Abstract
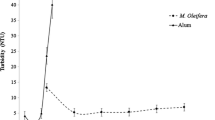
The production of personal hygiene and body products generates wastewater with a high load of surfactants, a high chemical oxygen demand (COD), and abundant oils and greases. Aluminum sulfate (AS) and two solutions of natural coagulant from Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds prepared with a 1M NaCl solution and 1.5M NaCl solution were used. Aluminum sulfate, Moringa oleifera Lam. in 1M NaCl, and Moringa oleifera Lam. in 1.5M NaCl solutions reduced turbidity at rates 94.48%, 98.07%, and 97.87%; reduced COD at rates 46.36%, 49.15%, and 42.7%; and reduced oil and grease at rates 98.72%, 78.65%, and 97.41%, respectively. Mutagenicity tests with guppies showed a lower toxicity of Moringa oleifera Lam. extract compared with aluminum sulfate. This work shows that Moringa oleifera Lam. extract has high potential for use as an alternative to aluminum sulfate; therefore, this study will contribute to proposals for the sustainable treatment of effluents from the cosmetic industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad AL, Sumathi S, Hameed BH (2006) Coagulation of residue oil and suspended solid in palm oil mill effluent by chitosan, alum and PAC. Chem Eng J 118:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.02.001
Almeida SDS, Rocha TL, Qualhato G et al (2019) Acute exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of benzophenone-3 induced genotoxicity in Poecilia reticulata. Aquat Toxicol 216:105293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105293
Aloui F, Kchaou S, Sayadi S (2009) Physicochemical treatments of anionic surfactants wastewater: effect on aerobic biodegradability. J Hazard Mater 164:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.009
Beltrán-Heredia J, Sánchez-Martín J (2009) Removal of sodium lauryl sulphate by coagulation/flocculation with Moringa oleifera seed extract. J Hazard Mater 164:713–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.053
Beltrán-Heredia J, Sánchez-Martín J, Muñoz-Serrano A, Peres JA (2012) Towards overcoming TOC increase in wastewater treated with Moringa oleifera seed extract. Chem Eng J 188:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.003
Bhatia S, Othman Z, Ahmad AL (2007) Coagulation–flocculation process for POME treatment using Moringa oleifera seeds extract: optimization studies. Chem Eng J 133:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.01.034
Bhuptawat H, Folkard GK, Chaudhari S (2007) Innovative physico-chemical treatment of wastewater incorporating Moringa oleifera seed coagulant. J Hazard Mater 142:477–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.044
Biavatti MW, Marensi V, Leite SN, Reis A (2007) Ethnopharmacognostic survey on botanical compendia for potential cosmeceutic species from Atlantic Forest. Rev Bras 17:640–653. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2007000400025
Boroski M, Rodrigues AC, Garcia JC, Sampaio LC, Nozaki J, Hioka N (2009) Combined electrocoagulation and TiO2 photoassisted treatment applied to wastewater effluents from pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. J Hazard Mater 162:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.062
Boulaadjoul S, Zemmouri H, Bendjama Z, Drouiche N (2018) A novel use of Moringa oleifera seed powder in enhancing the primary treatment of paper mill effluent. Chemosphere 206:142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.123
BRASIL (2005) Resolução CONAMA 357, de 17 de março de. Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. Disponível em:<www.mma.gov.br>
Brasil (2017) Portaria de Consolidação n° 5, de 28 de setembro de. Consolidação das normas sobre as ações e os serviços de Saúde do Sistema Único de Saúde. Diário Oficial da União. 5 Set 2017
Carballa M, Omil F, Lema JM (2007) Calculation methods to perform mass balances of micropollutants in sewage treatment plants. Application to Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs). Environ Sci Technol 41:884–890. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061581g
Carrasco KR, Tilbury KL, Myers MS (1990) Assessment of the piscine micronucleus test as an in situ biological indicator of chemical contaminant effects. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 47:2123–2136. https://doi.org/10.1139/f90-237
Costa GHG, de Freita CM, Mendes FQ, Mutton MJR (2016) Extrato de sementes de moringa como floculante de caldo de cana-de-açúcar. Pesqui Agropecuária Bras 51:1794–1798. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-204x2016001000012
Daughton CG, Ternes TA (1999) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environ Health Perspect 107:907–938. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107s6907
de Beluci, NCL, GAP M, Miyashiro CS et al (2019) Hybrid treatment of coagulation/flocculation process followed by ultrafiltration in TIO2-modified membranes to improve the removal of reactive black 5 dye. Sci Total Environ 664:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.199
de Melo ED, Mounteer A, Reis E et al (2018) Screening of physicochemical treatment processes for reducing toxicity of hair care products wastewaters. J Environ Manag 212:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.036
El-Gohary F, Tawfik A, Mahmoud U (2010) Comparative study between chemical coagulation/precipitation (C/P) versus coagulation/dissolved air flotation (C/DAF) for pre-treatment of personal care products (PCPs) wastewater. Desalination 252:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.10.016
Fejér J, Kron I, Pellizzeri V, Pľuchtová M, Eliašová A, Campone L, Gervasi T, Bartolomeo G, Cicero N, Babejová A, Konečná M, Sedlák V, Poráčová J, Gruľová D (2019) First report on evaluation of basic nutritional and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. from Caribbean Island of Saint Lucia. Plants 8:537. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120537
Fenech M, Chang W, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, HUman MicronNucleus project (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen 534:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00249-8
Gu X, Chiang S-H (1999) A novel flotation column for oily water cleanup. Sep Purif Technol 16:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(99)00004-0
Hopkins ZR, Blaney L (2016) An aggregate analysis of personal care products in the environment: Identifying the distribution of environmentally-relevant concentrations. Environ Int 92–93:301–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.04.026
Jung Y, Jung Y, Kwon M, Kye H, Abrha YW, Kang JW (2018) Evaluation of Moringa oleifera seed extract by extraction time: effect on coagulation efficiency and extract characteristic. J Water Health 16:904–913. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2018.078
Krupińska I (2020) Aluminium drinking water treatment residuals and their toxic impact on human health. Molecules 25:641. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030641
Larsen C, Yu ZH, Flick R, Passeport E (2019) Mechanisms of pharmaceutical and personal care product removal in algae-based wastewater treatment systems. Sci Total Environ 695:133772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133772
Lee CS, Robinson J, Chong MF (2014) A review on application of flocculants in wastewater treatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 92:489–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.04.010
Metcalf, Eddy (2004) Wastewater engineering: treatment disposal and reuse, 4th edition. Editor McGrew-Hill, New York, p 1878
Nardi IR, Fuzi TP, Del Nery V (2008) Performance evaluation and operating strategies of dissolved-air flotation system treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Resour Conserv Recycl 52:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2007.06.005
Okuda T, Baes AU, Nishijima W, Okada M (2001) Isolation and characterization of coagulant extracted from moringa oleifera seed by salt solution. Water Res 35:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00290-6
Oulton RL, Kohn T, Cwiertny DM (2010) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in effluent matrices: a survey of transformation and removal during wastewater treatment and implications for wastewater management. J Environ Monit 12:1956–1978. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0em00068j
Parish LC, Crissey JT (1988) Cosmetics: a historical review. Clin Dermatol 6:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/0738-081X(88)90024-7
Patil VV, Gogate PR, Bhat AP, Ghosh PK (2020) Treatment of laundry wastewater containing residual surfactants using combined approaches based on ozone, catalyst and cavitation. Sep Purif Technol 239:116594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116594
Peck AM (2006) Analytical methods for the determination of persistent ingredients of personal care products in environmental matrices. Anal Bioanal Chem 386:907–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0728-3
Pogue AI, Jaber V, Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ (2017) Systemic inflammation in C57BL/6J mice receiving dietary aluminum sulfate; up-regulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNFα, C-reactive protein (CRP) and miRNA-146a in blood serum. J Alzheimer’s Dis Park 7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0460.1000403
Puyol D, Monsalvo VM, Mohedano AF, Sanz JL, Rodriguez JJ (2011) Cosmetic wastewater treatment by upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. J Hazard Mater 185:1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.014
Qualhato G, Rocha TL, Lima ECO et al (2017) Genotoxic and mutagenic assessment of iron oxide (maghemite-γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticle in the guppy Poecilia reticulata. Chemosphere 183:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.061
Santos TM, Pereira DF, Santana CR, da Silva GF (2011) Estudo do tratamento físico químico da água produzida utilizando Moringa oleifera Lam em comparação ao sulfato de alumínio. Exacta 9:317–322. https://doi.org/10.5585/exacta.v9i3.3073
Stackelberg PE, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Zaugg SD, Henderson AK, Reissman DB (2004) Persistence of pharmaceutical compounds and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 329:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.015
Teixeira CMLL, Kirsten FV, Teixeira PCN (2012) Evaluation of Moringa oleifera seed flour as a flocculating agent for potential biodiesel producer microalgae. J Appl Phycol 24:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9773-1
Vaz LG d L, MRF K, Veit MT et al (2010) Avaliação da eficiência de diferentes agentes coagulantes na remoção de cor e turbidez em efluente de galvanoplastia. Eclética Química 35:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702010000400006
Venditti RA (2004) A simple flotation de-inking experiment for the recycling of paper. J Chem Educ 81:693. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed081p693
Violante IMP, Souza IM, Venturini CL, Ramalho AFS, Santos RAN, Ferrari M (2009) Avaliação in vitro da atividade fotoprotetora de extratos vegetais do cerrado de Mato Grosso. Rev Bras 19:452–457. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2009000300020
Yapıcıoğlu P, Yeşilnacar MI (2020) Energy cost assessment of a dairy industry wastewater treatment plant. Environ Monit Assess 192:536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08492-y
Zhang D, Gersberg RM, Ng WJ, Tan SK (2014) Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic plant-based systems: a review. Environ Pollut 184:620–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.009
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Federal University of Goias (UFG) for logistic and laboratories involved in this study.
Funding
The Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal do Ensino Superior (CAPES) in Brazil provided a scholarship to some of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NSA—conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization. NFS—conceptualization, validation. JMLF—conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, validation. ATSP—validation, formal analysis. PSS—validation. SMTSM—conceptualization, methodology, validation. HCRJ—conceptualization, methodology, validation. ECC—conceptualization, resources, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work including experimental studies on animals was approved by the ethics committee on the use of animals at the Federal University of Goiás under registration number 46/17.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 26 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araújo, .S., Souza, N.F., de Lima-Faria, J.M. et al. Treatment of cosmetic industry wastewater by flotation with Moringa oleifera Lam. and aluminum sulfate and toxicity assessment of the treated wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 1199–1209 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15722-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15722-4