Abstract
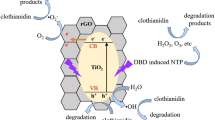
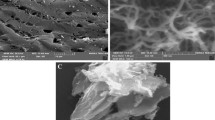
The objective of this study was to compare the transformation of by-products between single dielectric barrier discharge (SDBD) and double dielectric barrier discharge (DDBD), to optimize the preparation of graphene-based catalysts and apply them in combination with DBD for volatile organic compound degradation. We compared the degradation performance of SDBD and DDBD, prepared, and characterized graphene-based catalysts. SEM, BET, XRD, and FTIR analyses showed that the morphologies and internal structures of the three catalysts were the best when 0.25 mL of [BMIM]PF6 was added. When MnOx/rGO, FeOx/rGO, and TiOx/rGO were used in combination with DDBD, the degradation rates of benzene were found to be 83.5%, 77.2%, and 63.8%, respectively, whereas the O3 transformation rates were 60%, 79%, and 40%, respectively. Moreover, the NO2 transformation rates were 70%, 55%, and 42.5%, respectively, whereas the NO transformation rates were 69%, 39%, and 33.5%, respectively. The CO2 selectivity was 62%, 51%, and 49%, respectively. MnOx/rGO exhibited superior performance in the degradation of benzene series, NO transformation, NO2 transformation, CO2 selectivity, and energy efficiency. On the other hand, FeOx/rGO exhibited superior performance for O3 transformation. Based upon the XPS analysis, it was found that Mn3O4 and Fe3O4 played a leading role in promoting the degradation of benzene series and the transformation of by-products.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abidi M, Assadi AA, Bouzaza A, Hajjaji A, Bessais B, Rtimi S (2019) Photocatalytic indoor/outdoor air treatment and bacterial inactivation on CuxO/TiO2 prepared by HiPIMS on polyester cloth under low intensity visible light. Appl Catal B 259:118074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118074
Abidi M, Hajjaji A, Bouzaza A et al (2020) Simultaneous removal of bacteria and volatile organic compounds on Cu2O-NPs decorated TiO2 nanotubes: competition effect and kinetic studies. J Photochem Photobiol, A 400:112722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118074
Almasian MR, Na N, Wen F, Zhang S, Zhang X (2010) Development of a plasma-assisted cataluminescence system for benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes analysis. Anal Chem 82(9):3457. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac1006975
Alqahtani MS, Wang X, Gray J, Knecht SD, Bilén SG, Song C (2020) Plasma-assisted catalytic reduction of SO2 to elemental sulfur: influence of nonthermal plasma and temperature on iron sulfide catalyst. J Catal 391:260–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2020.08.013
An T, Huang Y, Li G, Chen J, Zhang C (2014) Pollution profiles and health risk assessment of VOCs emitted during e-waste dismantling processes associated with different dismantling methods. Environ Int 73:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.07.019
Assadi AA, Bouzaza A, Lemasle M, Wolbert D (2015) Removal of trimethylamine and isovaleric acid from gas streams in a continuous flow surface discharge plasma reactor. Chem Eng Res Des 93:640–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2014.04.026
Assadi AA, Bouzaza A, Wolbert D (2016) Comparative study between laboratory and large pilot scales for VOC’s removal from gas streams in continuous flow surface discharge plasma. Chem Eng Res Des 106:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2015.12.025
Brückner L, Beyer-Westendorf J, Tiebel O, Pietsch J (2021) Development and validation of an analytical method for the determination of direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) and the direct thrombin-inhibitor argatroban by HPLC-MS/MS. J Thromb Thrombolysis 15(3):103663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103663
Chen B, Gao X, Chen K et al (2018) Regulation characteristics of oxide generation and formaldehyde removal by using volume dbd reactor. Plasma Sci Technol 20(2):4009. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-6272/aa9b7a
Costa G, Assadi AA, Gharib-Abou Ghaida S, Bouzaza A, Wolbert D (2017) Study of butyraldehyde degradation and by-products formation by using a surface plasma discharge in pilot scale: process modeling and simulation of relative humidity effect. Chem Eng J 307:785–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.099
Dang X, Qin C, Huang J, Teng J, Huang X (2016) Adsorbed benzene/toluene oxidation using plasma driven catalysis with gas circulation: elimination of the byproducts. J Ind Eng Chem 37:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.03.051
De Souza RM, Meliande ALS, Da Silveira CLP, Aucélio RQ (2006) Determination of Mo, Zn, Cd, Ti, Ni, V, Fe, Mn, Cr and Co in crude oil using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and sample introduction as detergentless microemulsions. Microchem J 82(2):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2006.01.005
Durán FG, Barbero BP, Cadús LE, Rojas C, Centeno MA, Odriozola JA (2009) Manganese and iron oxides as combustion catalysts of volatile organic compounds. Appl Catal B 92(1–2):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.07.010
Ehn M, Thornton J, Kleist, et al (2014) A large source of low-volatility secondary organic aerosol. Nature 506:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13032
Fang B, Guo F, Yang L et al (2018) Phyllostachys edulis forest reduces atmospheric pm2.5 and pahs on hazy days at suburban area. Scientific Reports 8(1):12591. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30298-9
Hao Z, Ji S (2012) Optical and electric diagnostics of DBD plasma jet in atmospheric pressure Argon. International Conference on Condition Monitoring & Diagnosis. IEEE 1187–1190. https://doi.org/10.1109/CMD.2012.6416373
Han F, Li M, Zhong H et al (2020) Product analysis and mechanism of toluene degradation by low temperature plasma with single dielectric barrier discharge. J Saudi Chem Soc 24(9):673–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2020.07.004
He C, Cheng J, Zhang X, Douthwaite M, Pattisson S, Hao Z (2019) Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Platin Met Rev 119(7):109–113. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00408
Herrera F, Brown GH, Barboun P et al (2019) The impact of transition metal catalysts on macroscopic dielectric barrier discharge (dbd) characteristics in an ammonia synthesis plasma catalysis reactor. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 52(22):224002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab0c58
Huang K, Zhuang G, Lin Y, Fu J, Cao B (2012) Typical types and formation mechanisms of haze in an eastern Asia megacity Shanghai. Atmos Chem and Physics 12(1):105–124. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-105-2012
Huang H, Chu X, Lu H, Zhang B, Chen Y (2011) Dynamic adsorption performances and breakthrough curve model of some aromatic VOCs on MCM-41 and SBA-15. J Chem Eng Chin Univ 25(2):219–224. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00999
Ji H, Santos CA, Jo YM (2021) Energy efficient treatment of indoor volatile organic compounds using a serial dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Process Saf Environ Prot 153:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.07.009
Kalbande R, Bano S, Beig G (2021) Benzene and toluene from stubble burning and their implications for ozone chemistry and human health in the Indo-Gangetic Plain Region. 5(11):3226-3233. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00283
Kara M, Dumanoglu Y, Altiok H, Elbir T, Odabasi M, Bayram A (2014) Seasonal and spatial variations of atmospheric trace elemental deposition in the Aliaga industrial region, Turkey. Atmos Res 43(3):109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.06.009
Kizil R, Irudayaraj J, Seetharaman K (2002) Characterization of irradiated starches by using FT-Raman and FTIR spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry 50(14):3912–3918. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011652p
Li H, Wang Y, Liu F et al (2018) Volatile organic compounds in stormwater from a community of Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 239:554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.065
Liang P, Jiang W, Zhang L, Wu J, Zhang J, Yang D (2015) Experimental studies of removing typical VOCs by dielectric barrier discharge reactor of different sizes. Process Saf Environ Prot 94:380–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.09.003
Liu L, Qiang W, Song J, Ahmad S, Yang X, Sun Y (2017) Plasma-assisted catalytic reforming of toluene to hydrogen rich syngas. Catal Sci Technol 18:4216–4231. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cy00970d
Luo H, Li G, Chen J et al (2020) Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and ozone formation potentials of volatile organic compounds from three typical functional areas in China. Environ Res 183:109141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109141
Mao L, Chen Z, Wu X et al (2017) Plasma-catalyst hybrid reactor with CeO2/γ-Al2O3 for benzene decomposition with synergetic effect and nano particle by-product reduction. J Hazard Mater 347:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.12.064
Mustafa MF, Fu X, Liu Y, Abbas Y, Wang H, Lu W (2018) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) removal in non-thermal plasma double dielectric barrier discharge reactor. J Hazard Mater 347:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.021
Mishra RK, Upadhyay SB, Sahay PP (2013) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) response characteristics of the hydrothermally synthesized SnO2 nanocapsules. Sens Lett 11(9):1611–1616. https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2013.3020
Najafpoor AA, Jafari AJ, Hosseinzadeh A, Jazani RK, Bargozin H (2018) Optimization of non-thermal plasma efficiency in the simultaneous elimination of benzene, toluene, ethyl-benzene, and xylene from polluted airstreams using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 154(1):506–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0373-8
Park JH, Goldstein AH, Timkovsky J (2013) Active atmosphere-ecosystem exchange of the vast majority of detected volatile organic compounds. Science 341(6146):643–647. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1235053
Qin C, Guo M, Jiang C et al (2021) Simultaneous oxidation of toluene and ethyl acetate by dielectric barrier discharge combined with Fe, Mn and Mo catalysts. Sci Total Environ 782:146931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146931
Ran J, Qiu H, Sun S, Yang A, Tian L (2018) Are ambient volatile organic compounds environmental stressors for heart failure? Environ Pollut 242:1810–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.086
Saoud WA, Assadi AA, Guiza M et al (2019) Synergism between non-thermal plasma and photocatalysis: implications in the post discharge of ozone at a pilot scale in a catalytic fixed-bed reactor. Appl Catal B 241:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.029
Tseng TK, Lin Y, Chen Y, Chu H (2010) A review of photocatalysts prepared by sol-gel method for vocs removal. Int J Mol Sci 11(6):2336–2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11062336
Wu J, Huang Y, Xia Q, Li Z (2013) Decomposition of toluene in a plasma catalysis system with NiO, MnO2, CeO2, Fe2O3, and CuO catalysts. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33(6):1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9485-1
Yao X, Zhang J, Liang X, Long C (2018) Plasma-catalytic removal of toluene over the supported manganese oxides in dbd reactor: effect of the structure of zeolites support. Chemosphere 208:922–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.064
Yao X, Zhang J, Liang X, Long C (2019) Niobium doping enhanced catalytic performance of Mn/MCM-41 for toluene degradation in the ntp-catalysis system. Chemosphere 230:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.075
Yu L, Wang L, Xu WC et al (2017) Adsorption of VOCs on reduced graphene oxide. J Environ Sci 67(5):171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.08.022
Yukimura K, Kawamura K, Kambara S, Moritomi H, Yamashita T (2005) Correlation of energy efficiency of no removal by intermittent dbd radical injection method. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 33(2):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2005.844610
Zeng X, Li B, Liu R, Li X, Zhu T (2019) Investigation of promotion effect of cu doped MnO2 catalysts on ketone-type VOCs degradation in a one-stage plasma-catalysis system. Chem Eng J 384:123362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123362
Zhang H, Li K, Shu C, Lou Z, Sun T, Jia J (2014) Enhancement of styrene removal using a novel double-tube dielectric barrier discharge (DDBD) reactor. Chem Eng J 256:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.105
Zhang X, Xue Z, Li H (2017) Ambient volatile organic compounds pollution in China. J Environ Sci 55:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.05.036
Zhao L, Guo X, Hu Y, Cheng W, Wang L, Ma H (2015) Simultaneous determination of major elements Si, Al, Ca, Mg, Fe, Ti, Mn and P in graphite by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry with sodium carbonate fusion. Rock and Mineral analysis, (3):308–313(in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.03.008
Zhu X, Liu Y (2014) Characterization and risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds in apartment buildings in Harbin, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(1):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1129-x
Funding
Financial supports for this project were provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21676032), the Key Research and Development Project Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2020YFS0342), the Education Department of Sichuan Province (No.14TD0020), the Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2016-GH02-00032-HZ), which are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL did research experiments and analyzed the data; YW, GZ, and JY did the other experiments; ZL, along with SL, led the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
There are no ethical issues in this article.
Consent to participate
All the authors agree to participate in this paper.
Consent for publication
All the authors agree to the publication of this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, G. et al. Preparation of graphene-based catalysts and combined DBD reactor for VOC degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 51717–51731 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19483-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19483-6