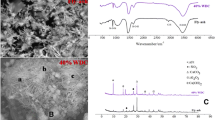
Abstract
Exploration and development of shale gas generate a lot of water-based drilling cuttings (WDC), which can then be used in concrete engineering. This work studied mix ratio optimization, mechanical properties, leaching characteristics and the microstructure of the WDC concrete. The results showed that the pH and COD values of these WDC were slightly above 9.0 and 60, respectively. All other indices satisfied the first grade standard of Chinese standard GB8978. On the other hand, a moderate amount of WDC can be improved concrete properties, especially its workability and compressive strength. When the water-binder ratio is 0.52 and the sand ratio is 41%, we can obtain C25 strength grade and 130 ~ 140 mm slump grade concrete by adding high efficiency water reducing agent and fly ash. XRD and SEM analysis showed that the silica and aluminum oxide in WDC reacted with calcium hydroxide to form secondary hydration products: C–S–H gel and ettringite, which are conducive to the formation of concrete strength and solidified the heavy metals and other contaminants. EDX analysis found it is known that the hydration products in WDC concrete can bind metal elements well. The environmental leaching test shows that the recycled WDC added to concrete products as aggregate and admixture is very environmentally friendly and sustainable.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aboutabikh M, Soliman AM, El Naggar MH (2016) Properties of cementitious material incorporating treated oil sands drill cuttings waste. Constr Build Mater 111:751–757
Alsubari B, Shafigh P, Jumaat Mohd Z (2016) Utilization of high-volume treated palm oil fuel ash to produce sustainable self-compacting concrete. J Clean Prod 137:982–996
Antemir A, Hills CD, Carey PJ, Magnie MC, Polettini A (2010) Investigation of 4-year-old stabilised/solidied and accelerated carbonated contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 181:543–555
Ayati B, Molineux C, Newport D, Cheeseman C (2019) Manufacture and performance of lightweight aggregate from waste drill cuttings. J Clean Prod 208:252–260
Bakke T, Klungsoyr J, Sanni S (2013) Environmental impacts of produced water and drilling waste discharges from the Norwegian offshore petroleum industry. Mar Environ Res 92:154–169
Ball AS, Stewart RJ, Schliephake K (2012) A review of the current options for the treatment and safe disposal of drill cuttings. Waste Manag Res 30:457–473
Chen L-R, Huang M, Jiang X-B, Li H, Chen Q, Zhang M, Li S-L (2015) Pilot tests of microbe-soil combined treatment of waste drilling sludge. Nat Gas Industr B 2:270–276
Galvín AP, Agrela F, Ayuso J, Beltrán MG, Barbudo A (2014) Leaching assessment of concrete made of recycled coarse aggregate: physical and environmental characterisation of aggregates and hardened concrete. Waste Manag 34:1693–1704
Kogbara RB, Al Tabbaa A, Yi Y, Stegemann JA (2013) Cement-Fly ash stabilisa-tion/solidi cation of contaminated soil: performance properties and initiation of operating envelopes. Appl Geochem 33:64–75
Kogbara RB, Ayotamuno Josiah M, Ikechukwu O, Victoria E, Damka TG (2016) Stabilisation/solidi cation and bioaugmentation treatment of petroleum drill cuttings. Appl Geochem 71:1–8
Leonard, Sunday A, Stegemann, Julia A (2010) Stabilization/solidification of petroleum drill cuttings: leaching studies. J Hazard Mater 174:484–491
Liu D-S, Wang C-Q, Mei X-D, Zhang C (2018) Environmental performance, mechanical and microstructure analysis of non-fifired bricks containing water-based drilling cuttings of shale gas. Constr Build Mater 183:215–225
Mohammadhosseini, Hossein, Mohamad YJ (2017) Microstructure and residual properties of green concrete composites incorporating waste carpet fibers and palm oil fuel ash at elevated temperatures. J Clean Prod 144:8–21
Mostavi E, Asadi S, Ugochukwu E (2015) Feasibility Study of the Potential Use of Drill Cuttings in Concrete. Proc Eng 118:1015–1023
Radwan MM, Farag LM, Abo-El-Enein SA, Abd El-Hamid HK (2013) Alkali activation of blended cements containing oil shale ash. Constr Build Mater 40:367–377
Sheng G-H, Li Q, Zhai J-P, Li F-H (2012) Investigation on the hydration of CFBC fly ash. Fuel 98:61–66
Shu J-C, Liu R-L, Liu Z-H, Chen H-L, Du J, Tao C (2016) Solidification/stabilization of electrolytic manganese residue using phosphate resource and low-grade MgO/CaO. J Hazard Mater 317:267–274
Vinter S, Montanes MT, Bednarik V, Hrivnova P (2016) Stabilization/solidification of hot dip galvanizing ash using different binders. J Hazard Mater 320:105–113
Wang, Chao-qiang, Xiong, De-ming (2021) Leaching assessment of aerated concrete made of recycled shale gas drilling cuttings: particular pollutants, physical performance and environmental characterization. J Clean Prod 282:125099
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry of Education (20kfck03), and Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Urban Pollutant Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KLUPC-KF-2020-2) and Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials (Tongji University), Ministry of Education (202103).
Funding
Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry of Education (20kfck03), and Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Urban Pollutant Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KLUPC-KF-2020-2) and Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials (Tongji University), Ministry of Education (202103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chao-qiang Wang mainly contribute to study design, experimental studies, data analysis, and manuscript editing and revision. Ke Liu mainly contribute to material preparation, manuscript preparation, and manuscript editing. De-ming Huang mainly contribute to experimental studies, statistical analysis, and manuscript editing and revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from individual participants.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, q., Liu, . & Huang, Dm. Property of concrete made of recycled shale gas drilling cuttings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 2098–2106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15817-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15817-y