiang Q, Ke K, Anderson T, Dong J (2013) The closed-loop supply chain network with competition, distribution channel investment, and uncertainties. Omega 41(2):186–194
Saxena K, Jain P, Sharma A (2018) A fuzzy goal programme with carbon tax policy for Brownfield Tyre remanufacturing strategic supply chain planning. Journal of Cleaner Production. 198:737–753
Saxena JP, Sharma A (2018) Tactical supply chain planning for tyre remanufacturing considering carbon tax policy. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 97(1):1505–1528
Tehrani M, Gupta M (2021) Designing a sustainable green closed-loop supply chain under uncertainty and various capacity levels. Logistics. 5(2):20
Üster H, Easwaran G, Akçali E, Çetinkaya S (2007) Benders decomposition with alternative multiple cuts for a multi-product closed-loop supply chain network design model. Naval research logistics (NRL) 54(8):890–907
Wei J, Govindan K, Li Y, Zhao J (2015) Pricing and collecting decisions in a closed-loop supply chain with symmetric and asymmetric information. Computers & operations research 54:257–265
Wei J, Zhao J (2013) Reverse channel decisions for a fuzzy closed-loop supply chain. Applied Mathematical Modelling. 37(3):1502–1513
Zhang D (2006) A network economic model for supply chain versus supply chain competition. Omega. 34(3):283–295
Maadanpour Safari F, Etebari F, Pourghader Chobar A (2021) Modelling and optimization of a tri-objective transportation-location-routing problem considering route reliability: using MOGWO, MOPSO, MOWCA and NSGA-II. Journal of Optimization in Industrial Engineering 14(2):99–114
Pourghader Chobar A, Adibi MA, Kazemi A (2021) A novel multi-objective model for hub location problem considering dynamic demand and environmental issues. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Studies 8(1):1–31
Rezaei Kallaj, M., Abolghasemian, M., Moradi Pirbalouti, S., Sabk Ara, M., & Pourghader Chobar, A. (2021). Vehicle routing problem in relief supply under a crisis condition considering blood types. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Javad Amirian: methodology, software, formal analysis, data curation, writing original draft, writing review and edit, and visualization
Hossein Amoozad Khalili: conceptualization, supervision, software, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, writing original draft, and visualization
Ahmad Mehrabian: methodology, validation, and writing review and edit
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and competing interests
All authors have participated in (a) conception and design or analysis and interpretation of the data, (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and (c) approval of the final version.
This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue and has no self-plagiarism.
The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Consent to participate and consent to publish
Furthermore, we hereby transfer the unlimited rights of publication of the above-mentioned paper in whole to “Environmental Science and Pollution Research.” The corresponding author signs for and accepts responsibility for releasing this material on behalf of any and all co-authors. This agreement is to be signed by at least one of the authors who have obtained the assent of the co-author(s) where applicable. After submission of this agreement signed by the corresponding author, changes of authorship or in the order of the authors listed will not be accepted.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirian, J., Amoozad Khalili, H. & Mehrabian, A. Designing an optimization model for green closed-loop supply chain network of heavy tire by considering economic pricing under uncertainty. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 53107–53120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19578-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19578-0