Abstract
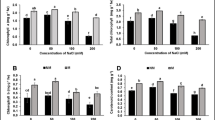
Because of global land surface warming, heavy metal toxicity is expected to occur more often and more intensely, affecting the growth and development of the major cereal crops such as maize (Zea mays L.) in several ways, thus affecting the production component of food security. Hence, it is important to know the best cultivars of Z. mays in abiotic stress environment to fulfill the market demand of this staple food. For this purpose, we investigate the present study to find the best Z. mays cultivar to be grown in chromium (Cr)-contaminated sand (200 µM). In this experiment, we have studied 10 cultivars (Malka, Sadaf, Pearl, CZP, YY, YH, MMRI-yellow, Sahiwal, EV-20, and EV-77) of Z. mays grown in plastic pots for 4 weeks (in addition with seed germination) under Cr − (0 µM) and Cr + (200 µM) in sand medium. Based on the findings of the current experiment, we illustrated that Cr toxicity induced a significant (P < 0.05) reduction in shoot length, root length, shoot fresh weight, root fresh weight, shoot dry weight and root dry weight, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, and carotenoid content and induced oxidative damage to membrane-bounded organelles by increasing the malondialdehyde and hydrogen peroxide which were manifested by flavonoid and phenolic contents. Moreover, Cr uptake was also higher in the plants grown in the Cr-contaminated sand compared to the plants grown without the Cr-contaminated sand. We also noticed that Pearl, CZP, and Sahiwal cultivars are suggested to be Cr-tolerant cultivars as showed better growth and development in Cr-contaminated sand while Sadaf, MMRI, and EV-77 showed lower growth and composition in Cr-contaminated sand. The overall pattern of Z. mays cultivars grown in Cr-contaminated sand is as follows: Pearl > CZP > Sahiwal > YY > YH > EV-20 > Malka > EV-77 > MMRI-yellow > Sadaf. Conclusively, it can be identified that when grown in Cr-contaminated sand, Pearl, CZP, and Sahiwal have greater ability to grow in polluted soils. Overall, Z. mays cultivars showed better growth in Cr-stressed environment due to defense mechanism but further experiments needed to be conducted on molecular level.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and material is available for research purpose and for reference.
References
Adhikari A, Adhikari S, Ghosh S, Azahar I, Shaw AK, Roy D, Roy S, Saha S, Hossain Z (2020) Imbalance of redox homeostasis and antioxidant defense status in maize under chromium (VI) stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany 169:103873
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Ibrahim M, Mehmood MA, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689
Afzal J, Wang X, Saleem M-H, Sun X, Hussain S, Khan I, Rana M-S, Ahmed S, Awan S-A, Fiaz S, Aziz O, Kubar K-A, Ali S, Hu C (2021) Application of ferrous sulfate alleviates negative impact of cadmium in rice (<i>Oryza sativa</i> L.). Biocell 45:1631–1649
Afzal J, Saleem MH, Batool F, Elyamine AM, Rana MS, Shaheen A, El-Esawi MA, Tariq Javed M, Ali Q, Arslan Ashraf M, Hussain GS, Hu C (2020): Role of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) in resistance to cadmium stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Biomolecules 10, 1693
Ahmad R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Dawood M, Farid M, Hussain A, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 168:289–300
Ahmad S, Mfarrej MFB, El-Esawi MA, Waseem M, Alatawi A, Nafees M, Saleem MH, Rizwan M, Yasmeen T, Anayat A, Ali S (2022) Chromium-resistant Staphylococcus aureus alleviates chromium toxicity by developing synergistic relationships with zinc oxide nanoparticles in wheat. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 230:113142
Ahmad R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Dawood M, Farid M, Hussain A, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019): Hydrogen sulfide alleviates chromium stress on cauliflower by restricting its uptake and enhancing antioxidative system. Physiologia plantarum
Ahmad K, Aslam M, Saleem Mh, Ijaz M, Ul-Allah S, El-Sheikh Ahma, Adnan M, Ali S Genetic diversity and characterization of salt stress tolerance traits in maize (Zea Mays L.) under normal and saline conditions. Pak. J. Bot 54, 3
Akram NA, Iqbal M, Muhammad A, Ashraf M, Al-Qurainy F, Shafiq S (2018) Aminolevulinic acid and nitric oxide regulate oxidative defense and secondary metabolisms in canola (Brassica napus L.) under drought stress. Protoplasma 255:163–174
Ali S, Bai P, Zeng F, Cai S, Shamsi IH, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The ecotoxicological and interactive effects of chromium and aluminum on growth, oxidative damage and antioxidant enzymes on two barley genotypes differing in Al tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 70:185–191
Ali MHS, Akhtar N, Saif-Ur-Rehman AS, Nadeem M, Tanveer MH (2020) Genetic analysis of Pakistani wheat germplasm for yield contributing traits under normal and heat stressed conditions. Pak J Agri Sci 57:1503–1508
Alsafran M, Usman K, Al Jabri H, Rizwan M (2021a) Ecological and health risks assessment of potentially toxic metals and metalloids contaminants: a case study of agricultural soils in Qatar. Toxics 9:35
Alsafran M, Usman K, Rizwan M, Ahmed T, Al Jabri H (2021b): The carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risks of metal (oid) s bioaccumulation in leafy vegetables: a consumption advisory. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 380
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris Plant Physiology 24:1
Azeem M, Haider MZ, Javed S, Saleem MH, Alatawi A (2022): Drought stress amelioration in maize (Zea mays L.) by inoculation of Bacillus spp. Strains under Sterile Soil Conditions. Agriculture 12, 50
Aziz H, Murtaza G, Saleem MH, Ali S, Rizwan M, Riaz U, Niaz A, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A (2021): Alleviation of chlorpyrifos toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.) by reducing its uptake and oxidative stress in response to soil-applied compost and biochar amendments. Plants 10, 2170
Bah AM, Dai H, Zhao J, Sun H, Cao F, Zhang G, Wu F (2011) Effects of cadmium, chromium and lead on growth, metal uptake and antioxidative capacity in Typha angustifolia. Biol Trace Elem Res 142:77–92
Bashir MA, Naveed M, Ashraf S, Mustafa A, Ali Q, Rafique M, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH (2021) Performance of Zea mays L. cultivars in tannery polluted soils: management of chromium phytotoxicity through the application of biochar and compost. Physiol Plant 173:129–147
Bray H, Thorpe W (1954): Analysis of phenolic compounds of interest in metabolism. Methods of biochemical analysis, 27–52
Chen Q, Zhang X, Liu Y, Wei J, Shen W, Shen Z, Cui J (2017) Hemin-mediated alleviation of zinc, lead and chromium toxicity is associated with elevated photosynthesis, antioxidative capacity; suppressed metal uptake and oxidative stress in rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 81:253–264
Danish S, Kiran S, Fahad S, Ahmad N, Ali MA, Tahir FA, Rasheed MK, Shahzad K, Li X, Wang D (2019) Alleviation of chromium toxicity in maize by Fe fortification and chromium tolerant ACC deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 185:109706
Ertani A, Mietto A, Borin M, Nardi S (2017) Chromium in agricultural soils and crops: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:190
Farid M, Ali S, Saeed R, Rizwan M, Bukhari SAH, Abbasi GH, Hussain A, Ali B, Zamir MSI, Ahmad I (2019): Combined application of citric acid and 5-aminolevulinic acid improved biomass, photosynthesis and gas exchange attributes of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) grown on chromium contaminated soil. International journal of phytoremediation, 1–8
Gautam V, Sharma P, Bakshi P, Arora S, Bhardwaj R, Paray BA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020b) Effect of Rhododendron arboreum leaf extract on the antioxidant defense system against chromium (VI) stress in Vigna radiata plants. Plants 9:164
Gautam V, Kohli SK, Kapoor D, Bakshi P, Sharma P, Arora S, Bhardwaj R, Ahmad P (2020a): Stress protective effect of Rhododendron arboreum leaves (MEL) on chromium-treated Vigna radiata plants. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 1–13
Ghani MA, Abbas MM, Ali B, Aziz R, Qadri RWK, Noor A, Azam M, Bahzad S, Saleem MH, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A, Ali S (2021): Alleviating role of gibberellic acid in enhancing plant growth and stimulating phenolic compounds in carrot (Daucus carota L.) under lead stress. Sustainability 13, 12329
Gill RA, Ali B, Cui P, Shen E, Farooq MA, Islam F, Ali S, Mao B, Zhou W (2016) Comparative transcriptome profiling of two Brassica napus cultivars under chromium toxicity and its alleviation by reduced glutathione. BMC Genomics 17:885
Handa N, Kohli S, Sharma A, Thukral A, Bhardwaj R, Alyemeni M, Wijaya L, Ahmad P (2018) Selenium ameliorates chromium toxicity through modifications in pigment system, antioxidative capacity, osmotic system, and metal chelators in Brassica juncea seedlings. S Afr J Bot 119:1–10
Handa N Kohli SK Sharma A Thukral AK Bhardwaj R Abd_Allah EF Alqarawi AA Ahmad P (2019): Selenium modulates dynamics of antioxidative defence expression, photosynthetic attributes and secondary metabolites to mitigate chromium toxicity in Brassica juncea L. plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany 161, 180-192
Hashmat S, Shahid M, Tanwir K, Abbas S, Ali Q, Niazi NK, Akram MS, Saleem MH, Javed MT (2021): Elucidating distinct oxidative stress management, nutrient acquisition and yield responses of Pisum sativum L. fertigated with diluted and treated wastewater. Agricultural Water Management 247, 106720
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Heile AO, Zaman Qu, Aslam Z, Hussain A, Aslam M, Saleem MH, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A, Ali S (2021) Alleviation of cadmium phytotoxicity using silicon fertilization in wheat by altering antioxidant metabolism and osmotic adjustment. Sustainability 13:11317
Hussain A Ali S Rizwan M ur Rehman MZ Hameed A Hafeez F Alamri SA Alyemeni MN Wijaya L (2018): Role of zinc–lysine on growth and chromium uptake in rice plants under Cr stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 37, 1413-1422
Hussain I, Saleem MH, Mumtaz S, Rasheed R, Ashraf MA, Maqsood F, Rehman M, Yasmin H, Ahmed S, Ishtiaq M (2021): Choline chloride mediates chromium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by restricting its uptake in relation to morpho-physio-biochemical attributes. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 1–21
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms: effect of heavy metals. Aquat Bot 11:67–77
Javed MT, Akram MS, Tanwir K, Chaudhary HJ, Ali Q, Stoltz E, Lindberg S (2017) Cadmium spiked soil modulates root organic acids exudation and ionic contents of two differentially Cd tolerant maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:216–225
Javed MT, Saleem MH, Aslam S, Rehman M, Iqbal N, Begum R, Ali S, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2020): Elucidating silicon-mediated distinct morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and organic acid exudation patterns of cadmium stressed Ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry
Javed MT, Tanwir K, Abbas S, Saleem MH, Iqbal R, Chaudhary HJ (2021): Chromium retention potential of two contrasting Solanum lycopersicum Mill. cultivars as deciphered by altered pH dynamics, growth, and organic acid exudation under Cr stress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–13
Jobby R, Jha P, Yadav AK, Desai N (2018) Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)]: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 207:255–266
Kant S, Sharma P, Kumar V (2018) Effect of chelating compounds on growth of maize and mustard in chromium contaminated soil. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 7:2964–2972
Kaya C, Şenbayram M, Akram NA, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Sulfur-enriched leonardite and humic acid soil amendments enhance tolerance to drought and phosphorus deficiency stress in maize (Zea mays L.). Sci Rep 10:1–13
Khan ZI, Mansha A, Saleem MH, Tariq F, Ahmad K, Ahmad T, Farooq Awan MU, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A, Ali S (2021) Trace metal accumulation in rice variety Kainat irrigated with canal water. Sustainability 13:13739
Madhu PM, Sadagopan RS (2020) Effect of heavy metals on growth and development of cultivated plants with reference to cadmium, chromium and lead–a review. Journal of Stress Physiology & Biochemistry 16:84–102
Maqbool A Ali S Rizwan M Ishaque W Rasool N ur Rehman MZ Bashir A Abid M Wu L (2018): Management of tannery wastewater for improving growth attributes and reducing chromium uptake in spinach through citric acid application. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 25, 10848-10856
Mwadzingeni L, Shimelis H, Tesfay S, Tsilo TJ (2016) Screening of bread wheat genotypes for drought tolerance using phenotypic and proline analyses. Front Plant Sci 7:1276
Nafees M, Ali S, Naveed M, Rizwan M (2018) Efficiency of biogas slurry and Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN to improve growth, physiology, and antioxidant activity of Brassica napus L. in chromium-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:6387–6397
Nawaz M, Wang X, Saleem MH, Khan MHU, Afzal J, Fiaz S, Ali S, Ishaq H, Khan AH, Rehman N, Shaukat S, Ali S (2021): Deciphering Plantago ovata Forsk leaf extract mediated distinct germination, growth and physio-biochemical improvements under water stress in maize (Zea mays L.) at early growth stage. Agronomy 11, 1404
Nazar Z, Akram NA, Saleem MH, Ashraf M, Ahmed S, Ali S, Abdullah Alsahli A, Alyemeni MN (2020): Glycinebetaine-induced alteration in gaseous exchange capacity and osmoprotective phenomena in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) under water deficit conditions. Sustainability 12, 10649
Parveen A, Saleem MH, Kamran M, Haider MZ, Chen J-T, Malik Z, Rana MS, Hassan A, Hur G, Javed MT (2020): Effect of citric acid on growth, ecophysiology, chloroplast ultrastructure, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) seedlings Exposed to Copper Stress. Biomolecules 10, 592
Pękal A, Pyrzynska K (2014) Evaluation of aluminium complexation reaction for flavonoid content assay. Food Anal Methods 7:1776–1782
Qadir M, Hussain A, Hamayun M, Shah M, Iqbal A, Murad W (2020): Phytohormones producing rhizobacterium alleviates chromium toxicity in Helianthus annuus L. by reducing chromate uptake and strengthening antioxidant system. Chemosphere 258, 127386
Qureshi FF, Ashraf MA, Rasheed R, Ali S, Hussain I, Ahmed A, Iqbal M (2020): Organic chelates decrease phytotoxic effects and enhance chromium uptake by regulating chromium-speciation in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Science of The Total Environment 716, 137061
Rehman M, Liu L, Bashir S, Saleem MH, Chen C, Peng D, Siddique KH (2019a) Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as forage in aged copper-contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:121–129
Rehman M, Yang M, Fahad S, Saleem MH, Liu L, Liu F, Deng G (2020b) Morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity, and nitrogen metabolism in ramie under nitrogen fertilizer. Agron J 112:2988–2997
Rehman MZ-u Rizwan M Ghafoor A Naeem A Ali S Sabir M Qayyum MF (2015): Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soils and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22, 16897-16906
Rehman M, Liu L, Wang Q, Saleem MH, Bashir S, Ullah S, Peng D (2019b): Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–14
Rehman M, Saleem MH, Fahad S, Maqbool Z, Peng D, Deng G, Liu L (2020a): Medium nitrogen optimized Boehmeria nivea L. growth in copper contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 128972
Rehman M, Saleem MH, Fahad S, Bashir S, Peng D, Deng G, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH, Khan SM, Shah RA (2021): Effects of rice straw biochar and nitrogen fertilizer on ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) morpho-physiological traits, copper uptake and post-harvest soil characteristics, grown in an aged-copper contaminated soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 1–14
Saleem MH, Ali S, Rehman M, Hasanuzzaman M, Rizwan M, Irshad S, Shafiq F, Iqbal M, Alharbi BM, Alnusaire TS (2020a) Jute: a potential candidate for phytoremediation of metals—a review. Plants 9:258
Saleem MH, Ali S, Seleiman MF, Rizwan M, Rehman M, Akram NA, Liu L, Alotaibi M, Al-Ashkar I, Mubushar M (2019): Assessing the correlations between different traits in copper-sensitive and copper-resistant varieties of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.). Plants 8, 545
Saleem MH, Ali S, Rehman M, Rana MS, Rizwan M, Kamran M, Imran M, Riaz M, Soliman MH, Elkelish A (2020b): Influence of phosphorus on copper phytoextraction via modulating cellular organelles in two jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) varieties grown in a copper mining soil of Hubei Province, China. Chemosphere 248, 126032
Saleem MH, Kamran M, Zhou Y, Parveen A, Rehman M, Ahmar S, Malik Z, Mustafa A, Anjum RMA, Wang B (2020c): Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. Journal of Environmental Management 257, 109994
Saleem MH, Rehman M, Kamran M, Afzal J, Noushahi HA, Liu L (2020d): Investigating the potential of different jute varieties for phytoremediation of copper-contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research
Saleem MH, Wang X, Ali S, Zafar S, Nawaz M, Adnan M, Fahad S, Shah A, Alyemeni MN, Hefft DI, Ali S (2021): Interactive effects of gibberellic acid and NPK on morpho-physio-biochemical traits and organic acid exudation pattern in coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) grown in soil artificially spiked with boron. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry
Sallah-Ud-Din R, Farid M, Saeed R, Ali S, Rizwan M, Tauqeer HM, Bukhari SAH (2017) Citric acid enhanced the antioxidant defense system and chromium uptake by Lemna minor L. grown in hydroponics under Cr stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:17669–17678
Shahid M, Shamshad S, Rafiq M, Khalid S, Bibi I, Niazi NK, Dumat C, Rashid MI (2017) Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: a review. Chemosphere 178:513–533
Singh S, Srivastava PK, Kumar D, Tripathi DK, Chauhan DK, Prasad SM (2015) Morpho-anatomical and biochemical adapting strategies of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings against lead and chromium stresses. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 4:286–295
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Kumar D, Chauhan DK (2012) Impact of exogenous silicon addition on chromium uptake, growth, mineral elements, oxidative stress, antioxidant capacity, and leaf and root structures in rice seedlings exposed to hexavalent chromium. Acta Physiol Plant 34:279–289
Ubando AT, Africa ADM, Maniquiz-Redillas MC, Culaba AB, Chen W-H, Chang J-S (2020) Microalgal biosorption of heavy metals: a comprehensive bibliometric review. Journal of Hazardous Materials 402:123431
UdDin I, Bano A, Masood S (2015) Chromium toxicity tolerance of Solanum nigrum L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. plants with reference to ion pattern, antioxidation activity and root exudation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:271–278
Ugwu EI, Agunwamba JC (2020) A review on the applicability of activated carbon derived from plant biomass in adsorption of chromium, copper, and zinc from industrial wastewater. Environ Monit Assess 192:1–12
Ulhassan Z, Gill RA, Huang H, Ali S, Mwamba TM, Ali B, Huang Q, Hamid Y, Khan AR, Wang J (2019) Selenium mitigates the chromium toxicity in Brassicca napus L. by ameliorating nutrients uptake, amino acids metabolism and antioxidant defense system. Plant Physiol Biochem 145:142–152
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Saleem MH, Imran M, Alnusairi GSH, Alharbi BM, Riaz M, Abbas Z, Rizwan M, Soliman MH (2020c) Role of iron–lysine on morpho-physiological traits and combating chromium toxicity in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) plants irrigated with different levels of tannery wastewater. Plant Physiol Biochem 155:70–84
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Saleem MH, Ali M, Riaz M, Javed S, Sehar A, Abbas Z, Rizwan M, El-Sheikh MA, Alyemeni MN (2020a): Interactive role of zinc and iron lysine on Spinacia oleracea L. growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant capacity irrigated with tannery wastewater. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Saleem MH, Arslan Ashraf M, Ali Q, Abbas Z, Rizwan M, El-Sheikh MA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2020b): Zinc-lysine supplementation mitigates oxidative stress in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by preventing phytotoxicity of chromium, when irrigated with tannery wastewater. Plants 9, 1145
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Saleem MH, Noor I, El-Esawi MA, Hayat K, Rizwan M, Abbas Z, El-Sheikh MA, Alyemeni MN (2020d): Iron–lysine mediated alleviation of chromium toxicity in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) plants in relation to morpho-physiological traits and iron uptake when irrigated with tannery wastewater. Sustainability 12, 6690
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Saleem MH, Yousaf HS, Malik A, Abbas Z, Rizwan M, Abualreesh MH, Alatawi A, Wang X (2022): Combined application of zinc and iron-lysine and its effects on morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity and chromium uptake in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). PLOS ONE 17, e0262140
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan. The authors highly acknowledge the Department of Botany, Government College University, Faisalabad, Pakistan for its support. The findings of this study are a part of Doctorate’s studies of Amara Hassan. We also acknowledge Dr Mobeen for her technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amara Hassan and Abida Parveen conceived and designed the study, and Saddam Hussain critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version. Abida Parveen executed the experiment and compiled data. Iqbal Hussain statistically analyzed the data and help in chemical analysis. Amara Hassan, Rizwan Rasheed, and Abida Parveen wrote the manuscript. Saddam Hussain and Rizwan Rasheed critically edited and revised the manuscript. Amara Hassan helped in sample collection and chemical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written consent was sought from each author to publish the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, A., Parveen, A., Hussain, S. et al. Investigating the role of different maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars by studying morpho-physiological attributes in chromium-stressed environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 72886–72897 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19398-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19398-2